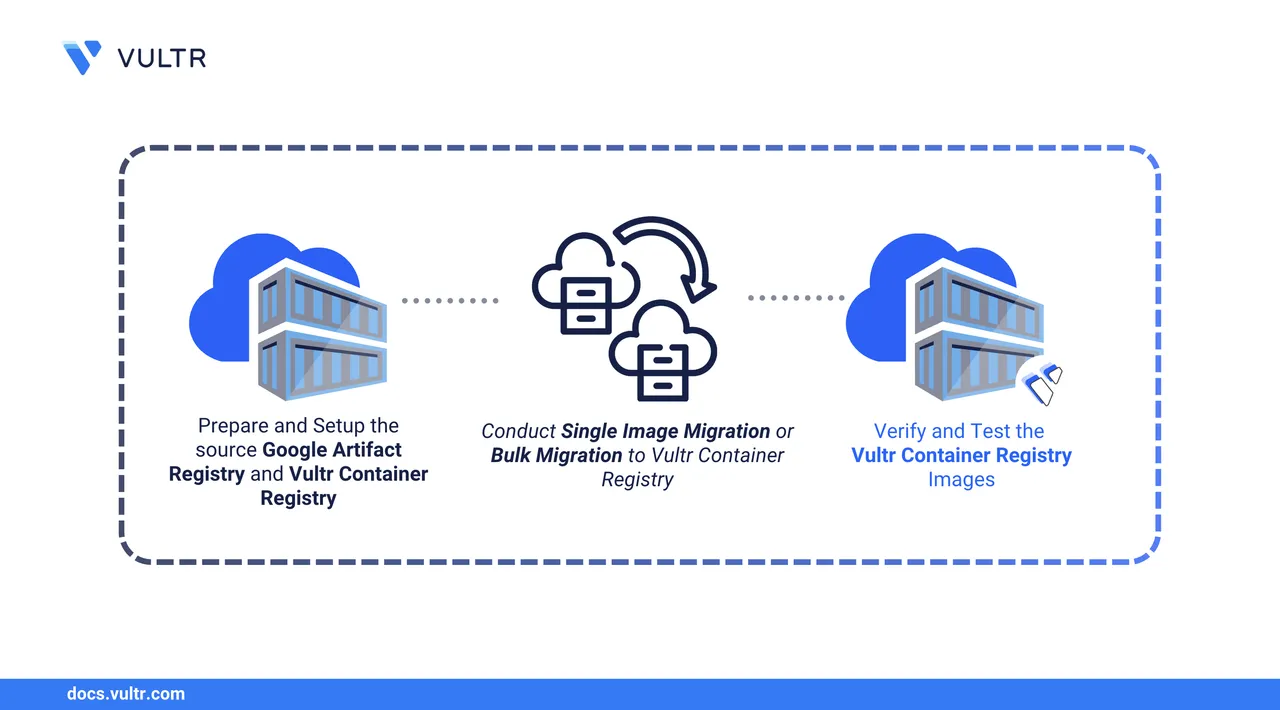
Container Registry is used to store and manage container images. Migrating your container images from Google Artifact Registry to Vultr Container Registry offers several benefits, such as improved performance, cost efficiency, integration with Vultr's cloud infrastructure, and straightforward management with Vultr's intuitive customer portal interface.
Follow this guide to migrate your Google Artifact Registry images with the Docker Artifact format to the Vultr Container Registry. You will migrate all the images and verify data integrity post-migration.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- Have access to an Ubuntu 24.04 based server as a non-root sudo user to use as the migration workstation.
- Install Docker on your migration workstation to manage container images.
- Install gcloud CLI and initialize it with access to your GCP project.
- Provision a Vultr Container Registry to use as your destination Registry.
- Assign appropriate roles to your User account or Service account to access your Google Artifact Registry.
Prepare the Source Google Cloud Artifact Registry
In this section, you configure access credentials for your Google Artifact Registry with Docker. There are several methods to configure Google Artifact Registry authentication with Docker. This guide uses the gcloud CLI credential helper.
Follow the steps below on your Ubuntu machine to configure the access credentials for your Google Artifact Registry with Docker.
Add your non-root sudo user to the Docker group to grant permission to run the
dockercommand.console$ sudo usermod -a -G docker $USER
Authenticate Docker with your Google Artifact Registry.
console$ gcloud auth configure-docker europe-central2-docker.pkg.dev
Replace
europe-central2with the location of your Google Artifact Registry.Example output:
Adding credentials for: europe-central2-docker.pkg.dev After update, the following will be written to your Docker config file located at [/home/linuxuser/.docker/config.json]: { "credHelpers": { "europe-central2-docker.pkg.dev": "gcloud" } } Do you want to continue (Y/n)?Enter Y at the prompt to continue.
