How to Install Virtualmin on Rocky Linux 9
Introduction
Virtualmin is an open-source web server administration control panel based on Webmin that lets you create, host, and deliver web applications using virtual server profiles. Virtualmin uses a graphical web-based interface that enables efficient management of server components such as databases, files, and web application files.
This article explains how to install Virtualmin on a Rocky Linux 9 server, host, and deliver web applications using virtual server profiles.
Prerequisites
- Deploy a Rocky Linux 9 instance on Vultr with at least
2GBRAM. - Create a domain A record pointing to the instance's IP address. For example,
virtualmin.example.com. - Access the server using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Install Virtualmin
Virtualmin is not available as a standalone package in the default Rocky Linux 9 repositories. Follow the steps below to download the latest Virtualmin installation script and install all required applications with a specific web server bundle on your server.
Change your server hostname to your Virtualmin domain. For example,
virtualmin.example.com.console$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname virtualmin.example.com
Create a new non-root user with sudo privileges to use with Virtualmin. For example,
webadmin.console$ sudo adduser webadmin && usermod -aG wheel webadmin
Assign the user a new strong password.
console$ passwd webadmin
Download the latest Virtualmin installation script and save it as
virtualmin.sh.console$ wget -O virtualmin.sh https://software.virtualmin.com/gpl/scripts/virtualmin-install.sh
Run the script to install Virtualmin and all required components on your server. Replace
LEMPwith your desired web server bundle such asLAMP.console$ sudo ./virtualmin.sh
Enter Y and press Enter to continue with the installation.
[SUCCESS] Installation Complete! [SUCCESS] If there were no errors above, Virtualmin should be ready [SUCCESS] to configure at https://virtualmin.example.com:10000 (or https://192.0.2.1:10000).Wait for at least
5minutes for the installation process to complete and verify the installed components in your output like the one below.
Secure Virtualmin
Follow the steps below to generate trusted Let's Encrypt SSL certificates and secure all network connections to the Virtualmin web administration interface.
Stop the Apache service to ensure Certbot can bind to port
80.console$ sudo systemctl stop apache2
Install the Certbot package Let's Encrypt client to manage your SSL certificates.
console$ sudo apt install certbot
Request a new SSL certificate using your domain. Replace
virtualmin.example.comandvirtualmin@example.comwith your actual details.console$ sudo certbot certonly --standalone -d virtualmin.example.com -m virtualmin@example.com --agree-tos
Enter U and press the Enter when prompted key to update the default SSL key type to ECDSA and apply changes to the
/etc/webmin/miniserv.confconfiguration file.Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log An RSA certificate named virtualmin.example.com already exists. Do you want to update its key type to ECDSA? (U)pdate key type/(K)eep existing key type:Your output should look like the one below when the SSL certificate request is successful.
Renewing an existing certificate for virtualmin.example.com Successfully received certificate. Certificate is saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/virtualmin.example.com/fullchain.pem Key is saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/virtualmin.example.com/privkey.pem This certificate expires on 2024-10-15. These files will be updated when the certificate renews. Certbot has set up a scheduled task to automatically renew this certificate in the background. If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by: * Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate * Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-leRestart the Webmin service to apply your configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart webmin
Start the Apache service.
console$ sudo systemctl start apache2
Set Up Firewall Rules
Virtualmin uses the firewalld utility to manage firewall processes on your server. Follow the steps below to allow all necessary Virtualmin ports and other services through the firewall.
View the
firewalldservice status and verify that it's running.console$ sudo systemctl status firewalld
Output:
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2024-07-17 04:31:35 UTC; 35min ago Docs: man:firewalld(1) Main PID: 36516 (firewalld) Tasks: 2 (limit: 2299) Memory: 40.8M CPU: 4.132s CGroup: /system.slice/firewalld.service └─36516 /usr/bin/python3 /usr/sbin/firewalld --nofork --nopidView all allowed ports in the firewall configuration.
console$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports
Output:
20/tcp 2222/tcp 10000-10100/tcp 20000/tcp 49152-65535/tcpView all allowed services.
console$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-services
Output:
dhcpv6-client dns dns-over-tls ftp http https imap imaps mdns pop3 pop3s smtp smtp-submission smtps ssh
Access Virtualmin
Virtualmin runs on the default TCP port 10000 by default. Follow the steos below to access the Virtualmin web administration interface and create a new virtual server.
