How to Deploy MatterMost - an Opensource Slack alternative
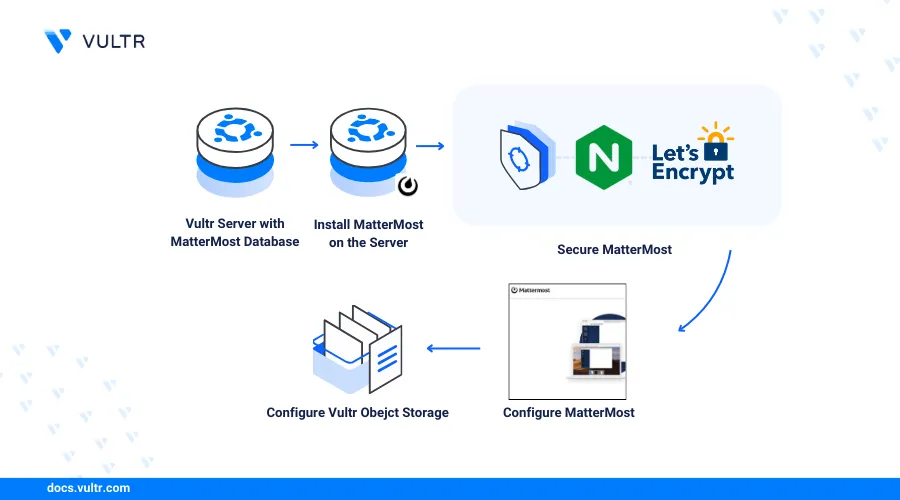
Introduction
Mattermost is an open-source messaging and collaboration platform that enables teams to securely connect using multiple communication options such as real-time messaging, voice calls, and screen sharing. It’s an alternative to instant messaging platforms such as Slack and highly extensible with features such as file sharing, notifications, webhooks, and integration with bots to customize the server based on your requirements.
This article explains how to deploy Mattermost and securely configure it on a Ubuntu server using your domain name. You will integrate Mattermost with a Vultr Managed Database for PostgreSQL to enable high availability and enable production features such as email notifications to enable multi-user access on your server.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- Deploy a Ubuntu 22.04 server instance on Vultr with at least
4GBRAM. - Deploy a Vultr Managed Database for PostgreSQL to use with Mattermost.
- Deploy a Vultr Object Storage instance and create a new bucket to store your Mattermost files. For example,
mattermost-data. - Create a new domain A record pointing to the server IP address. For example,
mattermost.example.com. - Access the server using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Create a new Mattermost Database
Mattermost supports MySQL and PostgreSQL databases to store the application data and runtime configurations. Integrating a managed database with Mattermost improves the application performance and offloads database storage functionalities from your server. Follow the steps below to connect to your Vultr Managed Database for PostgreSQL cluster and create a new database to use with Mattermost.
Install the PostgreSQL client package on your server.
console$ sudo apt install postgresql-client
Connect to your Vultr Managed Database for PostgreSQL cluster using the
psqlutility.console$ psql -h 7598276-0.vultrdb.com -U vultradmin -p 16751 -d defaultdb
Enter your Vultr Managed Database for PostgreSQL password to connect to the cluster.
Create a new database to use with Mattermost. For example,
mattermostdb.sqldefaultdb=> CREATE DATABASE mattermostdb;
Create a new PostgreSQL user role to use with the database. For example,
mmadmin.sqldefaultdb=> CREATE USER mmadmin WITH PASSWORD 'your-password';
Grant the user full privileges to the Mattermost database.
sqldefaultdb=> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE mattermostdb to mmadmin;
Grant the user access to all objects in the
publicschema.sqldefaultdb=> GRANT USAGE, CREATE ON SCHEMA PUBLIC TO mmadmin;
Grant the user ownership privileges to the
mattermostdbdatabase.sqldefaultdb=> ALTER DATABASE mattermostdb OWNER TO mmadmin;
Exit the PostgreSQL console.
sqldefaultdb=> \q
Connect to your Vultr Managed Database for PostgreSQL using your Mattermost database. Replace
mattermostdbandmmadminwith the actual database details you created.console$ psql -h 7598276-0.vultrdb.com -U mmadmin -p 16751 -d mattermostdb
Enter the PostgreSQL user password to log in and access the database.
Verify that the PostgreSQL console uses your Mattermost database. Then, list all databases available to the user.
sqlmattermostdb=> \l
Verify that the user has access to the Mattermost database. Your output should be similar to the one below:
List of databases Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges ------------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+----------------------- _dodb | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =T/postgres + | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres defaultdb | vultradmin | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | mattermostdb | mmadmin | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =Tc/mmadmin + | | | | | mmadmin=CTc/mmadmin template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres + | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres + | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres (5 rows)Exit the PostgreSQL console.
sqlmattermostdb=> \q
Install Mattermost
Add the latest Mattermost GPG public key to your server's keyrings.
console$ curl -sL -o- https://deb.packages.mattermost.com/pubkey.gpg | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/mattermost-archive-keyring.gpg > /dev/null
Download the Mattermost repository script and run it on your server.
console$ curl -o- https://deb.packages.mattermost.com/repo-setup.sh | sudo bash -s mattermost
The above command downloads the latest Mattermost repository script and outputs the file contents with
stdout. Then,bash –sexecutes the file contents with themattermostoption to import all repository information on your server.Update the server package index.
console$ sudo apt update
Install Mattermost.
console$ sudo apt install mattermost -y
View the Mattermost system service status to verify that the application is available on your server.
console$ sudo systemctl status mattermost
Output:
● mattermost.service - Mattermost Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mattermost.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: inactive (dead)Based on the above output, Mattermost is installed but not actively running on the server. Modify the Mattermost server configuration to set up the database connection details and securely configure the application for access using your domain.
Configure Mattermost
Mattermost creates the /opt/mattermost directory on your server that includes the full application and configuration files. Within the directory, the config subdirectory contains a config.json file that includes all Mattermost configurations required to run the application on your server. Follow the steps below to configure Mattermost to use your Vultr Managed Database for PostgreSQL and specify a domain to run the application on your server.
Navigate to the Mattermost configuration files directory.
console$ cd /opt/mattermost/config/
Copy the default Mattermost configuration file
config.defaults.jsonand rename it toconfig.json.console$ cp config.defaults.json config.json
Grant the Mattermost user ownership privileges to the
config.jsonfile.console$ sudo chown mattermost:mattermost config.json
Set the file permissions to
600to limit other system users or processes from accessing the file.console$ sudo chmod 600 config.json
Long list the directory files and verify the new user permission changes.
console$ ls -l
Output:
total 52 -rw-r--r-- 1 mattermost mattermost 1137 May 1 14:58 cloud_defaults.json -rw------- 1 mattermost mattermost 20036 May 1 14:58 config.defaults.json -rw------- 1 mattermost mattermost 22884 May 20 20:44 config.json -rw-r--r-- 1 mattermost mattermost 260 May 1 14:58 README.mdBased on the above output,
rw - - -means only the Mattermost user can read or write changes to theconfig.jsonfile. However, privileged users such asrootcan modify the file with elevated privileges.Open the Mattermost
config.jsonfile using a text editor such as Nano.console$ sudo nano config.json
Find the
ServiceSettingssection to set up your Mattermost connection settings.json"ServiceSettings": { "SiteURL": "https://mattermost.example.com", "WebsocketURL": "", "LicenseFileLocation": "", "ListenAddress": ":8065",
- Enter your Mattermost domain URL in the
SiteURLfield. Replacemattermost.example.comwith your actual domain.
json"SiteURL": "https://mattermost.example.com",
- Find the following
SqlSettingssection to set up your database settings.
json"SqlSettings": { "DriverName": "postgres", "DataSource": "postgres://mmuser:mostest@localhost/mattermost_test?sslmode=disable\u0026connect_timeout=10\u0026binary_parameters=yes", "DataSourceReplicas": [],
- Replace the default
DataSourcevalues with your Vultr Managed Database for PostgreSQL details you created earlier. In addition, change thesslmodeoption fromdefaulttorequire.
json"DataSource": "postgres://mmadmin:your-password@7598276-0.vultrdb.com:16751/mattermostdb?sslmode=require\u0026connect_timeout=10\u0026binary_parameters=yes",
Save and close the file.