Now your Docker client can connect to your Google Artifact Registry.
Set Up the Vultr Container Registry
Follow the steps below to authenticate your workstation with the Vultr Container Registry.
Log in to your Vultr Customer Portal.
Choose the newly provisioned Vultr Container Registry.
Copy the login command from the Overview page.
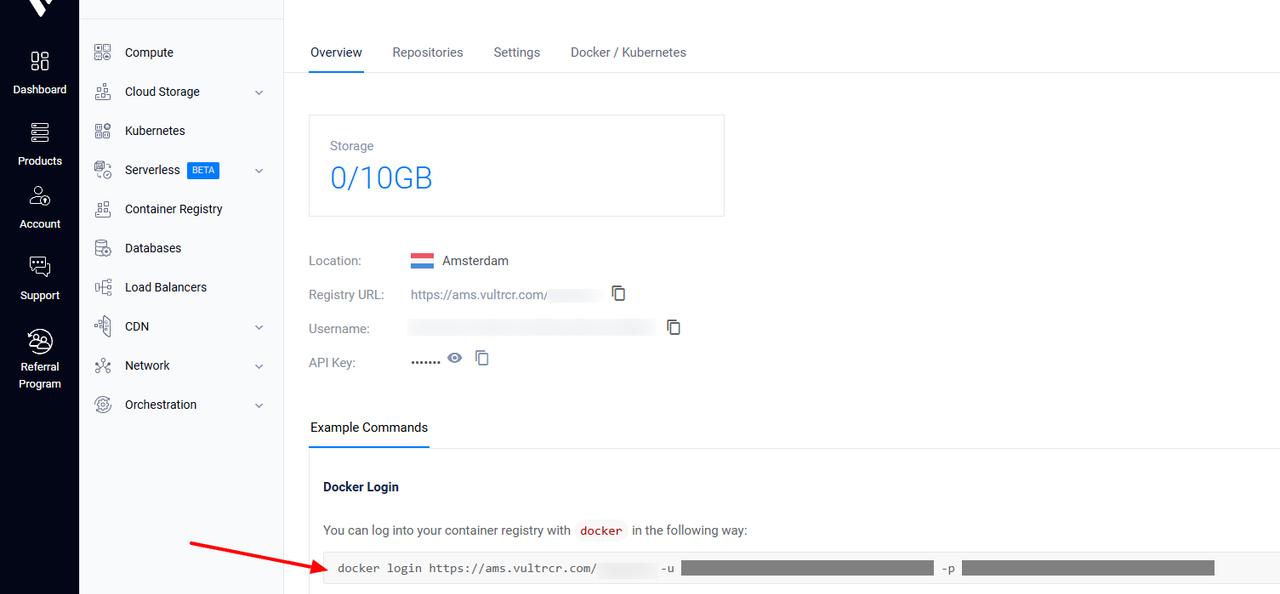
Also, note the
UsernameandAPI Keyvalues.Run the copied command to authenticate with your Vultr Container Registry. For example:
console$ docker login <vultr_registry_url> --username <your_vultr_username> --password <your_vultr_password>
Example output indicating successful login:
WARNING! Using --password via the CLI is insecure. Use --password-stdin. WARNING! Your credentials are stored unencrypted in '/home/linuxuser/.docker/config.json'. ... Login Succeeded
Migrate Repositories From the Google Cloud Artifact Registry to the Vultr Container Registry Using Docker
Follow the steps below to migrate all container images with all tags from your Google Artifact Registry to your Vultr Container Registry.
List the active registries.
console$ gcloud artifacts repositories list
Example output:
Listing items under project project-abc123, across all locations. ARTIFACT_REGISTRY REPOSITORY FORMAT MODE DESCRIPTION LOCATION LABELS ENCRYPTION CREATE_TIME UPDATE_TIME SIZE (MB) example-repo DOCKER STANDARD_REPOSITORY europe-central2 Google-managed key 2025-02-11T18:58:05 2025-02-12T16:38:05 3.475Note the location of your source repository, for instance,
europe-central2.Create a new file named
pull_images.sh.console$ nano pull_images.sh
Add the following code to the
pull_images.sh. Assign the variablesPROJECT_ID,LOCATION, andREPOwith your Google Cloud project ID, the location of your Google Artifact Registry, and its name as values.bash#!/bin/bash GCP_PROJECT_ID="project-abc123" LOCATION="europe-central2" GCP_REPO="example-repo" HOST="${LOCATION}-docker.pkg.dev" for image in $(gcloud artifacts docker images list "${HOST}/${GCP_PROJECT_ID}/${GCP_REPO}" --format="value(IMAGE)"); do for tag in $(gcloud artifacts docker tags list "${image}" --format="value(TAG)" 2>/dev/null); do docker pull "${image}:${tag}" done done
The script above automatically downloads all images and their tags from your artifact registry to your migration workstation.
