Introduction
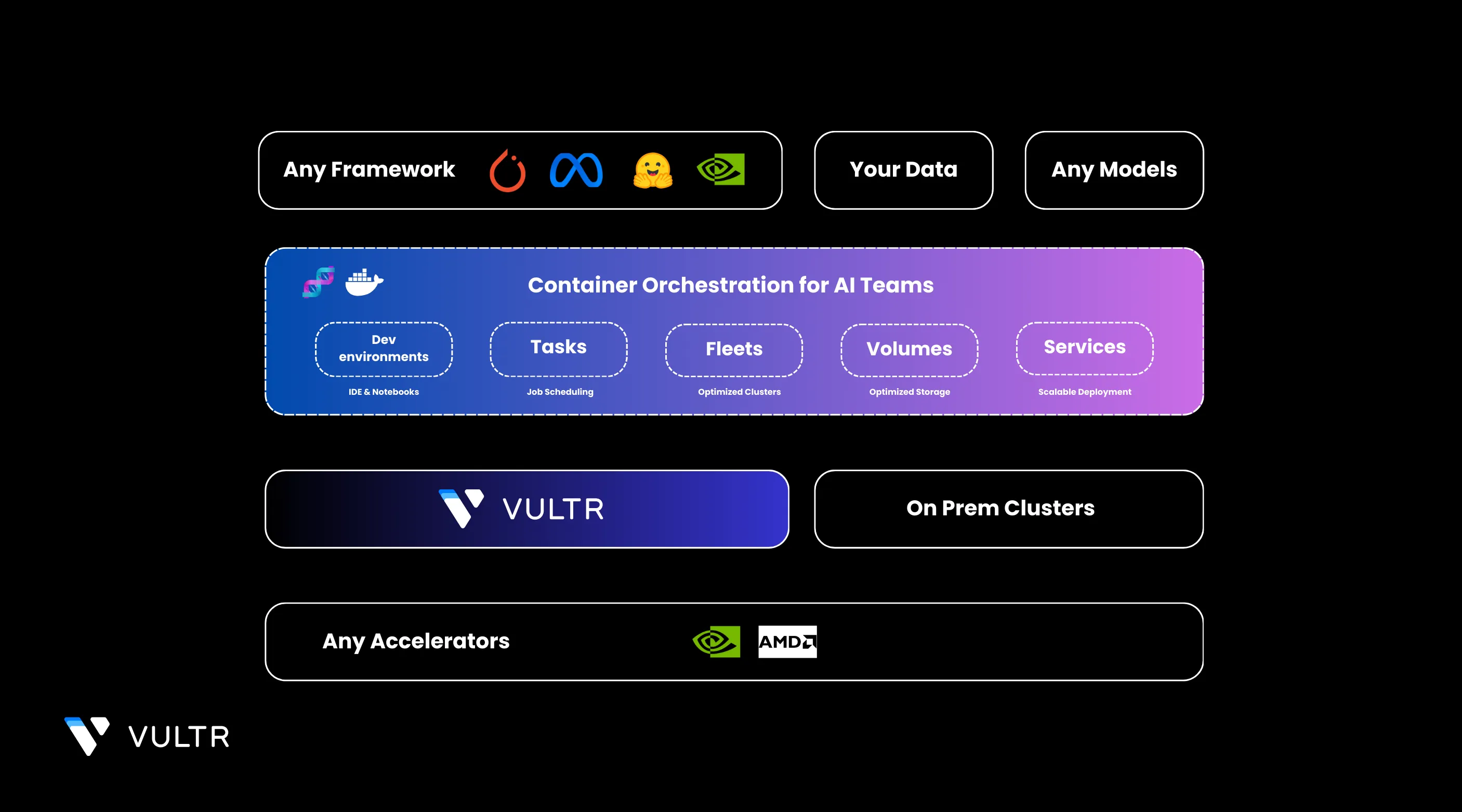
dstack is an open-source alternative to Kubernetes and Slurm, specifically designed to streamline AI development and deployment across cloud providers. It simplifies the complexity of managing infrastructure by providing a user-friendly interface and declarative YAML configurations, enabling developers to focus on building and scaling their applications without being bogged down by operational overhead. Ideal for machine learning workflows, distributed computing, and scalable application hosting, dstack integrates seamlessly with cloud environments and supports dynamic resource scaling, persistent storage, and secure service publication.
