How to Change the Hostname of a Vultr Cloud Server
Introduction
When you deploy a new Vultr cloud server, you can set the Server Hostname on the deployment page. Later, if you decide to change the server name, you can use the Change Hostname form in the server's Settings menu.
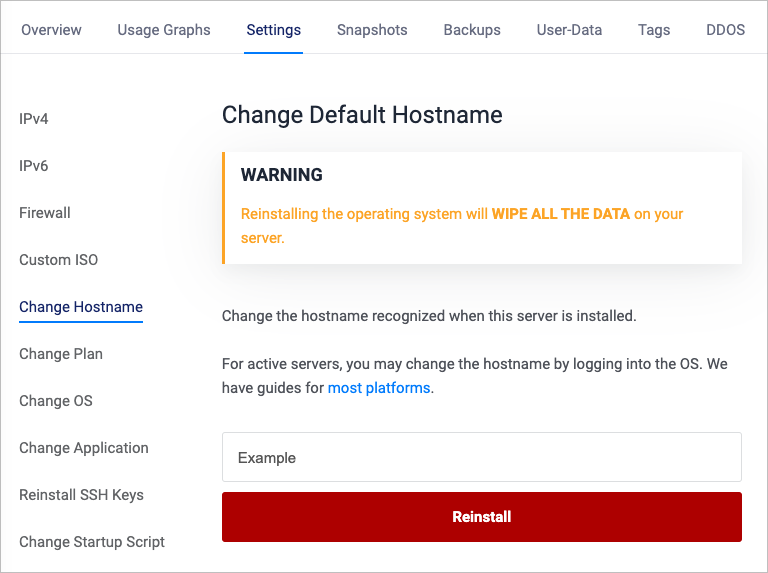
However, if you use this method to change the hostname, Vultr destroys the cloud server and reinstalls a new operating system image, which wipes all the data on the server.
How to Change Hostname without Erasing the Server
- Locate your operating system from the list below.
- Follow the steps for your operating system.
- (optional) Update your DNS. This procedure does not change your DNS name. If you use DNS and need to change that name, follow the guides from your DNS host. If you use Vultr DNS, you'll find our guide here.
This guide uses example names: olddog for the old name and newtricks for the new.
Change Hostname on AlmaLinux, CentOS, Fedora, Rocky Linux, and VzLinux
This section applies to:
- AlmaLinux
- CentOS 7 and later
- Fedora 31 and later
- Rocky Linux
- VzLinux
Procedure:
Important: Disable automatic hostname updates from cloud-init by editing
/etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.$ sudo nano /etc/cloud/cloud.cfgChange the value of
preserve_hostnametotrue.preserve_hostname: trueSave and exit the file.
Check the current hostname with the
hostnamecommand.$ hostname olddogYou can also use
hostnamectl.$ hostnamectl Static hostname: olddogChange the hostname to newtricks.
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname newtricksChange any instances of the old hostname in
/etc/hosts. If you have a DNS name pointed to this instance, it's also best practice to set that name here.$ sudo nano /etc/hostsExample of old hosts file:
127.0.0.1 olddog ::1 olddogExample of new hosts file.
127.0.0.1 newtricks newtricks.example.com ::1 newtricks newtricks.example.comReboot the server.
Test your change with
hostnamectlandhostname.$ hostnamectl Static hostname: newtricks $ hostname newtricks $ hostname -a newtricks.example.com
Change Hostname on Arch Linux
This section applies to any recently updated version of Arch Linux.
Procedure:
Important: Disable automatic hostname updates from cloud-init by editing
/etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.$ sudo nano /etc/cloud/cloud.cfgChange the value of
preserve_hostnametotrue.preserve_hostname: trueSave and exit the file.
Check the current hostname using the
hostnamectltool.$ hostnamectl Static hostname: olddogCheck the hosts file with the
getenttool.$ getent hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.1.1 olddog.localdomain olddogChange the hostname to newtricks.
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname newtricksChange any instances of the old hostname in
/etc/hosts. If you have a DNS name pointed to this instance, it's also best practice to set that name here.$ sudo vim /etc/hostsExample of old hosts file:
127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost 127.0.1.1 olddog.localdomain olddogExample of new hosts file:
127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost 127.0.1.1 newtricks.localdomain newtricksEither reboot the server or log out and back in again to your user session.
