Vultr Container Registry is a managed image storage solution that lets you securely store, manage, and distribute Docker container images. It integrates seamlessly with Vultr Kubernetes Engine and centralizes container image management for production workloads.
This guide demonstrates how to migrate container images from a Linode Private Docker Registry to Vultr Container Registry. You will use Docker and Skopeo to perform single-image and bulk transfers between the two registries.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:
- Access to an Ubuntu 24.04 instance as your migration workstation.
- Docker installed on Ubuntu 24.04.
- An existing Linode Private Docker Registry running on a remote instance.
- A provisioned Vultr Container Registry.
Prepare the Source Linode Docker Registry
This section sets up access to your Linode-hosted Docker registry from the migration workstation and verifies available repositories and image tags.
Add your user to the
dockergroup to run Docker commands withoutsudo.console$ sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
Apply the group change in your current shell.
console$ newgrp docker
Log in to the Linode Docker Registry.
console$ docker login <ip-address>:<port> -u <username>
Replace:
<ip-address>with your Linode registry’s IP address.<port>with the exposed registry port (e.g.,5000).<username>with your registry username.
If the registry is running behind Kubernetes, use the appropriate Ingress or LoadBalancer endpoint instead.
When prompted, enter your password. If successful, the output displays:
Login SucceededIf Docker returnsNotehttp: server gave HTTP response to HTTPS client, configure it to allow insecure registries.Open the Docker daemon config.
console$ sudo nano /etc/docker/daemon.json
Add the insecure registry address.
ini{ "insecure-registries": ["<ip-address>:<port>"] }
Save and close the file.
Restart Docker to apply the changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart docker
Re-run the Docker login command.
List all repositories in the Linode registry.
console$ curl -u <username>:<password> http://<ip-address>:<port>/v2/_catalog
Output:
{"repositories":["app1/alpine","app1/nginx","app2/busybox","app2/redis"]}List tags for a specific image, such as app1/nginx.
console$ curl -u <username>:<password> http://<ip-address>:<port>/v2/<repository>/tags/list
Output:
{"name":"app1/nginx","tags":["latest"]}Take note of the images and tags to migrate.
Set Up the Vultr Container Registry
