Configure IPv6 on your Vultr Cloud Server

Introduction
Vultr supports IPv6 for all VPS and Bare Metal instances. If you select Enable IPv6 in the Additional Features section when you deploy a new instance, you do not need to configure anything because all network configuration on a new instance is handled by cloud-init.
However, if you add IPv6 to a existing instance, use this guide to configure the new network address.
How to add IPv6 to an Instance
IPv6 autoconfiguration depends on ICMP protocol. Please verify you haven't blocked ICMP in the OS firewall.
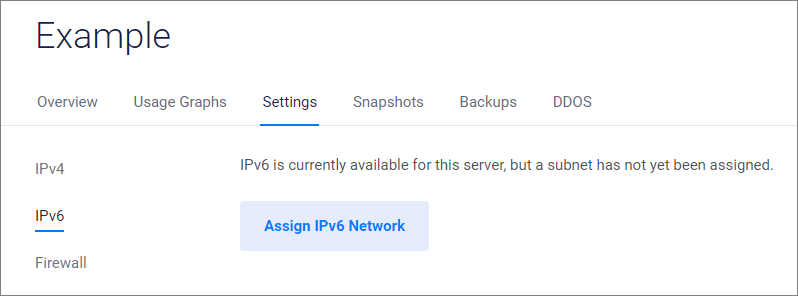
Navigate to the Settings tab for the instance.
Select the IPv6 menu.
Click the Assign IPv6 Network button.
Restart the server via the Vultr Customer Portal. Important: rebooting via SSH doesn't activate the new network.
Examples
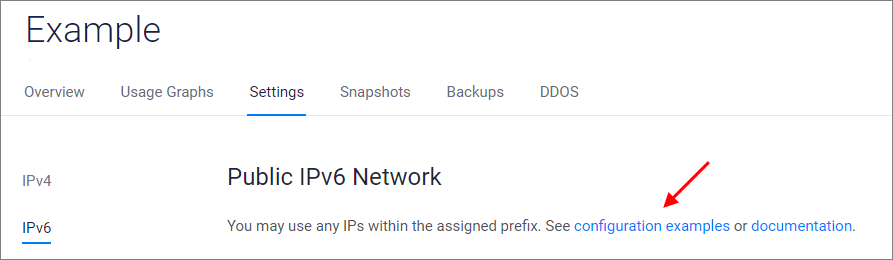
Vultr provides Configuration Examples on the IPv6 Settings menu. Please follow that link to see pre-configured configuration examples for your VPS instance.
IPv6 on CentOS
CentOS 8
Dynamic configuration
Populate /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens3 with:
TYPE="Ethernet"
DEVICE="ens3"
ONBOOT="yes"
BOOTPROTO="dhcp"
IPV6INIT="yes"
IPV6_AUTOCONF="yes"
IPV6ADDR_SECONDARIES="2001:db8:1000::100 2001:db8:1000::200"- The primary IPv6 is dynamic.
- 2001:db8:1000::200 is the optional static secondary IPv6. Remove the
IPV6ADDR_SECONDARIESline if a secondary address isn't required, or replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
Restart the connection, or reboot.
nmcli con load /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens3
nmcli con up 'System ens3'CentOS 6 through 7
Add the following lines to /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0.
IPV6INIT="yes"
IPV6ADDR="2001:db8:1000::100/64"
IPV6_AUTOCONF="yes"
IPV6ADDR_SECONDARIES="2001:db8:1000::200/64"- 2001:db8:1000::100 is the primary IPv6, replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
- 2001:db8:1000::200 is the optional secondary IPv6. Remove the
IPV6ADDR_SECONDARIESline if a secondary address isn't required, or replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
Restart networking or reboot.
service network restartIP forwarding
If you have IP forwarding enabled, such as when using your server as a VPN, add the following lines to /etc/sysctl.conf:
net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_ra=2
net.ipv6.conf.eth0.accept_ra=2These variables default value is 1, which prevents IPv6 from working. To verify the status of IP forwarding, run:
# sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forwardIPv6 on Debian
Debian 9 and later
Dynamic configuration
For dynamic configuration, add the following lines to /etc/network/interfaces.
iface ens3 inet6 autoRestart networking or reboot.
systemctl restart networking.serviceStatic configuration
For static configuration, add the following lines to /etc/network/interfaces.
iface ens3 inet6 static
address 2001:db8:1000::100
netmask 64
up /sbin/ip -6 addr add dev ens3 2001:db8:1000::200- 2001:db8:1000::100 is the primary IPv6, replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
- 2001:db8:1000::200 is the optional secondary IPv6. Remove the example IP address line if a secondary address isn't required, or replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
Restart networking or reboot.
systemctl restart networking.serviceDebian 8
Dynamic configuration
For dynamic configuration, add the following lines to /etc/network/interfaces.
iface eth0 inet6 autoRestart networking or reboot.
systemctl restart networking.serviceStatic configuration
For static configuration, add the following lines to /etc/network/interfaces.
iface eth0 inet6 static
address 2001:db8:1000::100
netmask 64
up /sbin/ip -6 addr add dev eth0 2001:db8:1000::200- 2001:db8:1000::100 is the primary IPv6, replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
- 2001:db8:1000::200 is the optional secondary IPv6. Remove the example IP address line if a secondary address isn't required, or replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
Restart networking or reboot.
systemctl restart networking.serviceIPv6 on Fedora
Fedora 29 through 32
Add the following lines to /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens3.
nmcli con mod 'Wired connection 1' ipv6.method 'auto' ipv6.addresses ''
nmcli con mod 'Wired connection 1' +ipv6.addresses '2001:db8:1000::200/128'
nmcli con up 'Wired connection 1'- The primary IPv6 is dynamic.