- Enter your Mattermost domain URL in the
Start the Mattermost server to validate and apply your configuration.
console$ sudo systemctl start mattermost
Wait at least
5minutes for the Mattermost server to apply all configurations and write data to the PostgreSQL database. When the process is complete, verify that your output does not include any errors. If you receive any errors similar to the one below, open yourconfig.jsonfile and verify your configuration changes.Job for mattermost.service failed because the control process exited with error code. See "systemctl status mattermost.service" and "journalctl -xe" for details.Run the following command to view the Mattermost log entries and troubleshoot any application errors.
console$ sudo cat /var/log/syslog | tail -n 20
View the Mattermost server status and verify that the application is active.
console$ sudo systemctl status mattermost
Your output should be similar to the one below.
● mattermost.service - Mattermost Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mattermost.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2024-05-20 18:57:10 UTC; 2h 54min ago Main PID: 34945 (mattermost) Tasks: 42 (limit: 2213) Memory: 368.2M CPU: 27.937s CGroup: /system.slice/mattermost.service ├─34945 /opt/mattermost/bin/mattermost ├─34954 plugins/com.mattermost.nps/server/dist/plugin-linux-amd64 ├─34961 plugins/com.mattermost.calls/server/dist/plugin-linux-amd64 ├─34969 plugins/playbooks/server/dist/plugin-linux-amd64 └─35192 plugins/github/server/dist/plugin-linux-amd64You have configured Mattermost to run on your server and use your Vultr Managed Database for PostgreSQL. Configure your web server to serve Mattermost using your domain to securely access the application.
Set Up Nginx as a Reverse Proxy to Access Mattermost
Mattermost listens for incoming connections on the host port 8065 by default and securely accepts simultaneous connection requests through a reverse proxy such as Nginx. Follow the steps below to install the Nginx and configure it as a reverse proxy to securely forward all connection requests to Mattermost.
Update the server package index.
console$ sudo apt update
Install Nginx.
console$ sudo apt install nginx -y
Disable the default Nginx configuration to avoid conflicts on the HTTP port
80.console$ sudo rm /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
Create a new Nginx configuration file to use with Mattermost. For example,
mattermost.example.conf.console$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/mattermost.example.conf
Add the following configurations to the file. Replace
mattermost.example.comwith your actual domain.nginxupstream mattermost { server 127.0.0.1:8065; keepalive 32; } server { listen 80 default_server; server_name mattermost.example.com; return 301 https://$server_name$request_uri; } server { listen 443 ssl http2; listen [::]:443 ssl http2; server_name mattermost.example.com; http2_push_preload on; # Enable HTTP/2 Server Push ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/mattermost.example.com/fullchain.pem; ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/mattermost.example.com/privkey.pem; ssl_session_timeout 1d; ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; ssl_early_data on; ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384'; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:50m; add_header Strict-Transport-Security max-age=15768000; ssl_stapling on; ssl_stapling_verify on; add_header X-Early-Data $tls1_3_early_data; location ~ /api/v[0-9]+/(users/)?websocket$ { proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; client_max_body_size 50M; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; proxy_set_header X-Frame-Options SAMEORIGIN; proxy_buffers 256 16k; proxy_buffer_size 16k; client_body_timeout 60s; send_timeout 300s; lingering_timeout 5s; proxy_connect_timeout 90s; proxy_send_timeout 300s; proxy_read_timeout 90s; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_pass http://mattermost; } location / { client_max_body_size 100M; proxy_set_header Connection ""; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; proxy_set_header X-Frame-Options SAMEORIGIN; proxy_buffers 256 16k; proxy_buffer_size 16k; proxy_read_timeout 600s; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_pass http://mattermost; } } map $ssl_early_data $tls1_3_early_data { "~." $ssl_early_data; default ""; }
Save and close the file.
The above configuration forwards all connection requests to the backend Mattermost application port
8065. In addition, all HTTP connections redirect to HTTPS with HTTP/2 support to secure connections on the Mattermost server.Link the configuration file to the
/sites-enableddirectory to enable it on your server.console$ sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/mattermost.example.com /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
You have created a new Mattermost configuration to securely accept and forward connections on your server. Do not restart the Nginx web server until you generate SSL certificates that match your domain to avoid configuration errors.
Secure the Mattermost Server
The default Mattermost port 8065 is secure from direct connections on the server when using Nginx as a reverse proxy. Follow the steps below to allow connections to the HTTP and HTTPS ports on your server. Then, generate trusted Let’s Encrypt SSL certificates to secure all connections on your Mattermost server and validate your Nginx configuration.
The Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) is active and limits connections on your Ubuntu server by default. Allow the HTTP port
80through the firewall to enable Let's Encrypt domain validations on your server.console$ sudo ufw allow 80 comment 'mattermost http'
Allow the HTTPS port
443to enable secure access to the Mattermost server.console$ sudo ufw allow 443 comment 'mattermost http'
Restart UFW to apply changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
View the firewall table to verify that the new connection rules are available.
console$ sudo ufw status
Output:
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- 22/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 80 ALLOW Anywhere # mattermost http 443 ALLOW Anywhere # mattermost http 22/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) # mattermost http 443 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) # mattermost http
Generate Let's Encrypt SSL Certificates to use with Mattermost
Install the Certbot Let’s Encrypt plugin for Nginx.
console$ sudo apt install python3-certbot-nginx -y
Generate new SSL certificates using the
certonlyoption to disable modifications to your Nginx configuration. Replacemattermost.example.comwith your actual domain.console$ sudo certbot --standalone certonly -d mattermost.example.com --agree-tos
Your output should be similar to the one below when the certificate request is successful.
Obtaining a new certificate Performing the following challenges: http-01 challenge for mattermost.example.com Waiting for verification... Cleaning up challengesTest your Nginx configuration for errors.
console$ sudo nginx -t
Output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successfulRestart Nginx to apply your Mattermost configurations.
console$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Access Mattermost
Access your Mattermost domain using a web browser such as Chrome.
https://mattermost.example.comVerify that the Mattermost configuration interface displays in your web browser.
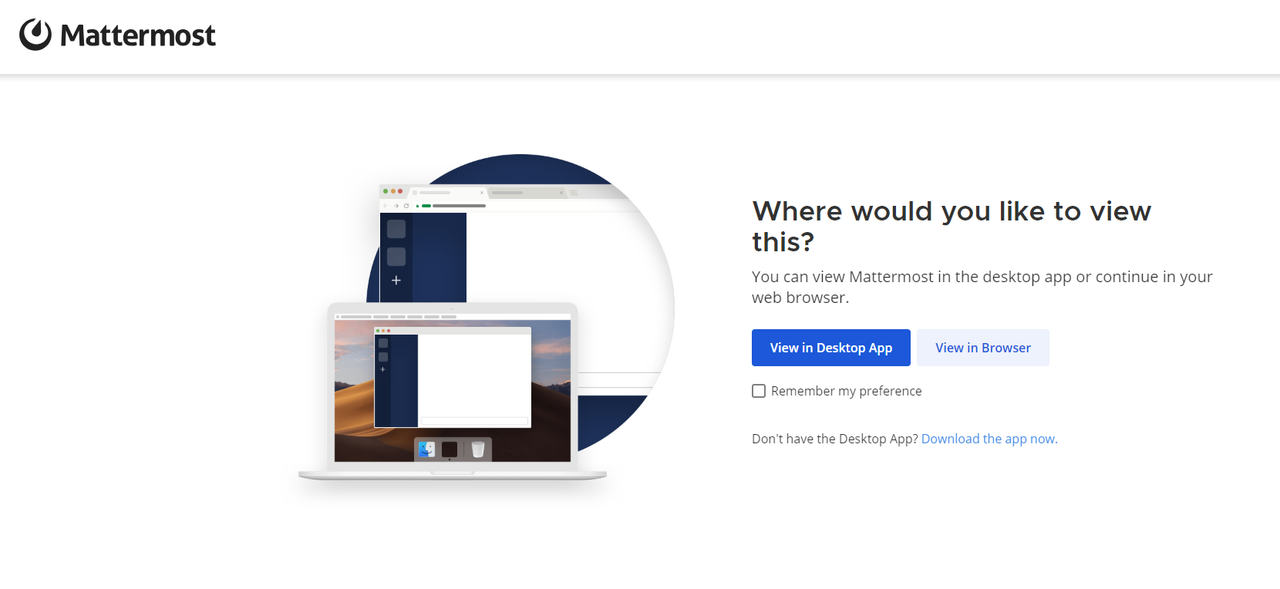
Click View in Browser to access the Mattermost account setup options.
Enter your email address in the Email address field within the Create your account form.
Enter your administrator username in the Choose a Username field. Then, enter a strong password to assign to the new user.