Test the change with the
hostnamectltool.$ hostnamectl Static hostname: newtricksTest the change with the
getenttool.$ getent hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.1.1 newtricks.localdomain newtricks
統 Note: For a system with a permanent IP address, that permanent IP address should be used instead of 127.0.1.1. The order of hostnames in /etc/hosts is significant. The first string is the canonical hostname. Subsequent names on the same line are aliases.
Change Hostname on Debian & Ubuntu
This section applies to:
- Debian GNU/Linux 9 "Stretch" and later
- Ubuntu version 16.04 and later
Procedure:
Important: Disable automatic hostname updates from cloud-init by editing
/etc/cloud/cloud.cfg.$ sudo nano /etc/cloud/cloud.cfgChange the value of
preserve_hostnametotrue.preserve_hostname: trueSave and exit the file.
Check the current hostname with the
hostnamecommand.$ hostname olddogYou can also use
hostnamectl.$ hostnamectl Static hostname: olddogChange the hostname to newtricks.
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname newtricksChange any instances of the old hostname in
/etc/hosts. If you have a DNS name pointed to this instance, it's also best practice to set that name here.$ sudo nano /etc/hostsExample of old hosts file:
127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.1.1 olddogExample of new hosts file.
127.0.0.1 localhost 127.0.1.1 newtricks.example.com newtricksReboot the server.
Test your change with
hostnamectlandhostname.$ hostnamectl Static hostname: newtricks $ hostname newtricks $ hostname -f newtricks.example.com
Change Hostname on Fedora CoreOS
Fedora CoreOS (FCOS) uses the Ignition file to set the server hostname. If you decide to rename a running server, you'll need to update the name from the command line.
Connect to your FCOS instance and change to the root user.
$ sudo su - rootCheck the hostname with
hostname.# hostname olddogYou can also use
hostnamectl.# hostnamectl Static hostname: olddogChange the hostname to newtricks.
# hostnamectl set-hostname newtricksReboot the server.
# rebootTest your change with
hostnamectlandhostname.$ hostnamectl Static hostname: newtricks $ hostname newtricks
Change Hostname on FreeBSD
This section applies to all versions of FreeBSD.
Procedure:
Check the current hostname with the
hostnamecommand.$ hostname olddogChange the hostname to newtricks using a text editor.
- Change all occurrences in /etc/rc.conf.
- Change all occurrences in /etc/hosts.
Reboot the server.
Test your change with
hostname.$ hostname newtricks
Change Hostname on OpenBSD
This section applies to all versions of OpenBSD.
Procedure:
Check the current hostname with the
hostnamecommand.$ hostname olddogChange the hostname to newtricks using a text editor:
- Change all occurrences in /etc/myname.
- Change all occurrences in /etc/hosts.
Reboot the server.
Test your change with
hostname.$ hostname newtricks
Change Hostname on Windows
This section applies to Windows Server 2012 and later.
How to Change the Hostname in PowerShell
Open an elevated PowerShell. If you are in standard PowerShell, elevate your access as shown:
PS C:\> Start-Process PowerShell -Verb RunasCheck the hostname with
$env:computername.PS C:\> $env:computername OLDDOGChange the hostname to NEWTRICKS. Using the -Restart parameter will also immediately restart the server. Full documentation on the Rename-Computer cmdlet is available at Microsoft.
PS C:\> Rename-Computer -NewName "NEWTRICKS" -RestartVerify the hostname has changed with
$env:computername.PS C:\> $env:computername NEWTRICKS
How to Change the Hostname with the GUI
- Log in to the server via RDP.
- Navigate to the "This PC" screen and click "System properties".
- Click "Change settings" next to the current computer name.
- Click the "Change" button.
- Enter a new computer name and confirm by clicking "OK".
- Restart the server.
About Windows Hostnames
A hostname is what identifies a server. Most Windows Server users name their servers with the hostname consisting of two parts: role.domain. The role part is the role installed on the server, followed by the number. For example, if dc01 is the first server that acts as a DC in this particular network, Windows makes this an FQDN by putting the Active Directory domain as the domain part. For example, if this is the third web server in this network, and the domain is example.com, the hostname would be:
ws03.example.comNote that changing the hostname on Windows Server may conflict with some installed roles. Changing the hostname before installing roles on the server is a good idea. For recovery purposes, make a snapshot first if you decide to change the hostname on a Windows Server.