
Introduction
The touch command is a file modification tool that enables you to create new files, update file timestamps, and empty files. It's an essential tool used in administrative and scripting tasks that require file creation or timestamp manipulation.
This article explains how to use the touch in Linux to create and manage files.
touch Command Syntax
Below is the basic touch command syntax:
$ touch [options] filename
Within the above command, filename specifies the filename to create or update while [options] modifies how the touch operates.
touch Command Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-a |
Change only the access time of a file. |
-m |
Change only the modification time of a file. |
-c |
Do not create the file if it does not exist. |
-t |
Use a specific time format (example, [[CC]YY]MMDDhhmm[.ss]). |
-r |
Use the access and modification times of another file. |
-d |
Update the access and modification times using a string. |
Practical Examples of the touch Command
Create a new empty file.
console$ touch file1.txt
The above command creates a new empty file
file1.txtif it does not already exist in your working directory.Output:
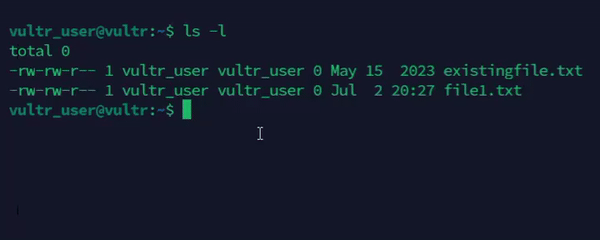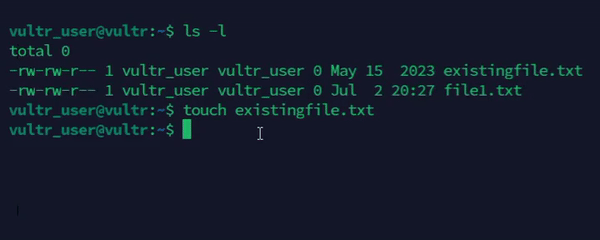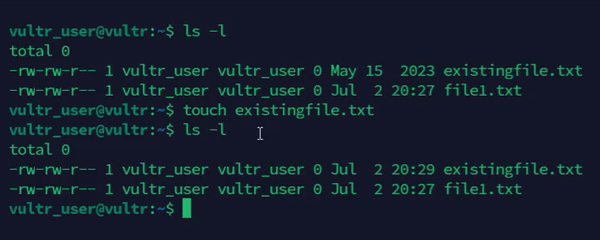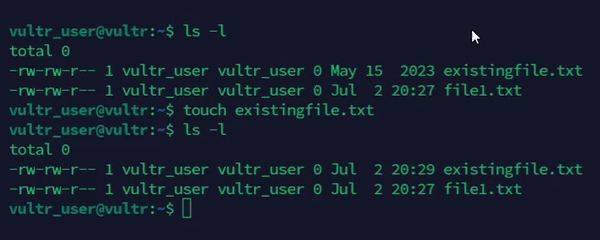
Update the timestamps of an existing file.
console$ touch existingfile.txt
The above command updates the access and modification timestamps of the
existingfile.txtfile using the system time.Output:
Create multiple empty files.