Log in to the Vultr Customer Portal and go to Products > Container Registry.
Select the container registry you created. For example, the registry name might be
myvultrregistry.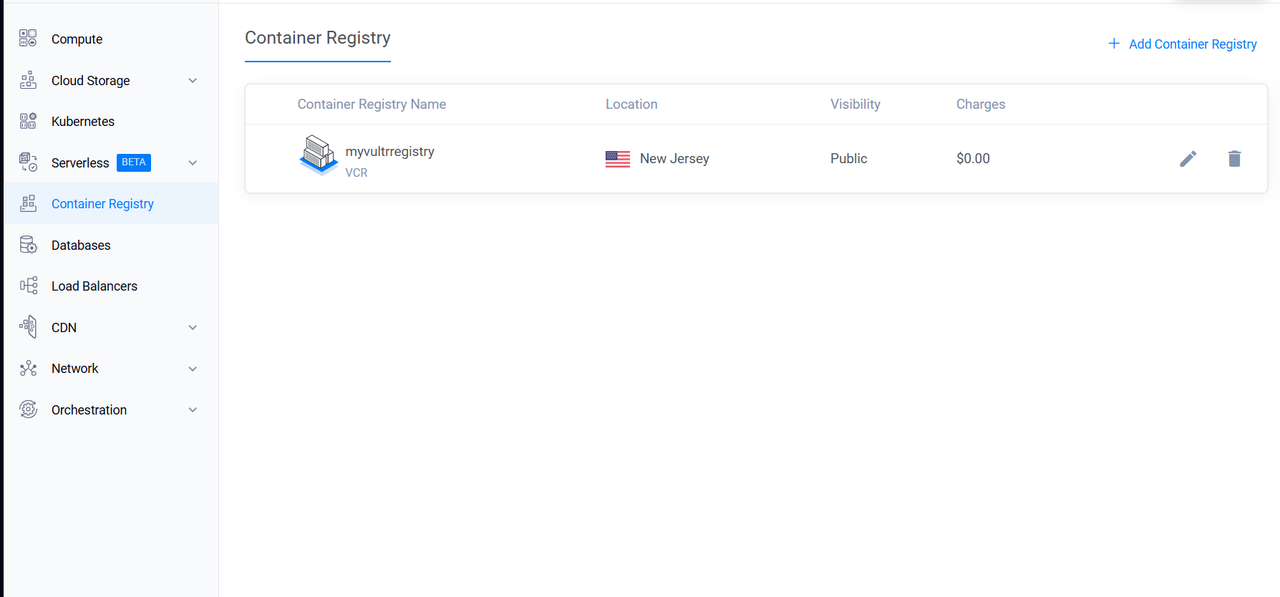
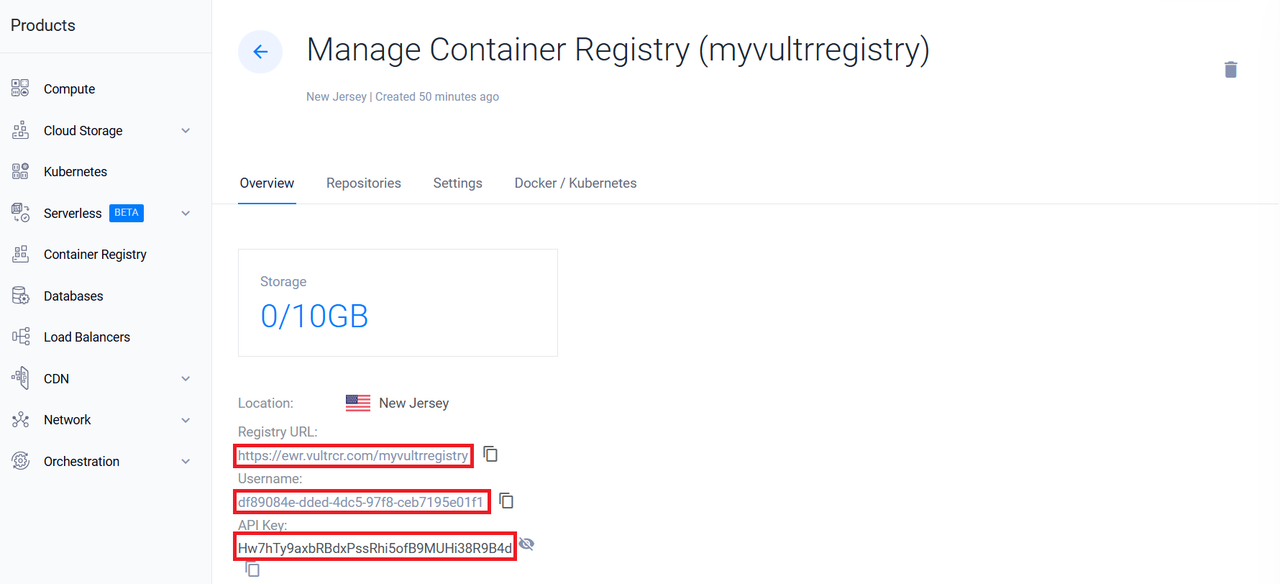
Note down the following from the registry overview:
- Registry URL
- Username
- API Key
These values will be used for authentication and image pushes in later steps.
Migrate the Container Registries
In this section, you will migrate images from your Linode Docker Registry to the Vultr Container Registry using Docker and Skopeo.
Use Docker for simple or small-scale migrations. This method pulls an image from the Linode registry, retags it, and pushes it to the Vultr Container Registry.
Pull an image from your Linode registry:
console$ docker image pull <ip-address>:<port>/<repository>/<image>:<tag>
Replace:
<ip-address>:<port>with the Linode registry address.<repository>/<image>:<tag>with the full image path and tag.
Retag the image for the Vultr registry.
console$ docker image tag <ip-address>:<port>/<repository>/<image>:<tag> <registry-url>/<image>:<tag>
Verify that the new tag was applied.
console$ docker image ls
Output:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE 172.238.161.214:5000/app1/nginx latest 1e5f3c5b981a 8 weeks ago 192MB ewr.vultrcr.com/myvultrregistry/nginx latest 1e5f3c5b981a 8 weeks ago 192MBLog in to the Vultr Container Registry.
console$ docker login <vultr-registry-url> -u <vultr-username>
Enter your Vultr API key when prompted.
Output:
... Login SucceededPush the tagged image to Vultr.
console$ docker image push <vultr-registry-url>/<image>:<tag>
Pull the image from Vultr to confirm availability.
console$ docker image pull <vultr-registry-url>/<image>:<tag>
Output:
latest: Pulling from myvultrregistry/nginx Digest: sha256:114dff0fc8ee3d0200c3a12c60e3e2b79d0920dd953175ecb78a0b157425b25e Status: Image is up to date for ewr.vultrcr.com/myvultrregistry/nginx:latest ewr.vultrcr.com/myvultrregistry/nginx:latestRun the container to verify the image works.
console$ docker container run -d --name test-image <vultr-registry-url>/<image>:<tag>
Verify that the container is running.
console$ docker container ls
Output:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 4123435c65df ewr.vultrcr.com/myvultrregistry/nginx:latest "/docker-entrypoint.…" 5 seconds ago Up 5 seconds 80/tcp test-image
Automate Docker Image Migration
To migrate multiple images, create and run a shell script.