Access your domain on port
10000to open the Virtualmin control panel interface.https://virtualmin.example.com:10000Enter your sudo user account details to log in to the Virtualmin interface.
Click Next within the Post-Installation Wizard to set up any additional configurations on your server.
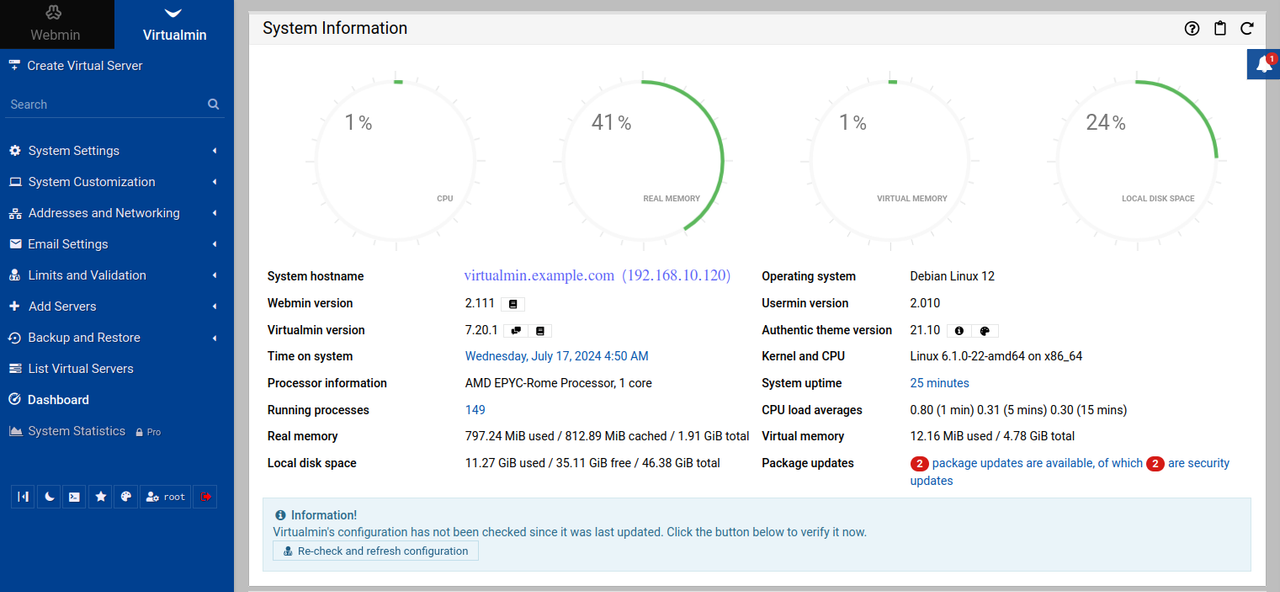
Find and click Dashboard on the left navigation bar to access the system performance page.
Enable 2-Factor Authentication
2-factor authentication (2FA) enables an extra layer of security for password-based authentication methods. 2FA allows you to generate a one-time code on your mobile device to use when logging in to Virtualmin to verify your identity. Follow the steps below to protect Virtualmin login with 2FA using the Google Authenticator application.
Scroll down on the left navigation bar and click your username at the bottom of the page.