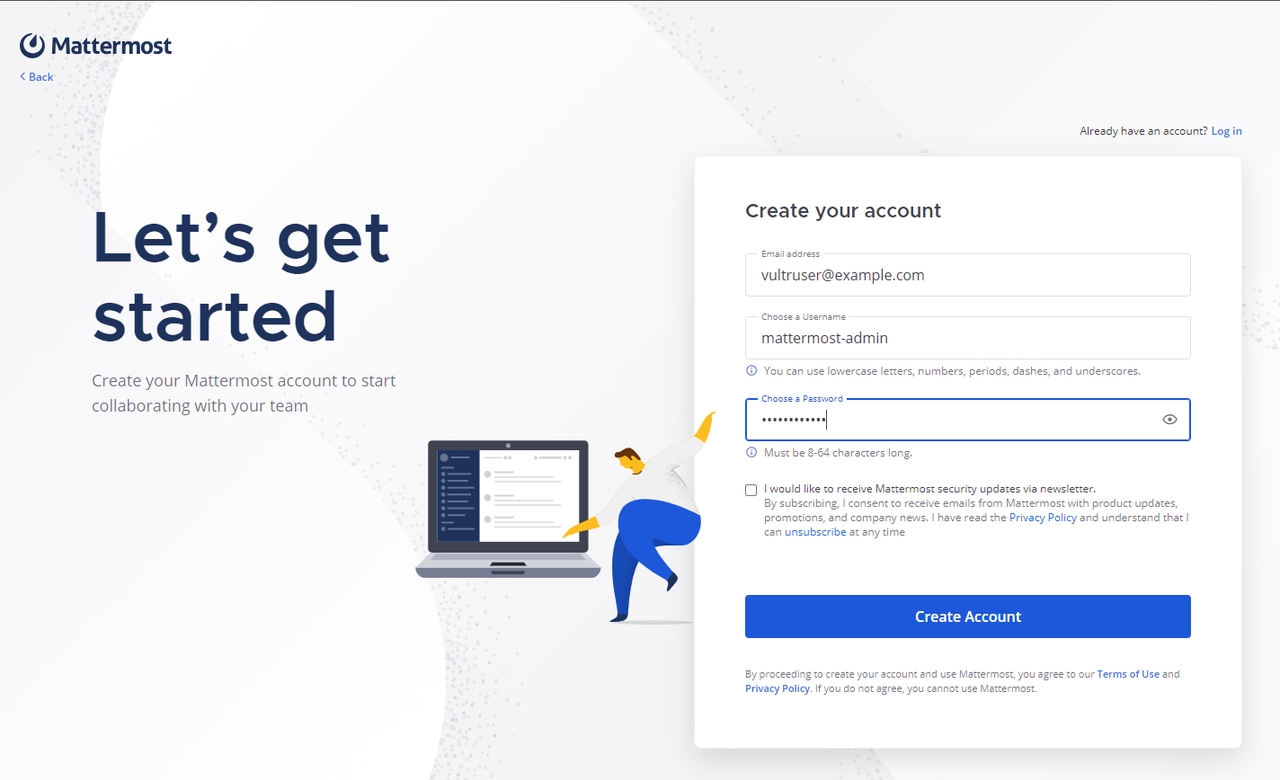
Click Create Account to apply the new Mattermost administrator account on your server.
Wait for the account creation process to complete and enter your workspace name in the Organization name field.
Select the external tools to activate in your Mattermost workspace and click Continue to save changes. For example, select
GitHubandZoomto enable the tools on your server.
Click Copy Link to copy and share your new Mattermost invite link with your target users.
Click Finish setup to apply your configuration changes and redirect to the Mattermost application interface.
Click Browse or Create Channels next to your Mattermost team name to set up a new channel.
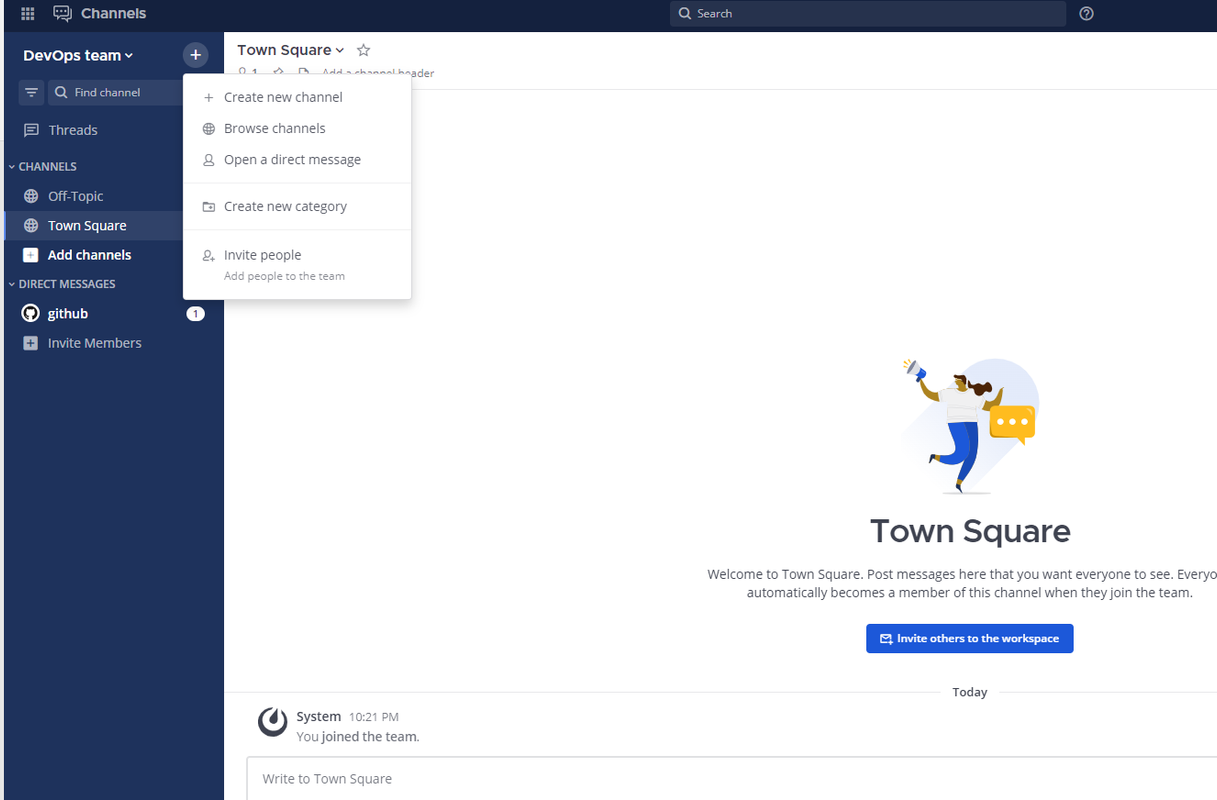
Select Create new channel from the list of options to create a new Mattermost channel on your server.
Enter a new channel name and set your visibility options. For example, enter
mynewteamand select Public Channel to allow all users in the Mattermost workspace to access the channel.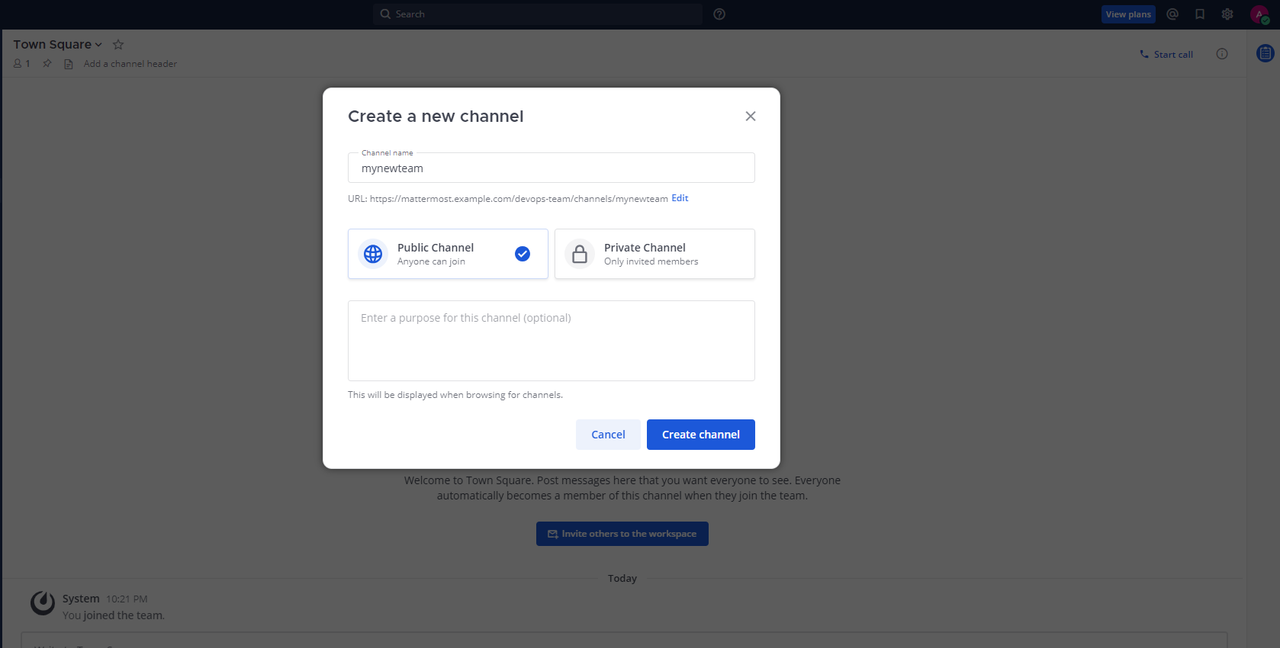
Enter a new channel description and click Create channel to apply the new channel on your Mattermost server.