console$ touch file1.txt file2.txt file3.txt
The above command creates three empty files
file1.txt,file2.txt, andfile3.txt.Output:

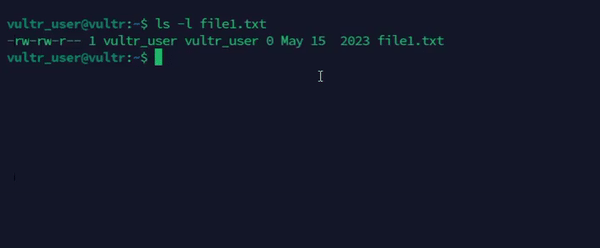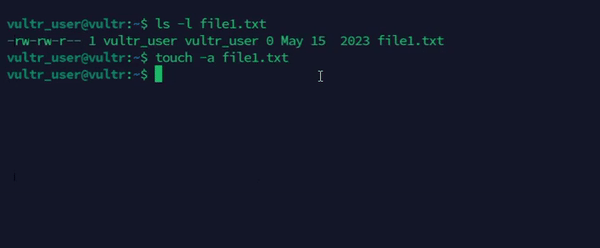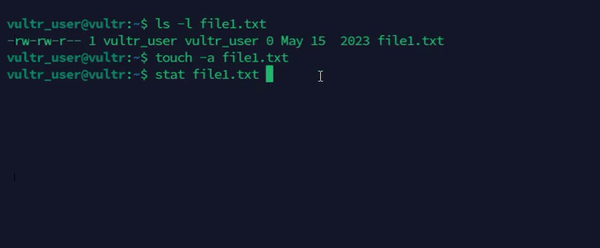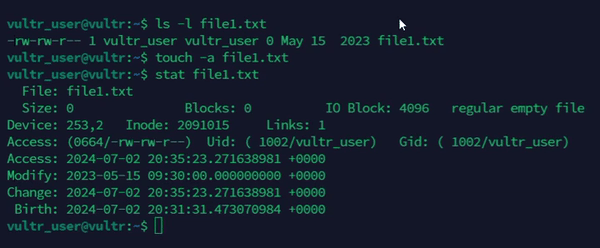
Change the access time of a file.
console$ touch -a file1.txt
The above command updates the access time of the
file1.txtfile.Output:
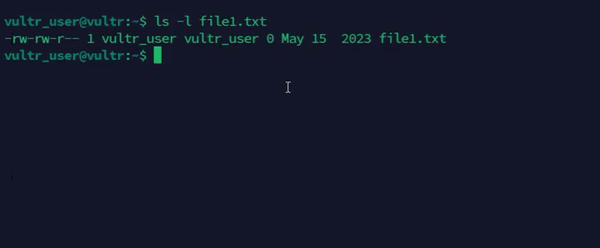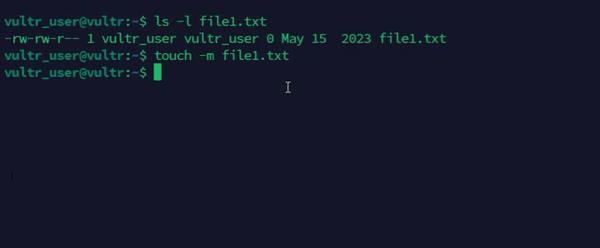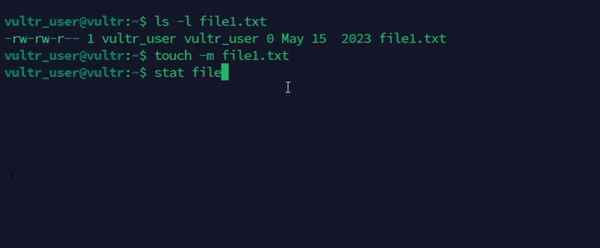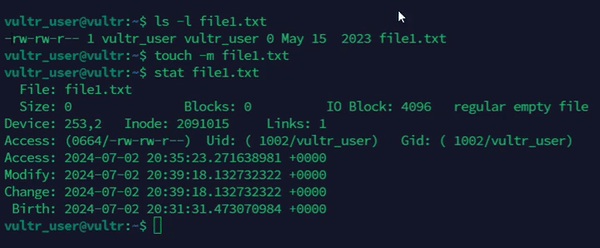
Change the file modification time.