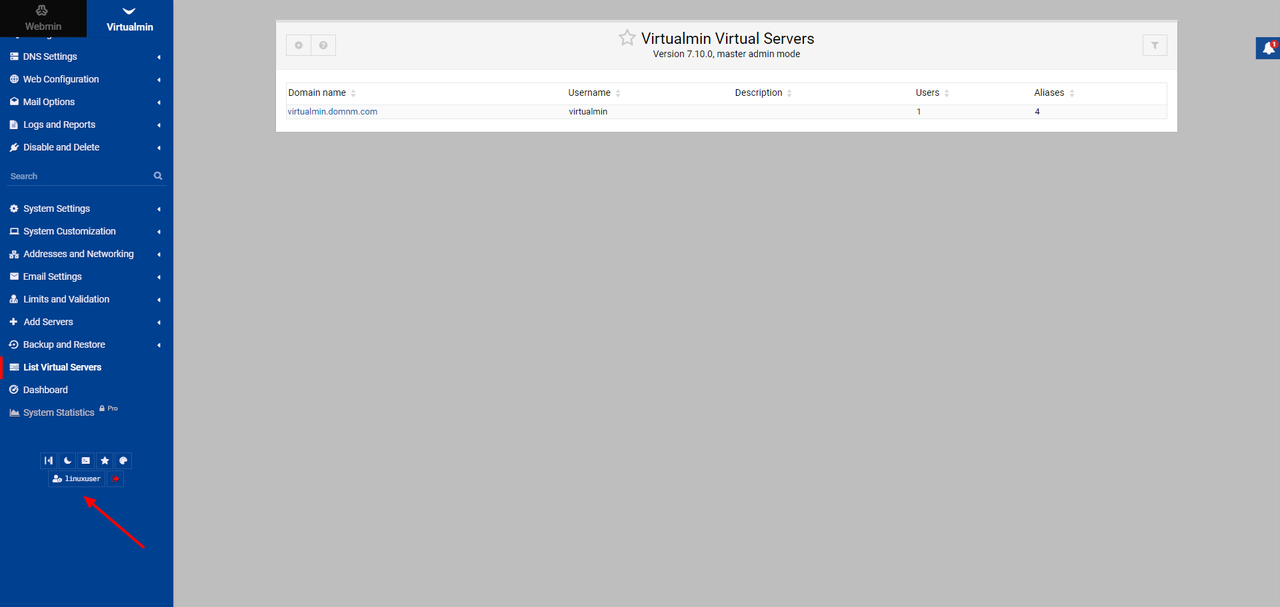
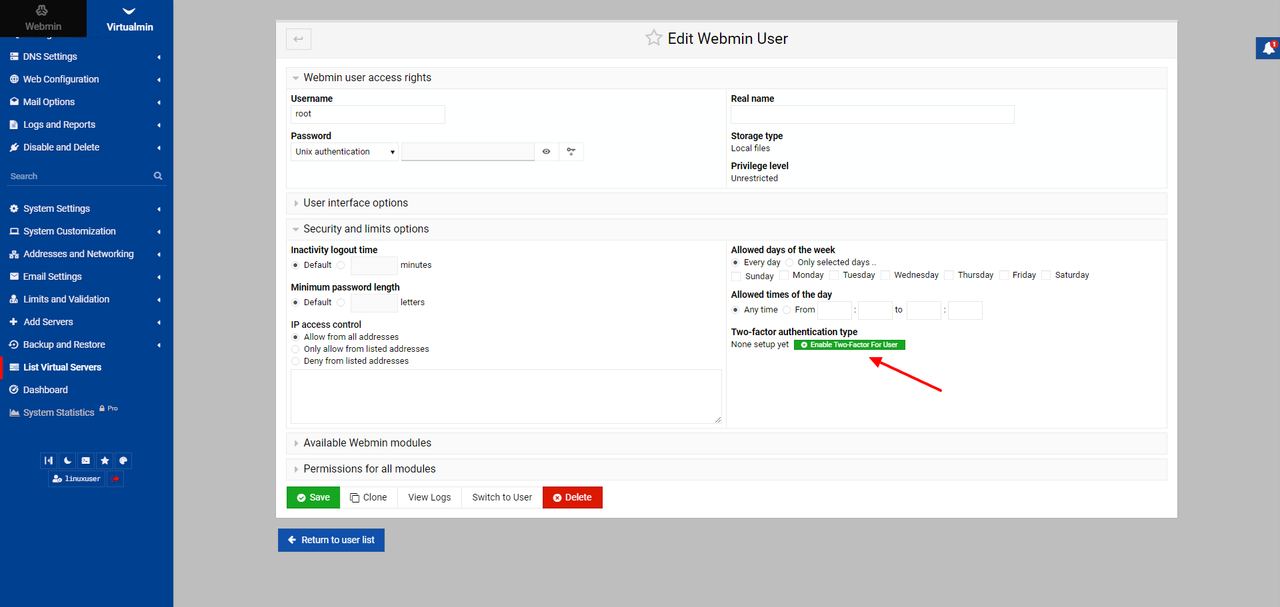
Expand the Security and limits options section.