Verify that the Mattermost channel is created and available on your Channels list.
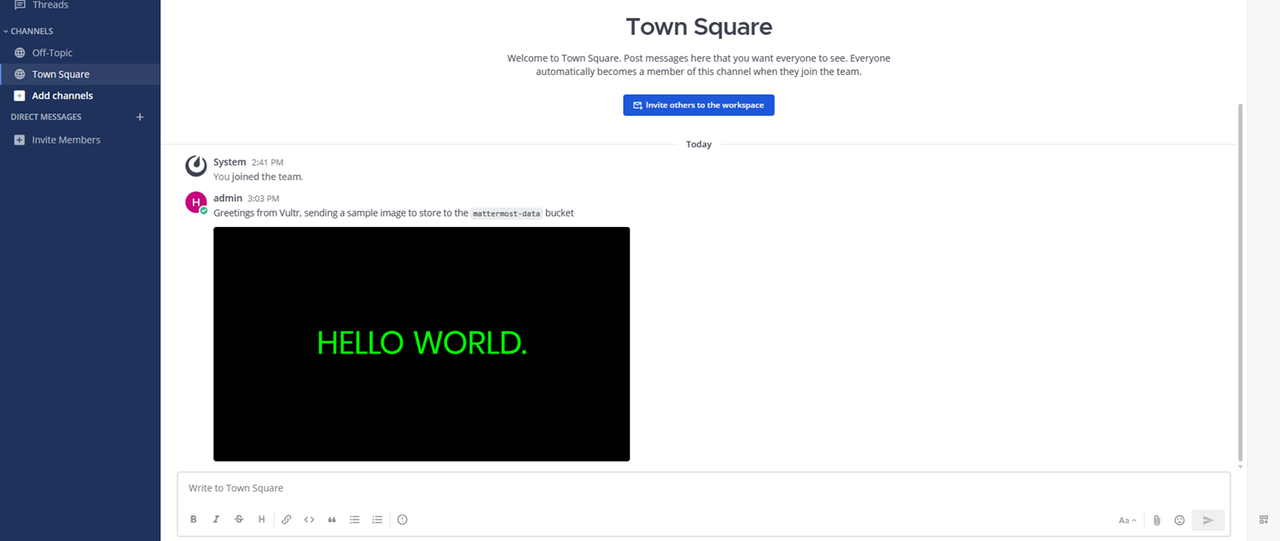
Enter a sample message in the new channel to verify that your Mattermost server works correctly. For example, enter
Hello World! This is a new Mattermost serverand press Enter to send the message.Verify that your new message is sent and available in the channel messages.
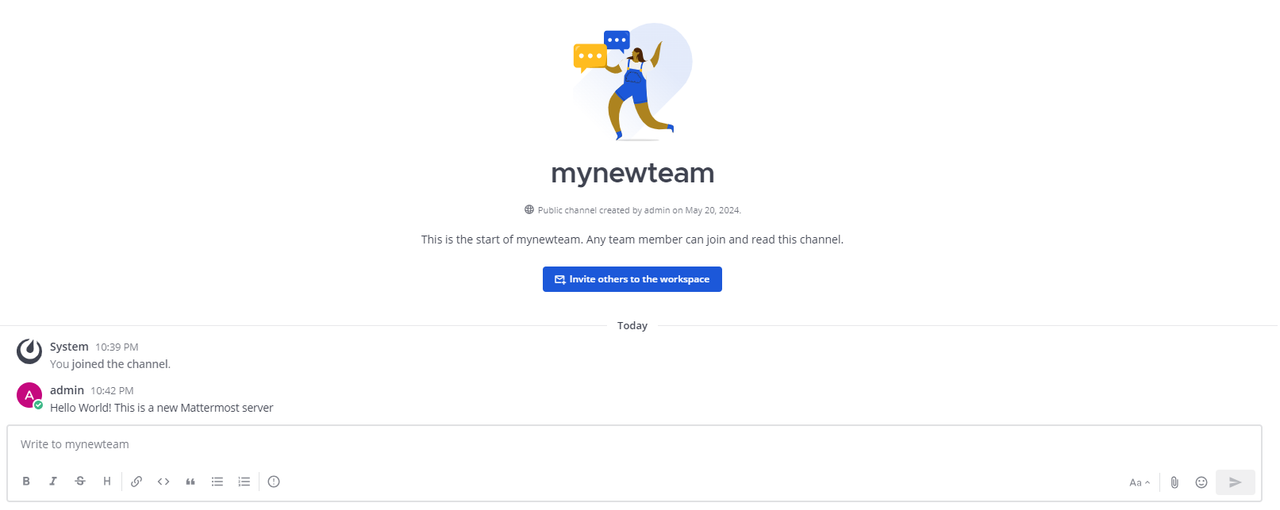
Expand the main Mattermost menu next to Channels on the top navigation bar to access the system configuration options.
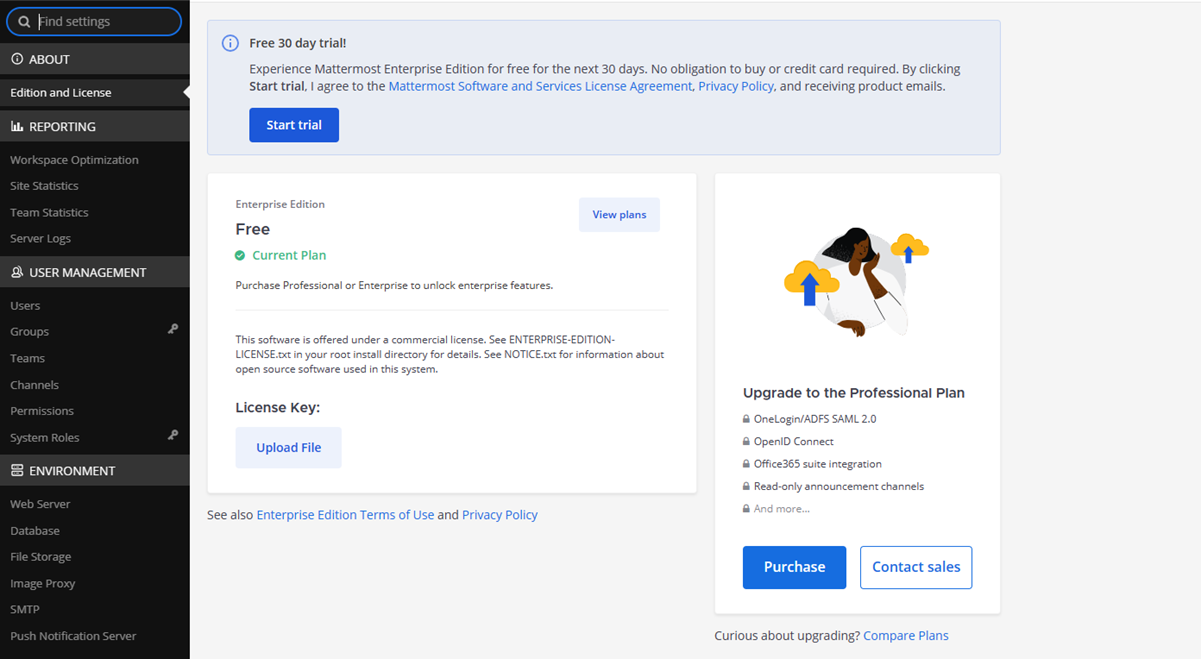
Select System Console from the list of options to open the administrator console. Alternatively, access the
/admin_consolepath using your domain in a new browser tab.https://mattermost.example.com/admin_consoleVerify that the Mattermost administrator console displays in your browser and view the Mattermost edition and license version installed on your server.