In this guide, you are going to understand the configurations offered by dstack. Later you will install and activate the dstack server and finally deploy a dev environment using Vultr servers and dstack.
dstack Configurations
Dev environment: dstack allows you to set up interactive development environments tailored for desktop IDEs. These environments provide developers with the flexibility to code, debug, and test applications efficiently, all while leveraging the power of cloud resources. With dev environments, teams can ensure consistency across setups and speed up the development process by avoiding local dependency issues.
Tasks: Tasks in dstack are designed to automate and schedule jobs, making them incredibly versatile for various use cases. Whether you need to process data workflows, run batch jobs, or execute periodic tasks, tasks can handle it all. They also support distributed workloads and can be used to run web applications, making them an essential component for streamlining automation and workflows.
Services: With dstack, deploying and managing long-running services is straightforward and efficient. Services are ideal for hosting APIs, web servers, or machine learning models, ensuring they are consistently available and performant.
Fleets: Fleets enable developers to manage and scale clusters of resources seamlessly across cloud or on-premise environments. Designed for dynamic scaling, fleets automatically adjust resource allocation based on demand, ensuring optimal efficiency.
Create a Virtual Environment
In this section, you are going to create virtual environment on your machine and prepare the environment for the dstack dev environment deployment.
Install the
venvpackage.console$ apt install python3-venv -y
Create a virtual environment.
console$ python3 -m venv dstack-env
Activate the virtual environment.
console$ source dstack-env/bin/activate
Install dstack
In this section, you are going to install all the necessary dependencies for dstack and activate the dstack server for the dev environment deployment in the later section.
Create a directory and navigate into it to store the backend file.
console$ mkdir -p ~/.dstack/server
Create a backend
ymlfile to declare Vultr as the provider.console$ nano ~/.dstack/server/config.yml
Copy and paste the below configuration.
YAMLprojects: - name: main backends: - type: vultr creds: type: api_key api_key: <vultr-account-api-key>
Save and close the file.
Install dstack.
console$ pip install "dstack[all]" -U
Activate the dstack server.
console$ dstack server
Note down the URL on which the dstack server is running and token provided in the output.
Point the CLI to the dstack server.
console$ dstack config --url <URL> \ --project main \ --token <TOKEN>
Deploy Dev Environment
In this section, you are to run the configuration for the dstack dev environment and deploy the dev environment on a Vultr server.
Continue in the
dstack-envvirtual environment, and create a directory and navigate into it.console$ mkdir quickstart && cd quickstart
Initialize the directory.
console$ dstack init
Create a YAML file to define the dstack dev environment configuration.
console$ nano .dstack.yaml
Copy and paste the below configuration.
YAMLtype: dev-environment name: vscode python: '3.11' ide: vscode spot_policy: auto
The above configuration sets up a dev environment named
vscodeusing Python 3.11, tailored for interactive coding with Visual Studio Code. It provisions resources automatically using either spot or on-demand instances based on availability and cost.The configuration can be extended to pre-install additional tools, libraries, or dependencies to better prepare the environment
Save and close the file.
Apply the configuration.
console$ dstack apply -f .dstack.yaml
The configuration may take up to 10 minutes to execute. You can monitor its progress by visiting the Vultr Customer Portal and checking the status of the server provisioning, which is automatically initiated when you apply the configuration.
Access the environment in VS Code desktop.
vscode://vscode-remote/ssh-remote+vscode/workflow
Conclusion
With dstack and Vultr, setting up and deploying development environments becomes seamless, enabling developers to focus on building and scaling applications without worrying about infrastructure complexities. By following this guide, you’ve learned how to configure dstack, activate its server, and deploy a dev environment tailored to your needs. Whether for machine learning workflows, distributed computing, or scalable app hosting, dstack provides a robust solution to streamline your development process. Visit the dstack documentation