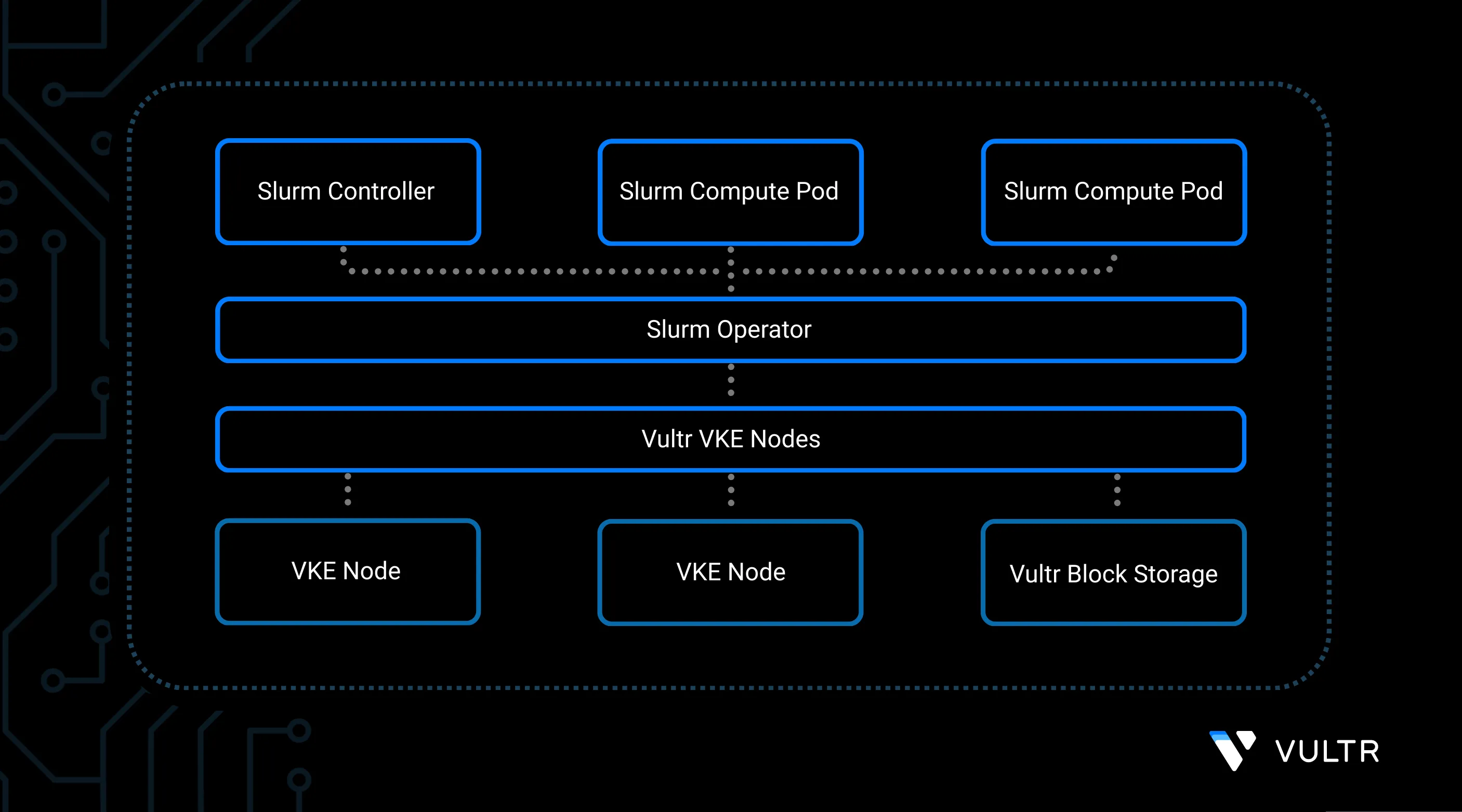
Slurm is an open-source job scheduler widely used in High-performance Computing (HPC) environments to efficiently allocate resources, manage job queues, and orchestrate workloads across clusters. It powers many of the world’s largest supercomputers and is renowned for its scalability, flexibility, and support for complex batch workflows.
This guide shows you how to deploy a production-ready Slurm cluster on Vultr Kubernetes Engine (VKE) using the community-maintained Slurm Operator. The operator simplifies the deployment process and abstracts away the underlying operational complexity, allowing you to focus on running your jobs rather than managing the control plane.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:
- Have a Vultr Kubernetes Engine (VKE) cluster.
- Have
kubectl, andhelminstalled on your machine.
Prepare the Environment
Before deploying the Slurm cluster, you need to configure a few core services in your VKE environment. This section walks you through setting up the required Helm repositories, installing foundational components (such as cert-manager and Prometheus), and downloading the configuration files used by the Helm charts for Slurm.
Add the required Helm repos.
console$ helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts $ helm repo add metrics-server https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/metrics-server/ $ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami $ helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io $ helm repo update
Install cert-manager.
console$ helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \ --namespace cert-manager \ --create-namespace \ --set crds.enabled=true
Install the Prometheus monitoring stack.
console$ helm install prometheus prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack \ --namespace prometheus \ --create-namespace \ --set installCRDs=true
Download configuration files for the operator and the Slurm cluster.
console$ curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SlinkyProject/slurm-operator/refs/tags/v0.3.0/helm/slurm-operator/values.yaml \ -o values-operator.yaml $ curl -L https://raw.githubusercontent.com/SlinkyProject/slurm-operator/refs/tags/v0.3.0/helm/slurm/values.yaml \ -o values-slurm.yaml
Install the Slurm operator into the
slinkynamespace.console$ helm install slurm-operator oci://ghcr.io/slinkyproject/charts/slurm-operator \ --values=values-operator.yaml \ --version=0.3.0 \ --namespace=slinky \ --create-namespace
Verify the operator is running.
console$ kubectl get pods -n slinky
Deploy the Slurm Cluster
Once the operator is running, you can deploy the actual Slurm cluster on top of your VKE environment. In this section, the Helm chart installs the Slurm controller, compute nodes, and required database using Vultr Block Storage for persistent volumes.
Install the Slurm cluster using the Vultr Block Storage class.
console$ helm install slurm oci://ghcr.io/slinkyproject/charts/slurm \ --values=values-slurm.yaml \ --set global.storageClass=vultr-block-storage \ --set mariadb.primary.persistence.storageClass=vultr-block-storage \ --set controller.persistence.storageClass=vultr-block-storage \ --version 0.3.0 \ --namespace slurm \ --create-namespace
Verify the Slurm cluster is deployed.
console$ kubectl get pods -n slurm
Log in to the Slurm controller pod.
console$ kubectl --namespace=slurm exec -it statefulsets/slurm-controller -- bash --login
Run Slurm client commands inside the container.
console$ sinfo $ srun -N5 hostname
Conclusion
You now have a fully functional Slurm environment deployed on Vultr Kubernetes Engine. You can use it to run and scale batch jobs for HPC, research, or large-scale automation tasks.
For advanced configuration, visit the Slurm Operator GitHub repository or consult the Slurm documentation.
No comments yet.