Find the USER MANAGEMENT section on your main navigation menu and click Users to access the list of Mattermost users in your workspace.
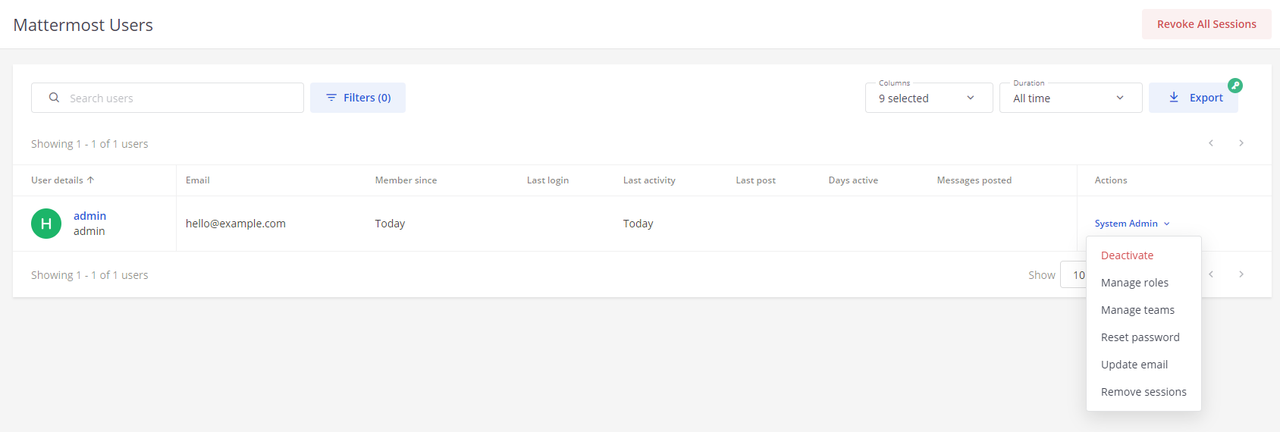
Verify the list of Mattermost users on your server and click the Actions menu to modify the user roles.
Click Save to apply your new Mattermost user changes.
Find the AUTHENTICATION section on the main navigation menu and click Signup to modify how users register on your Mattermost server.
Enter a list of domain names separated by
,in the Restrict new system and team members…. field to limit your Mattermost server to specific users. For example, enterexample.com,example.netto only accept new user emails with your target domains to sign up on the server.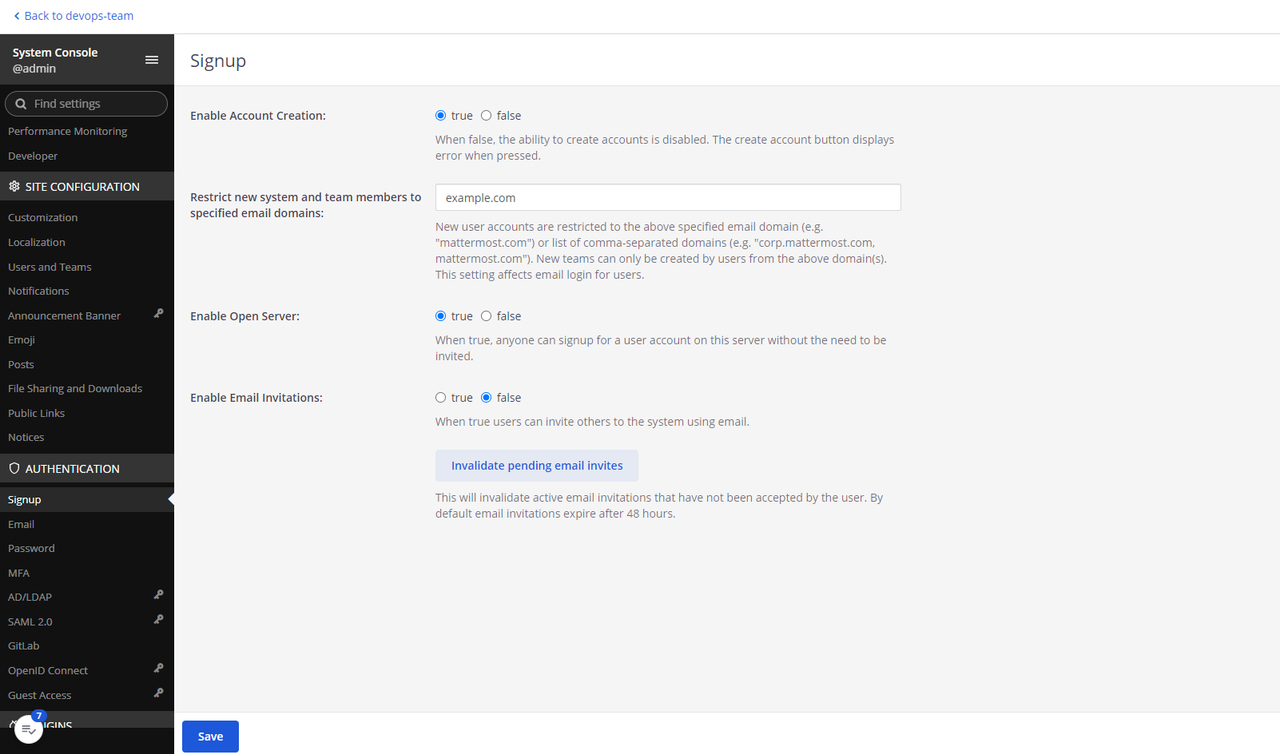
Set the Enable Open Server option to true to allow new users with email addresses that match your permitted domains to create accounts on your Mattermost server. Keep the option set to false to disable the signup page and strictly accept invitations on your server.
Click Save to apply your Mattermost workspace configurations.
Enable Mattermost Email Notifications
Mattermost sends multiple emails to workspace users when an SMTP server is enabled. A Preview Mode: Email notifications have not been configured. alert displays in your Mattermost interface when email services are not enabled. Use an existing SMTP service such as Sendgrid or install a self-hosted send-only email server using applications such as Postfix. Follow the steps below to enable SMTP connections using Postfix on your server to securely send email notifications on the Mattermost server.
25 is blocked on Vultr servers by default. Contact Vultr Support to enable the SMTP port 25 on your account.
Update your server package index.
console$ sudo apt update
Set your server hostname to your Mattermost domain. For example,
mattermost.example.com.console$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname mattermost.example.com
Install the Postfix
mailutilspackage.console$ sudo apt install mailutils -y
Select Internet Site and enter your domain
mattermost.example.comas thesystem mail namewhen prompted.Back up the original Postfix configuration file.
console$ sudo cp /etc/postfix/main.cf /etc/postfix/main.ORIG
Open the Postfix configuration file.
console$ sudo nano /etc/postfix/main.cf
Find the following Postfix
interfacesdirective.iniinet_interfaces = all
- Change the
inet_interfacesvalue fromalltoloopback-only.
iniinet_interfaces = loopback-only
- Find the
mydestinationdirective.
inimydestination = $myhostname, your_domain, localhost.com, , localhost
- Replace the existing values with the following domain values.
inimydestination = localhost.$mydomain,localhost,$myhostname
Save and close the file.
- Change the
Restart Postfix to apply your configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart postfix
Send a test email from your Postfix server to your active email address. For example,
johndoe@example.com.console$ echo "The Mattermost SMTP Server is ready to use" | mail -s "Hello from the Mattermost Server" johndoe@example.com
View your server logs and verify that the email is successfully sent to your email address.
console$ sudo cat /var/log/syslog | tail -n 10
Output:
mattermost postfix/smtp[3869]: 0316A1FEBED: to=<johndoe@example.com>, relay=mail.example.com[192.0.2.200]:25, delay=2, delays=0/0/1/1, dsn=2.0.0, status=sent (250 OK id=1s99jD-005ocG-6w)Visit your email inbox and verify that a new email from
server-username@your-mattermostdomainis available. Emails sent to domains such asgmail.commay bounce due to missing MX and SPF DNS records on your domain.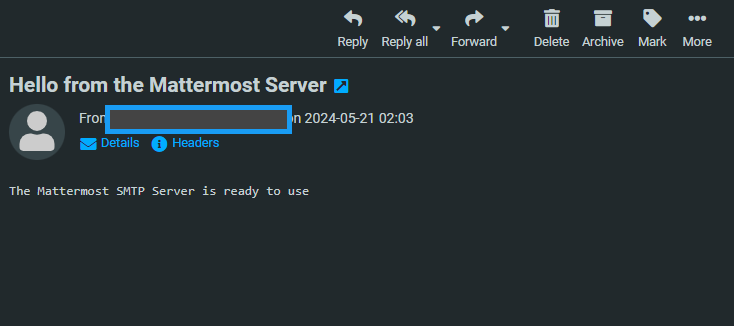
You have installed and configured Postfix on your server to handle outgoing email communications on your server. Configure your domain with DNS records with new SPF and DKIM values to approve the authenticity of emails sent from your SMTP server.