Create the script file with a text editor such as
nano.console$ nano migrate-images.sh
Add the following content to the file:
bash#!/bin/bash LINODE_REGISTRY="<ip-address>:<port>" VULTR_REGISTRY="<vultr-registry-url>" IMAGES=("<image1:tag>" "<image2:tag>") # Update with your actual image names and tags for IMAGE in "${IMAGES[@]}"; do echo "Migrating image: $IMAGE" docker image pull "$LINODE_REGISTRY/$IMAGE" docker image tag "$LINODE_REGISTRY/$IMAGE" "$VULTR_REGISTRY/$IMAGE" docker image push "$VULTR_REGISTRY/$IMAGE" done echo "Migration completed."
Save the file and make it executable.
console$ chmod +x migrate-images.sh
Run the script.
console$ ./migrate-images.shOutput:
... Migration completed.
Skopeo is ideal for bulk image migration because it transfers images directly between registries without storing them locally. This improves speed and conserves disk space.
Update the package index on your migration workstation.
console$ sudo apt update
Install required tools.
console$ sudo apt install -y jq skopeo
Verify the Skopeo installation.
console$ skopeo --version
Output:
skopeo version 1.13.3This guide uses
skopeo v1.13.3. The commands are expected to work onv1.12+, but behavior may vary in older versions.Copy a single image from the Linode registry to your Vultr registry:
console$ skopeo copy \ --src-tls-verify=false \ docker://<linode-ip>:<port>/<repository>/<image>:<tag> \ docker://<vultr-registry-url>/<image>:<tag> \ --src-creds <linode-username>:<linode-password> \ --dest-creds <vultr-username>:<vultr-api-key>
Replace all placeholders with the correct values for your Linode and Vultr registries.
Output:
Getting image source signatures Copying blob 14d59e6670a4 done Copying config 6d3e4188a3 done Writing manifest to image destinationAutomate bulk image migration with a script:
bash#!/bin/bash LINODE_REGISTRY="<linode-ip>:<port>" VULTR_REGISTRY="<vultr-registry-url>" LINODE_CREDS="<username>:<password>" VULTR_CREDS="<username>:<api-key>" REPOS=("app1/image") # Replace with your repositories for repo in "${REPOS[@]}"; do TAGS=$(skopeo list-tags --tls-verify=false \ docker://"$LINODE_REGISTRY/$repo" --creds "$LINODE_CREDS" | jq -r '.Tags[]') for tag in $TAGS; do echo "Migrating $repo:$tag" skopeo copy --src-tls-verify=false \ docker://"$LINODE_REGISTRY/$repo:$tag" \ docker://"$VULTR_REGISTRY/$repo:$tag" \ --src-creds "$LINODE_CREDS" \ --dest-creds "$VULTR_CREDS" done done echo "Skopeo migration process completed."
Save the script as
migrate-images-skopeo.shand make it executable.console$ chmod +x migrate-images-skopeo.sh
Run the migration.
console$ ./migrate-images-skopeo.shOutput:
Migrating app1/image:latest Writing manifest to image destination Skopeo migration process completed.
Verify and Test the Vultr Container Registry Images
After completing the migration, confirm that the images are available in your Vultr Container Registry and function as expected.
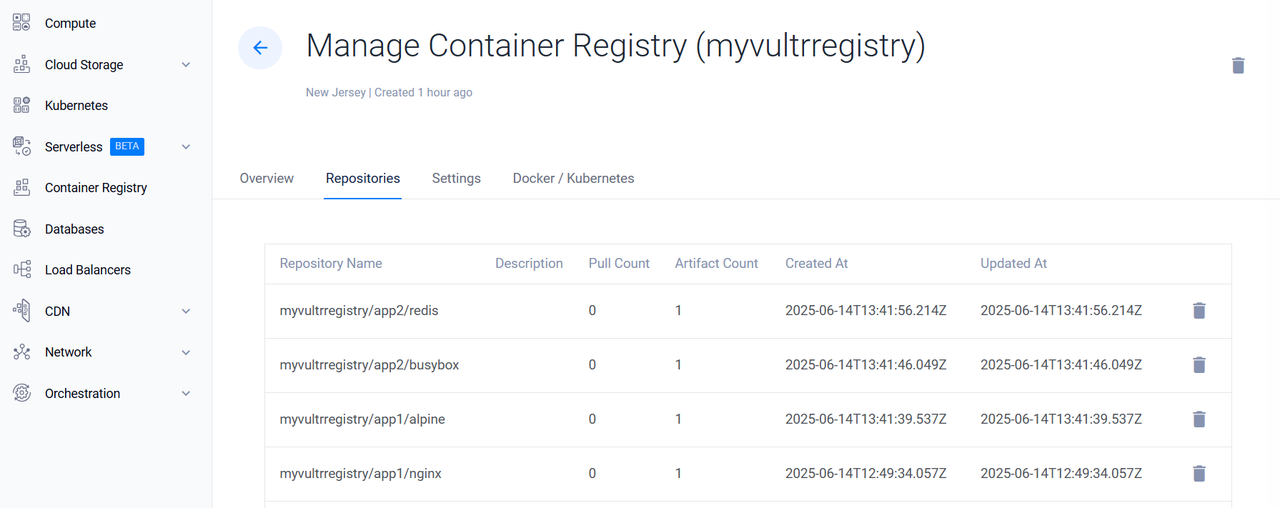
Open the Vultr Customer Portal and navigate to Container Registry > Repositories. Confirm that your expected repositories and images are present.