Save and exit the file.
Make the
pull_images.shfile executable.console$ chmod +x pull_images.sh
Run the script to pull all GCP images.
console$ ./pull_images.shCreate a new file named
push_images.sh.console$ nano push_images.sh
Add the following code to the
push_images.shfile. Replace the valueams.vultrcr.com/examplefor the variableVULTR_REGISTRY_URLwith your Vultr Container Registry URL, without thehttps://prefix at the beginning of the URL.bash#!/bin/bash GCP_HOST="europe-central2-docker.pkg.dev" GCP_PROJECT_ID="project-abc123" GCP_REPO="example-repo" VULTR_REGISTRY_URL="ams.vultrcr.com/example" for image in $(docker images --format "{{.Repository}}:{{.Tag}}" | grep "^${GCP_HOST}/${GCP_PROJECT_ID}/${GCP_REPO}"); do IMAGE_BASENAME=$(basename "${image}" | cut -d: -f1) IMAGE_TAG=$(basename "${image}" | cut -d: -f2) NEW_IMAGE="${VULTR_REGISTRY_URL}/${IMAGE_BASENAME}:${IMAGE_TAG}" echo "--- Migrating ${IMAGE_BASENAME}:${IMAGE_TAG} ---" docker tag "${image}" "${NEW_IMAGE}" docker push "${NEW_IMAGE}" echo "Successfully migrated to ${NEW_IMAGE}" echo "" done
The script above finds local Docker images that originate from the specified Google Artifact Registry. It then automatically retags each image for your Vultr Container Registry and pushes it to the new destination.
Save and exit the file.
Make the
push_images.shfile executable.console$ chmod +x push_images.sh
Run the script to push the images to the Vultr Container Registry.
console$ ./push_images.sh
skopeo is a tool for working with container registries and images. It has a copy functionality that allows you to migrate images between two remote registries. In this section, you migrate your images from Google Cloud Artifact Registry to the Vultr Container Registry.
Sign in to your Vultr Customer Portal and navigate to your Container Registry.
Note the
Registry URL,Username, andAPI Key.To migrate an image from Google Cloud Artifact Registry, use the following command:
console$ skopeo copy \ --src-creds oauth2accesstoken:$(gcloud auth print-access-token) \ --dest-creds 'VULTR_USERNAME:VULTR_API_KEY' \ docker://europe-central2-docker.pkg.dev/PROJECT_ID/YOUR_REPO/YOUR_IMAGE:TAG \ docker://VULTR_REGISTRY_URL/NEW_IMAGE:TAG
In the above command, replace:
europe-central2with the location of your Google Artifact Registry.PROJECT_IDwith your Google Cloud project ID.YOUR_REPOwith the repository name.YOUR_IMAGE:TAGwith your source image name and tag.VULTR_REGISTRY_URLwith your Vultr registry's URL (e.g.,sgp.vultrcr.com/vcr1).NEW_IMAGE:TAGwith the desired destination image name and tag.VULTR_USERNAMEandVULTR_API_KEYwith your Vultr container registry credentials.
To migrate all images from your Google Cloud Artifact Registry to your Vultr Container Registry, create a script
migrate.sh.console$ nano migrate.sh
Add the following content to the file.
bash#!/bin/bash # Configuration GCP_PROJECT="project-abc123" GAR_LOCATION="europe-central2" GAR_REPO="example-repo" VULTR_USERNAME="your-vultr-username" VULTR_API_KEY="your-vultr-api-key" VULTR_REGISTRY_URL="ams.vultrcr.com/example" IMAGES=$(gcloud artifacts docker images list "${GAR_LOCATION}-docker.pkg.dev/${GCP_PROJECT}/${GAR_REPO}" --format="get(IMAGE)") for IMAGE_PATH in $IMAGES; do IMAGE_NAME=$(basename "$IMAGE_PATH") TAGS=$(gcloud artifacts docker tags list "$IMAGE_PATH" --format="value(TAG)") for TAG in $TAGS; do SRC_IMAGE="docker://${GAR_LOCATION}-docker.pkg.dev/${GCP_PROJECT}/${GAR_REPO}/${IMAGE_NAME}:${TAG}" DST_IMAGE="docker://${VULTR_REGISTRY_URL}/${IMAGE_NAME}:${TAG}" skopeo copy \ --src-creds "oauth2accesstoken:$(gcloud auth print-access-token)" \ --dest-creds "${VULTR_USERNAME}:${VULTR_API_KEY}" \ "$SRC_IMAGE" "$DST_IMAGE" done done
In the above file, provide the variables of the
# Configurationsection with your actual values. Using your credentials, this script:- Fetches all the image names and their tags from your Google Cloud Artifact Registry.