console$ touch -m file1.txt
The above command updates the modification time of the
file1.txtfile.Output:
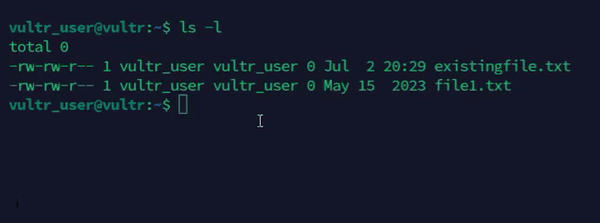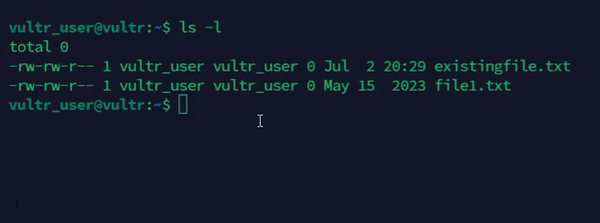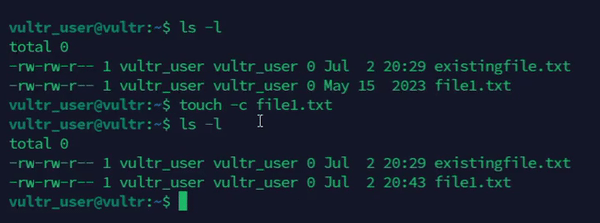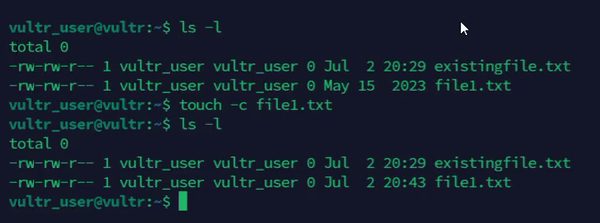
Do not create a file if it does not exist.
console$ touch -c file1.txt
The above command does not create
file1.txtif exists and updates the existing file's timestamp.Output:
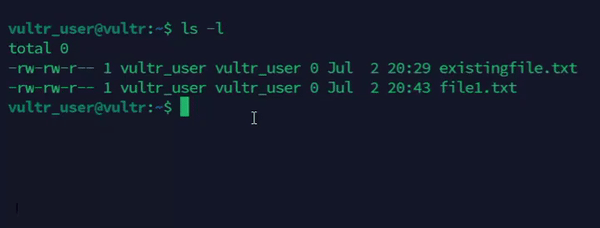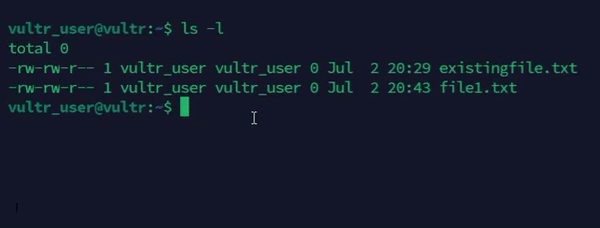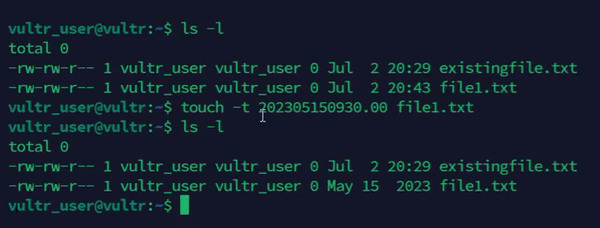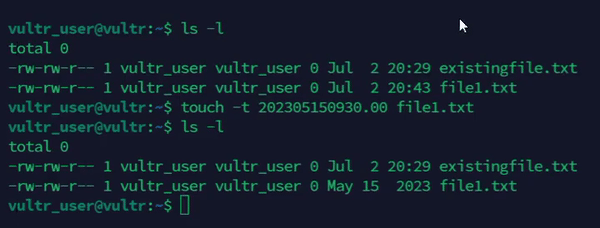
Set a specific timestamp on a file.