Configure Mattermost to use the Postfix SMTP server
Access the Mattermost administrator console.
https://mattermost.example.com//admin_consoleFind the ENVIRONMENT section on the main navigation menu and click SMTP to modify your Mattermost email configurations.
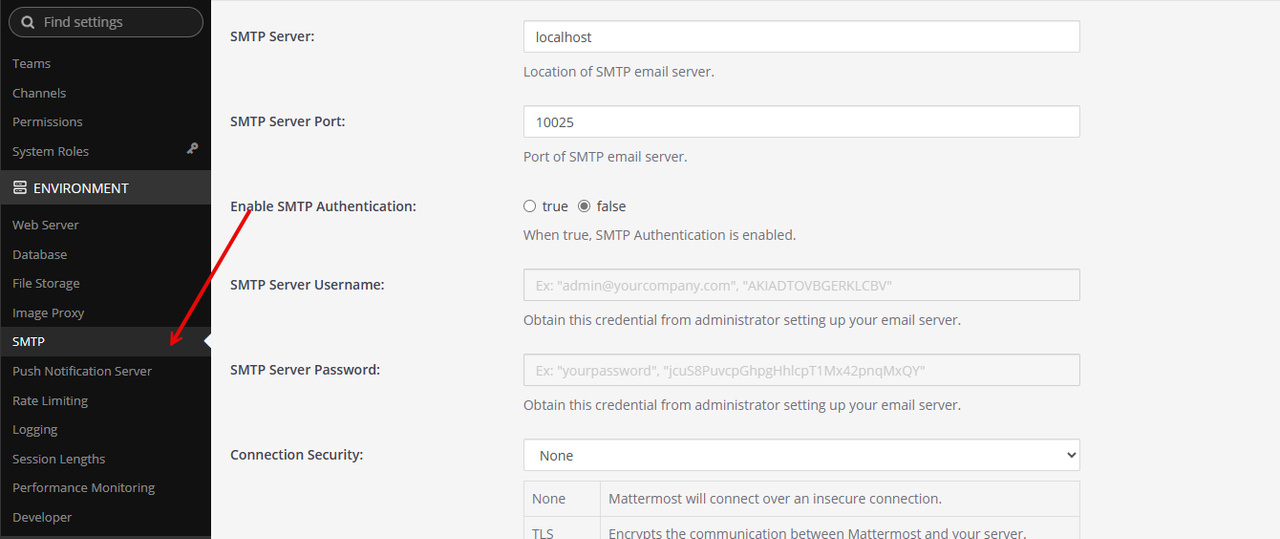
Keep
localhostas the SMTP Server value.Replace the default value
10025with25in the SMTP Server Port field.Set the Skip Server Certificate Verification option to true to disable verification of the Postfix email server certificate.
Click Save to apply your SMTP configuration.
Click Test Connection to validate your SMTP connection. Verify that a new message
No errors were reported while sending an email. Please check your inbox to make sure.displays in your interface to confirm that Mattermost can send email notifications to all registered users.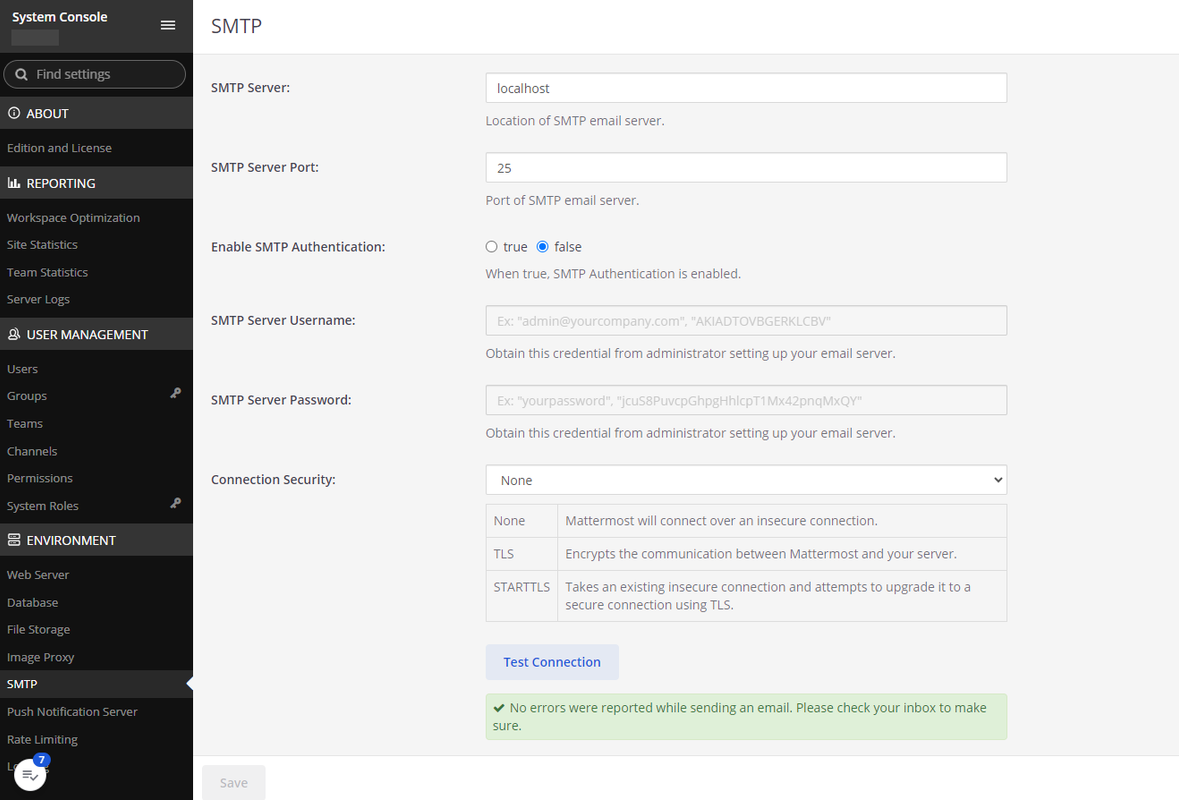
You have configured email settings on your server. Mattermost can send multiple email notifications to all users depending on your workspace configurations. Modify your Mattermost email templates to create a standard format to send specific emails such as password resets, authentication, verifications, and channel notifications on your server.
Enable Vultr Object Storage as the Default Mattermost Storage
Mattermost stores files and image attachments to the /opt/mattermost/data directory. In addition, it supports S3-compatible storage such as Vultr Object Storage to store the files and image attachments on your remote storage instead of server storage. Follow the steps below to configure Mattermost to use Vultr Object Storage as the default file storage system.
Access your Mattermost administrator console in your web browser.
https://mattermost.example.com//admin_consoleFind the ENVIRONMENT category on the main navigation menu and click File Storage from the list of options.
Click the File Storage System dropdown and select Amazon S3 .