- Copies the images from Google Cloud Artifact Registry to your Vultr Container Registry using
skopeo.
Save and exit the file.
Add execute permission to the file.
console$ chmod +x migrate.sh
Run the script to start the migration.
console$ ./migrate.sh
Verify and Test the Vultr Container Registry Images
To ensure the integrity of transferred images, you can compare the SHA256 digests of the images. In this section, you will use a Bash script to automatically compare the digests of the images in the Google Cloud Artifact Registry with the Vultr Container Registry. Follow the steps below to verify the integrity.
Create a new file named
integrity_check.sh.console$ nano integrity_check.sh
Add the following code to the file. Provide
GCP_LOCATION,GCP_REPO,GCP_PROJECT_ID, andVULTR_REGISTRY_URLvariables with your values.bash#!/bin/bash GCP_LOCATION="europe-central2" GCP_REPO="example-repo" VULTR_REGISTRY_URL="ams.vultrcr.com/example" GCP_PROJECT_ID="project-abc123" GCP_HOST="${GCP_LOCATION}-docker.pkg.dev" for image in $(docker images --format "{{.Repository}}:{{.Tag}}" | grep "^${GCP_HOST}/${GCP_PROJECT_ID}/${GCP_REPO}"); do IMAGE_BASENAME=$(basename "${image}" | cut -d: -f1) IMAGE_TAG=$(basename "${image}" | cut -d: -f2) GCP_IMAGE="${image}" VULTR_IMAGE="${VULTR_REGISTRY_URL}/${IMAGE_BASENAME}:${IMAGE_TAG}" echo "--- Verifying: ${IMAGE_BASENAME}:${IMAGE_TAG} ---" docker pull "$GCP_IMAGE" > /dev/null 2>&1 docker pull "$VULTR_IMAGE" > /dev/null 2>&1 GCP_DIGEST=$(docker inspect --format='{{index .RepoDigests 0}}' "$GCP_IMAGE" | awk -F'@' '{print $2}' 2>/dev/null) VULTR_DIGEST=$(docker inspect --format='{{index .RepoDigests 0}}' "$VULTR_IMAGE" | awk -F'@' '{print $2}' 2>/dev/null) if [[ -z "$GCP_DIGEST" || -z "$VULTR_DIGEST" ]]; then echo "Error: Could not retrieve digest for one or both images from the local daemon." elif [[ "$GCP_DIGEST" == "$VULTR_DIGEST" ]]; then echo "Integrity verified, digests match: ${GCP_DIGEST}" else echo "Digests are different!" echo "GCP Digest (local): $GCP_DIGEST" echo "Vultr Digest (local): $VULTR_DIGEST" fi echo "" done
The script above finds local Docker images that originate from the specified Google Artifact Registry. For each image tag, it pulls both the Google Artifact Registry and corresponding Vultr Container Registry versions to ensure they are present locally. It then calculates their SHA256 digests from the local Docker daemon and compares them. If there are no differences, it indicates a successful transfer without errors.
Make the script executable.
console$ chmod +x integrity_check.sh
Run the script.
console$ ./integrity_check.shExample output indicating a successful transfer:
Integrity verified, digests match: sha256:7b9b6a044d921dfcaea2a843ff19d725948590352198f93cb878fd2c19d7ba3c
Cutover to the Vultr Container Registry
This section describes transitioning your applications and workflows to use the new registry. Follow the recommendations below to cut over your containers to the Vultr Container Registry.
Update your Docker files to use the Vultr Container Registry.
Before:
app: image: europe-central2-docker.pkg.dev/example-project/example-repo/my-app:1.0.0After:
app: image: <vultr_registry_url>/my-app:1.0.0Replace
<vultr_registry_url>with your Vultr Container registry URL without thehttps://prefix.
Update your Kubernetes Deployments files.
Before:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: my-app spec: replicas: 3 template: spec: containers: - name: my-app image: europe-central2-docker.pkg.dev/project-abc123/example-repo/my-app:1.0.0After:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: my-app spec: replicas: 3 template: spec: containers: - name: my-app image: <vultr_registry_url>/my-app:1.0.0Replace
<vultr_registry_url>with your Vultr Container registry URL without thehttps://prefix.
After transferring your production workloads to the Vultr Container Registry, you may delete the old GCP registry to avoid unnecessary billing costs.
Conclusion
You've migrated your container images from your Google Artifact Registry to your Vultr Container Registry and verified post-migration data integrity. For more information on Vultr Container Registry, refer to the official Vultr Container Registry documentation.