Click Enable Two-Factor For User.
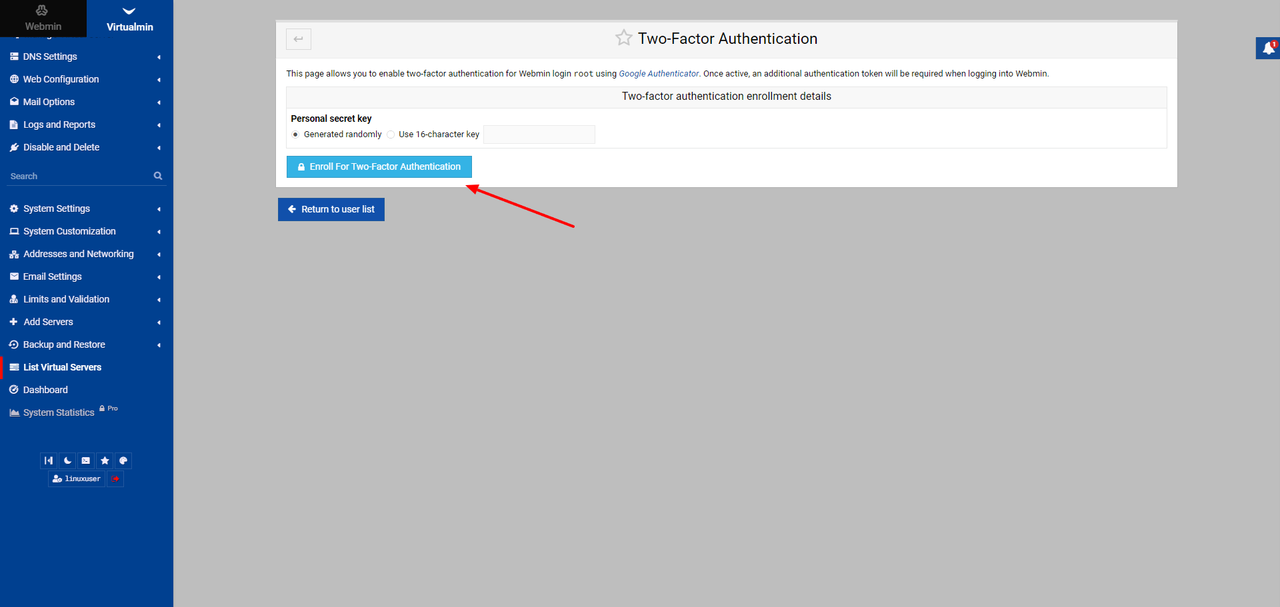
Click Enroll For Two-Factor Authentication.