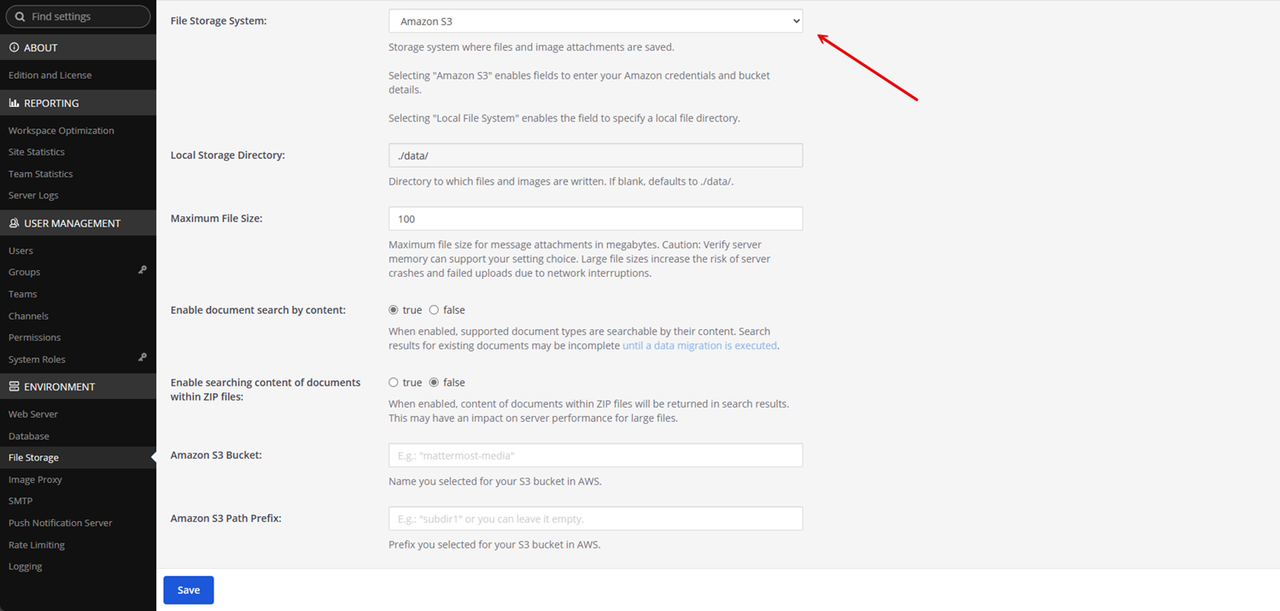
Enter your Vultr Object Storage bucket name in the Amazon S3 Bucket field to use with Mattermost.
Keep the Amazon S3 Path Prefix and Amazon S3 Region fields empty.
Enter your Vultr Object Storage access key in the Amazon S3 Access Key ID field.
Enter your Vultr Object Storage hostname in the Amazon S3 Endpoint field.
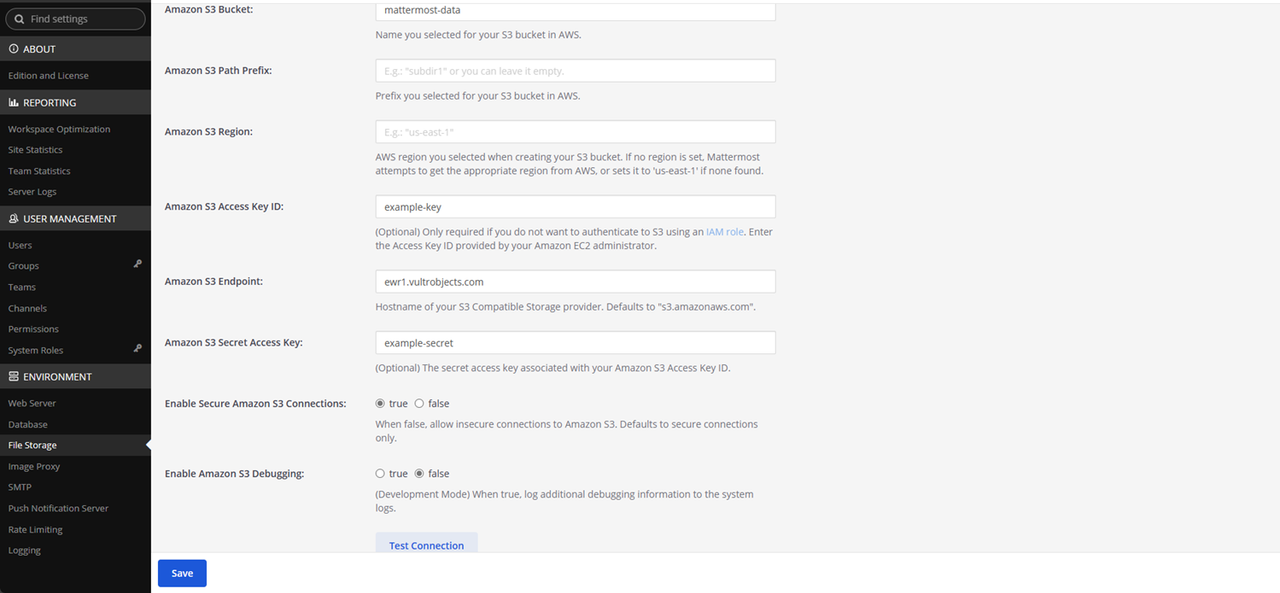
Enter your Vultr Object Storage secret key in the Amazon S3 Secret Access Key field.
Keep the Enable Secure Amazon S3 Connections option set to
true.Click Save to apply your Mattermost file storage configurations.
Click Test Connection to validate your Vultr Object Storage credentials and verify that a
Connection was successfulmessage displays in your interface.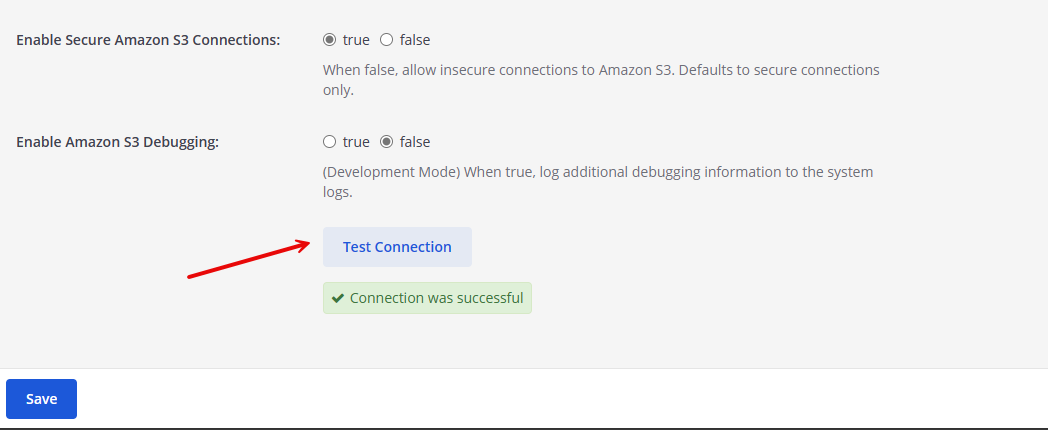
You have enabled Mattermost to use Vultr Object Storage as the default file storage system to store all workspace files and image attachments to your bucket instead of server storage.
Connect Client Applications to the Mattermost Server
Mattermost supports client applications on multiple device versions such as Android, desktop, and IOS. Follow the steps below to connect your client application to the Mattermost server.
Download and install the official Mattermost application for your device from the official website. For example, Mattermost for Android.
Open the Mattermost application on your device.
Click Get Started within the application interface.

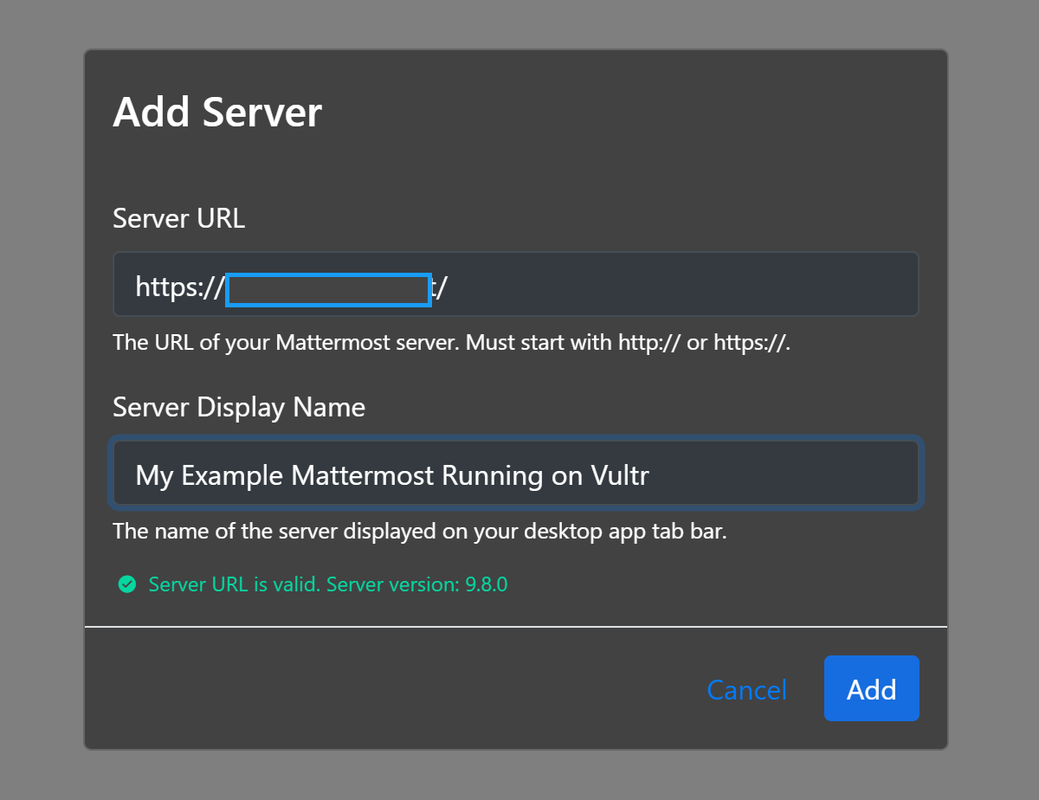
Enter your Mattermost server domain URL in the Server URL field.