- 2001:db8:1000::200 is the optional static secondary IPv6. Remove that line if a secondary address isn't required, or replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet. Additional addresses can be added in the same fashion.
Restart networking or reboot.
systemctl restart network.serviceFedora 26 through 28
Add the following lines to /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens3.
IPV6INIT="yes"
IPV6ADDR="2001:db8:1000::100/64"
IPV6_AUTOCONF="yes"
IPV6ADDR_SECONDARIES="2001:db8:1000::200/64"- 2001:db8:1000::100 is the primary IPv6, replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
- 2001:db8:1000::200 is the optional secondary IPv6. Remove the
IPV6ADDR_SECONDARIESline if a secondary address isn't required, or replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
Restart networking or reboot.
systemctl restart network.serviceIPv6 on FreeBSD
This applies to FreeBSD version 10 through 13.
Dynamic configuration
Add the following lines to the /etc/rc.conf file.
ifconfig_vtnet0_ipv6="inet6 accept_rtadv"
ipv6_activate_all_interfaces="YES"
rtsold_enable="YES"
rtsold_flags="-aF"Static configuration
Add the following lines to the /etc/rc.conf file. Replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
rtsold_enable="YES"
ipv6_activate_all_interfaces="YES"
rtsold_flags="-aF"
ifconfig_vtnet0_ipv6="inet6 2001:db8:1000::100 prefixlen 64"Start the router solicitation daemon or reboot.
service rtsold startAdd Second IPv6 to an Instance
Optionally, you may configure a secondary IPv6 address for your instance.
Add the following line to
/etc/rc.conf. Replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.ifconfig_vtnet0_alias0="inet6 2001:db8:1000::200 prefixlen 64"Start the router solicitation daemon or reboot.
# service rtsold start
IPv6 on OpenBSD
Requirements
Please ensure that slaacd is enabled and running.
IPv6 autoconfiguration depends on ICMP protocol. Please verify you haven't blocked ICMP
routeradv,neighbrsol,neighbradvpacket types. For example, this ruleset for pf.conf passes the required traffic:pass in on egress inet6 proto icmp6 all icmp6-type { echoreq routeradv neighbrsol neighbradv }
Procedure
Add the following line to
/etc/hostname.vio0.If using OpenBSD 6.0 through 6.2:
inet6 autoconf -autoconfprivacyIf using OpenBSD 6.3 through 6.8:
inet6 autoconf -autoconfprivacy -soiiIf using OpenBSD 6.9 or later:
inet6 autoconf -soii -temporary
Restart the interface or reboot.
# sh /etc/netstart vio0Verify the interface status with slaacctl.
# slaacctl show interface
Add Second IPv6 to an Instance
Optionally, you may configure a secondary IPv6 address for your instance.
Add the following line to
/etc/hostname.vio0. Replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.inet6 alias 2001:db8:1000::200 64Restart the interface or reboot.
# sh /etc/netstart vio0Verify the interface status with slaacctl.
# slaacctl show interface
IPv6 on Ubuntu
This guide applies to Ubuntu 14.04 and later.
Ubuntu 17.10 and later
Populate the /etc/netplan/10-ens3.yaml file with the following text.
network:
version: 2
renderer: networkd
ethernets:
ens3:
dhcp4: yes
addresses:
- '2001:db8:1000::200/64'- The primary IPv6 is dynamic.
- 2001:db8:1000::200 is the optional static secondary IPv6. Remove
addresses:and the example IPv6 if a secondary address isn't required, or replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
Update networking or reboot.
netplan applyUbuntu 16.04 through 17.04
Dynamic configuration
For dynamic configuration, add the following lines to the /etc/network/interfaces file.
iface ens3 inet6 autoRestart networking or reboot.
systemctl restart networking.serviceStatic configuration
For static configuration, add the following lines to the /etc/network/interfaces file.
iface ens3 inet6 static
address 2001:db8:1000::100
netmask 64
up /sbin/ip -6 addr add dev ens3 2001:db8:1000::200- 2001:db8:1000::100 is the primary IPv6, replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
- 2001:db8:1000::200 is the optional secondary IPv6. Remove the example IP address line if a secondary address isn't required, or replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
Restart networking or reboot.
systemctl restart networking.serviceUbuntu 14.04
Dynamic configuration
For dynamic configuration, add the following lines to the /etc/network/interfaces file.
iface eth0 inet6 autoReboot the instance.
Static configuration
For static configuration, add the following lines to the /etc/network/interfaces file.
iface eth0 inet6 static
address 2001:db8:1000::100
netmask 64
up /sbin/ip -6 addr add dev eth0 2001:db8:1000::200- 2001:db8:1000::100 is the primary IPv6, replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
- 2001:db8:1000::200 is the optional secondary IPv6. Remove the example IP address line if a secondary address isn't required, or replace the example with an address in your IPv6 subnet.
Reboot the instance.
IP forwarding
If you have IP forwarding enabled, such as when using your server as a VPN, add the following lines to /etc/sysctl.conf:
net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_ra=2
net.ipv6.conf.eth0.accept_ra=2These variables default value is 1, which prevents IPv6 from working. To verify the status of IP forwarding, run:
# sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forwardIPv6 on Windows Server
This applies to Windows Server 2012 R2 and later.
Find the public interface name on your system. You can use
ipconfig /allor navigate the Windows Control Panel.Run the following commands.
Replace Ethernet with your public interface name, and replace the example addresses with an address in your IPv6 subnet. You can skip the second address if you don't have one.
netsh interface ipv6 set global randomizeidentifiers=disabled netsh interface ipv6 add address interface="Ethernet" address="2001:db8:1000::100/64" netsh interface ipv6 add address interface="Ethernet" address="2001:db8:1000::200/64"