Pull a migrated image from the Vultr Container Registry.
console$ docker image pull <registry-url>/<image>:<tag>
Run the container to verify that it starts successfully.
console$ docker container run -d --name test-image2 <registry-url>/<image>:<tag>
List running containers to confirm the image is up and running:
console$ docker container ls
Output:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 67f14735ae8d ewr.vultrcr.com/myvultrregistry/app1/alpine "/bin/sh" 3 seconds ago Up 2 seconds test-imageThis confirms that the container was successfully pulled and launched from the Vultr registry.
Validate Image Integrity with Skopeo
You can verify the consistency of image digests between the source and destination registries using Skopeo.
Create a script named
verify-images.sh:bash#!/bin/bash LINODE_REGISTRY="<ip-address>:<port>" LINODE_USERNAME="<username>" LINODE_PASSWORD="<password>" VULTR_REGISTRY="<vultr-registry-url>" REPOS=("app1/alpine" "app1/nginx" "app2/busybox" "app2/redis") for repo in "${REPOS[@]}"; do tags=$(curl -s -u "$LINODE_USERNAME:$LINODE_PASSWORD" http://"$LINODE_REGISTRY/v2/$repo/tags/list" \ | grep -o '"tags":\[[^]]*\]' | sed 's/"tags":\[//' | sed 's/\]//' \ | tr ',' '\n' | sed 's/"//g' | grep -v "^$repo$") for tag in $tags; do linode_digest=$(skopeo inspect --tls-verify=false docker://"$LINODE_REGISTRY/$repo:$tag" | grep Digest | sed 's/.*"\([^"]*\)".*/\1/') vultr_digest=$(skopeo inspect docker://"$VULTR_REGISTRY/$repo:$tag" | grep Digest | sed 's/.*"\([^"]*\)".*/\1/') [ "$linode_digest" = "$vultr_digest" ] && echo "$repo:$tag OK" || echo "$repo:$tag FAIL" done done
Make the script executable.
console$ chmod +x verify-images.sh
Run the script.
console$ ./verify-images.shOutput:
app1/alpine:latest OK app1/nginx:latest OK app2/busybox:latest OK app2/redis:latest OKThis confirms that the image digests are identical in both Linode and Vultr registries, validating the integrity of your migrated images.
Cutover to Vultr Container Registry
After completing the image migration, update all configurations and systems to use your Vultr Container Registry.
Update configuration files
Modify any Dockerfiles, Kubernetes manifests, Helm charts, and Docker Compose files to pull images from your Vultr Container Registry.
yaml... image: <vultr-registry-url>/<image>:<tag> ...
Update CI/CD pipelines
Point your CI/CD workflows to the new Vultr registry and update any related image paths or authentication configurations.
Verify authentication
Ensure that all CI/CD tools and orchestration platforms (such as Kubernetes or Nomad) are properly authenticated against your Vultr Container Registry using the correct credentials or secrets.
Monitor deployment behavior
Review logs, container statuses, and deployment outputs to verify that services are pulling and running images from the correct (Vultr) source.
Decommission the Linode registry
Once migration is complete and validated:
Shut down and remove the Linode-hosted Docker registry container.
Clean up old Docker credentials and environment-specific configurations tied to the Linode registry.
If you configured Docker to allow insecure connections to the Linode registry, remove the entry from
/etc/docker/daemon.json:json{ "insecure-registries": [] }
Then restart Docker to apply the changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart docker
Conclusion
In this guide, you migrated container images from a Linode Private Docker Registry to the Vultr Container Registry using both Docker and Skopeo. You verified the migration, ensured image integrity, and updated your infrastructure to use the Vultr Container Registry for ongoing deployments.
For more information, refer to the official Vultr Container Registry documentation.