Enter a display name in the Server display name field to identify your Mattermost workspace on the device.
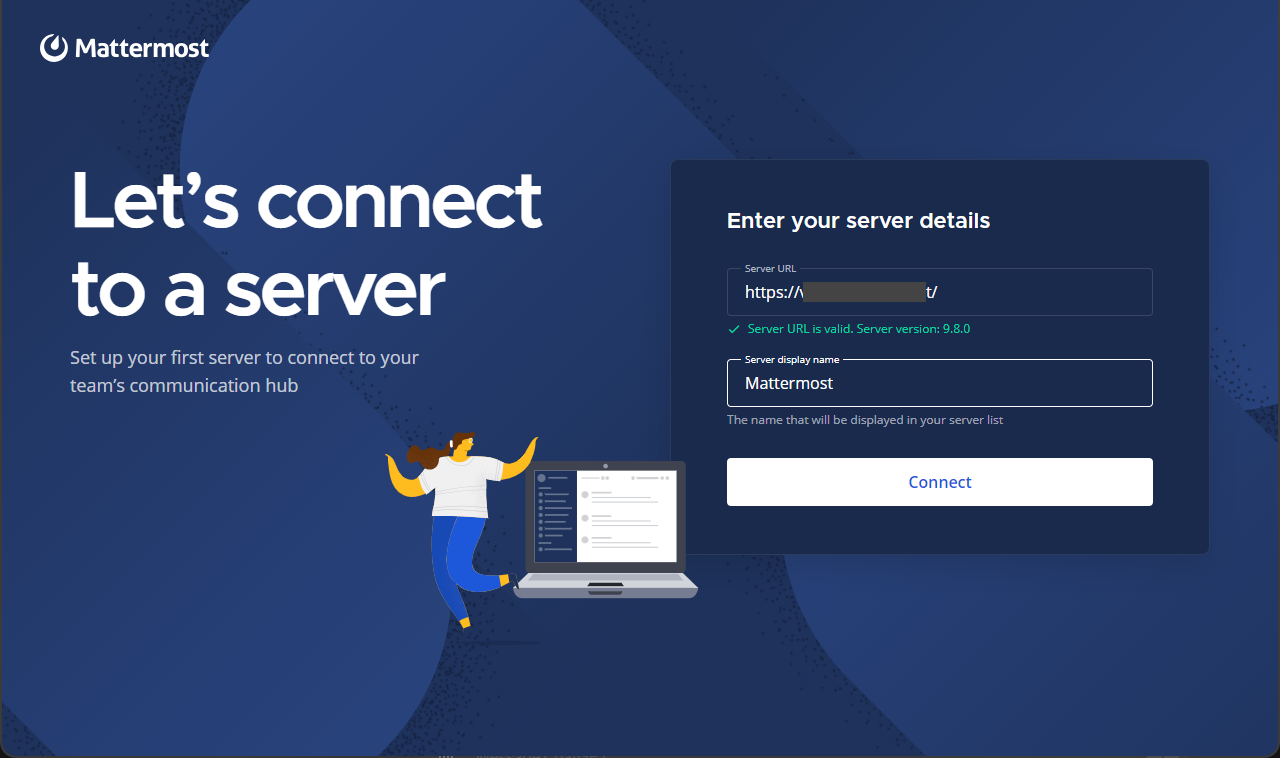
Verify that a
Server URL is valid. Server version:prompt appears below your workspace URL and click Connect to establish a connection to your server.Enter your workspace email and password to log in to the server.
To create a new user, click Don’t have an account to access the signup form and fill in all required fields to create a new account in your Mattermost workspace. When the process is successful, open your invite link in a new web browser tab and log in to your account to join a specific Mattermost channel.
Verify that your Mattermost client application can access all enabled channels available on your server to start interacting with other teams.
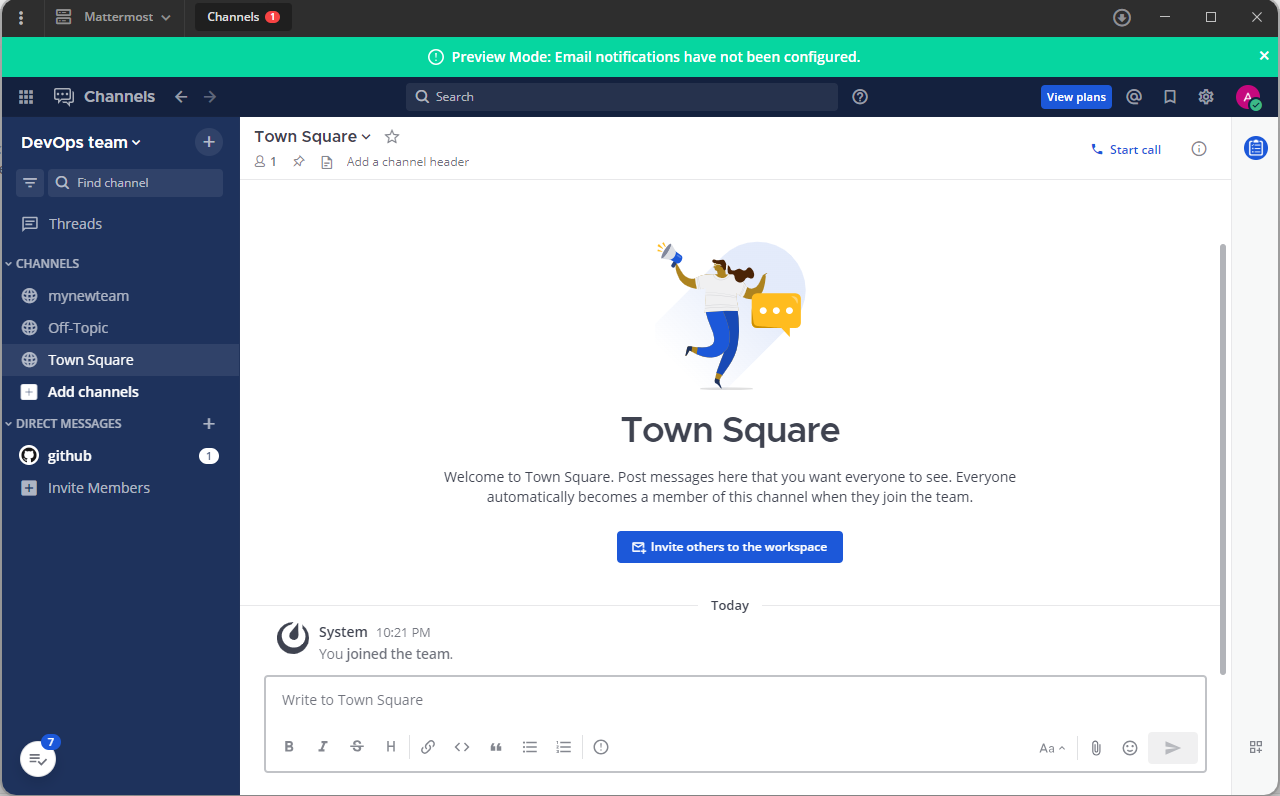
Conclusion
You have deployed Mattermost and secured your workspace with production environment configurations on a Ubuntu server. Mattermost is an efficient collaboration platform that lets you manage multiple teams using workspaces. As a result, by offloading critical server roles such as database and file storage to managed services such as Vultr Object Storage, your Mattermost server can process large amounts of user requests and traffic in your workspace. For more information, please visit the Mattermost documentation to find more options you can enable in your workspace.