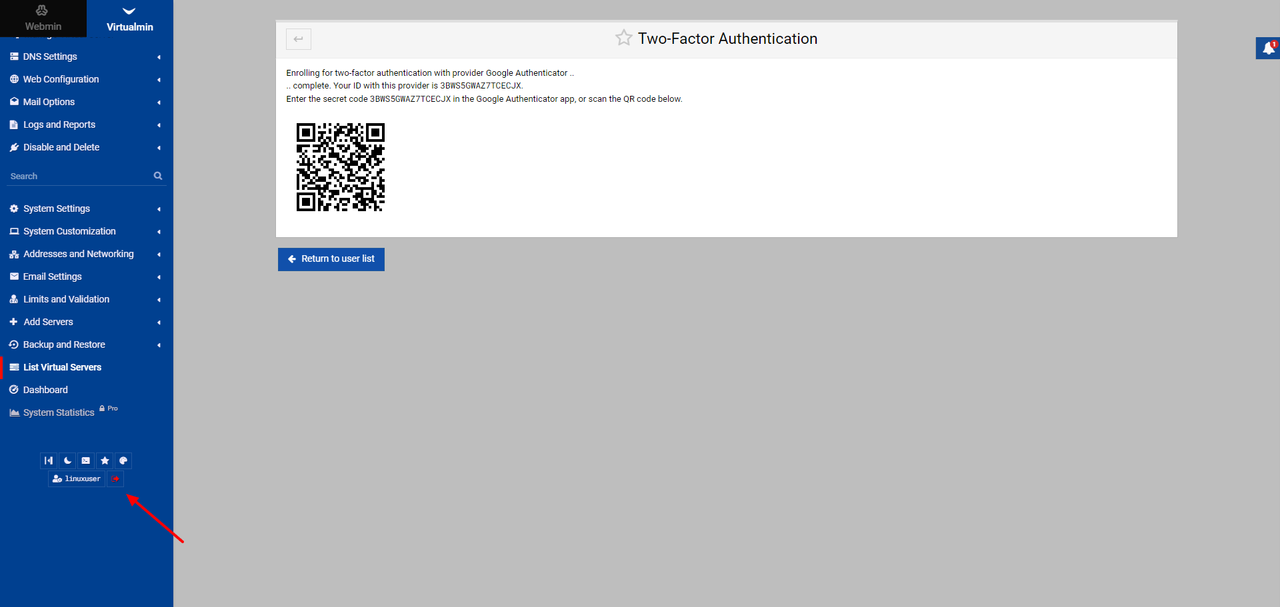
Scan the displayed QR code on the page with your authenticator application.
Scroll down on the left navigation bar to log out of Virtualmin.
Log in with your non-root user credentials to test 2FA.
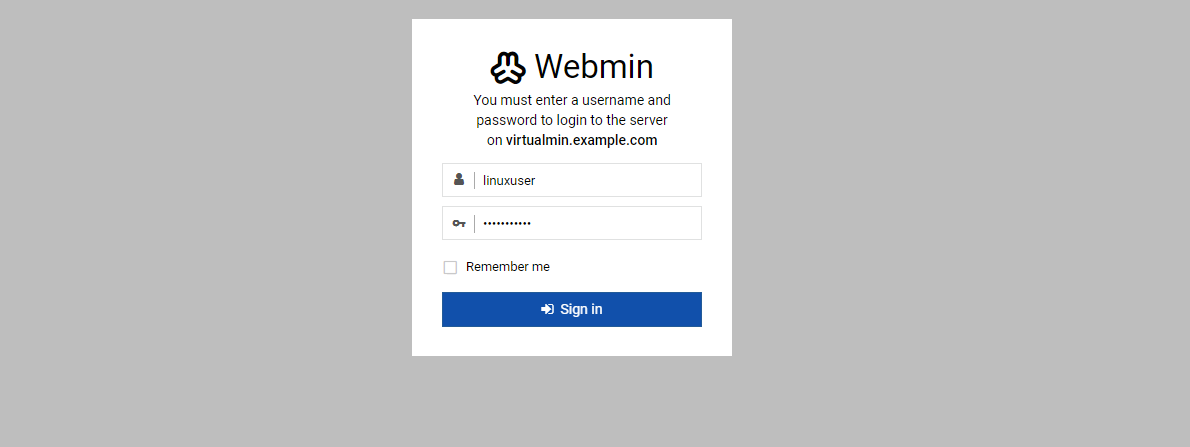
Verify that Virtualmin requires the 2FA token to log in.
Enter the 2FA token from the app.

Press Verify to log in to the Virtualmin web administration interface.
Conclusion
You have installed Virtualmin on your Ubuntu 24.04 server and enabled access to the web administration control panel. You have used the control panel to perform server operations and secured the application with 2-factor authentication. For more information about Virtualmin, visit the official documentation.