console$ touch -t 202405150930.00 file1.txt
The above command sets the access and modification time of the
file1.txtfile toMay 15, 2024, 09:30 AM.Output:
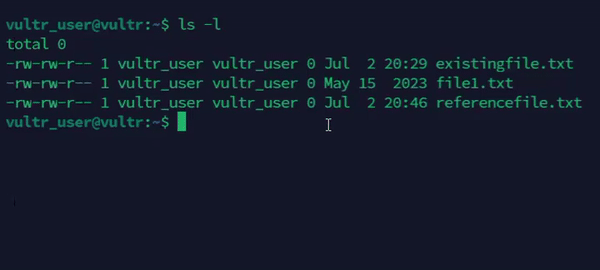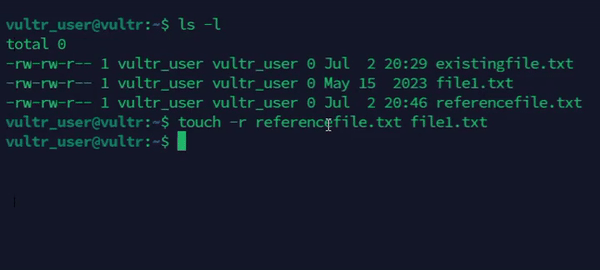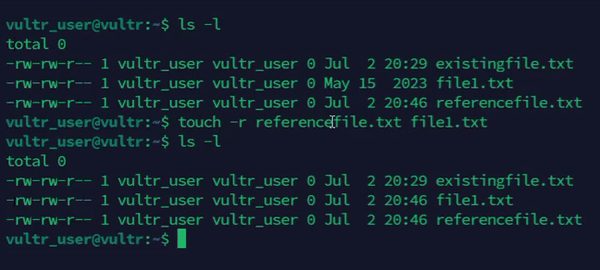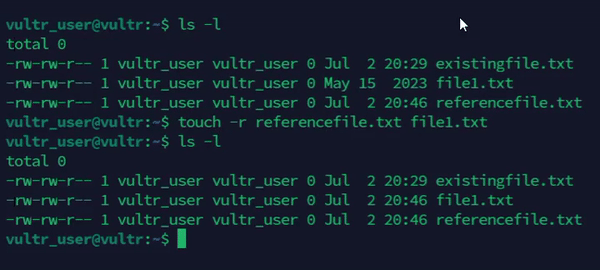
Copy the timestamps of an existing file to a new file.
console$ touch -r referencefile.txt file1.txt
The above command sets the access and modification times of the
file1.txtfile to match thereferencefile.txtfile.Output:
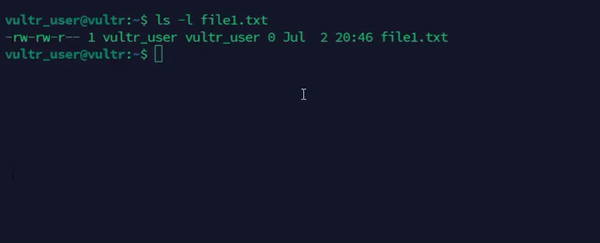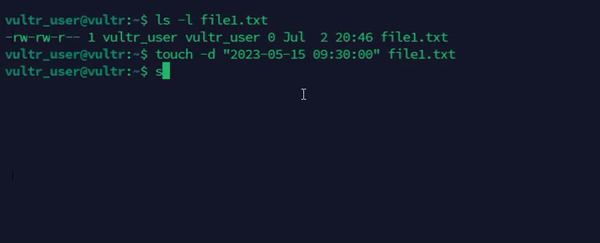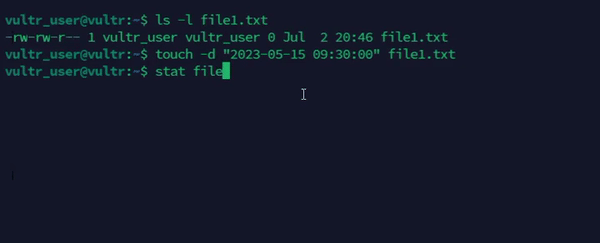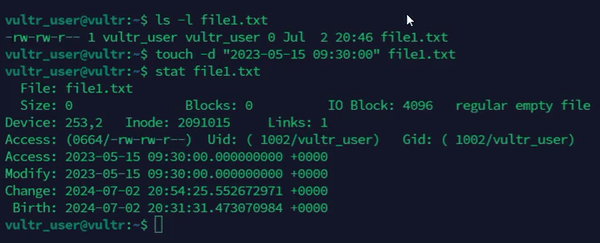
Update timestamps using a string.
console$ touch -d "2023-05-15 09:30:00" file1.txt
The above command updates the access and modification time of the
file1.txtfile using the specified date and time string.Output:
Advanced Usage Scenarios
Create a file with a specific time.
console$ touch -t 199001010000.00 file1.txt
The above command sets the access and modification time of
file1.txttoJanuary 1, 1990, 00:00 AM.Output:

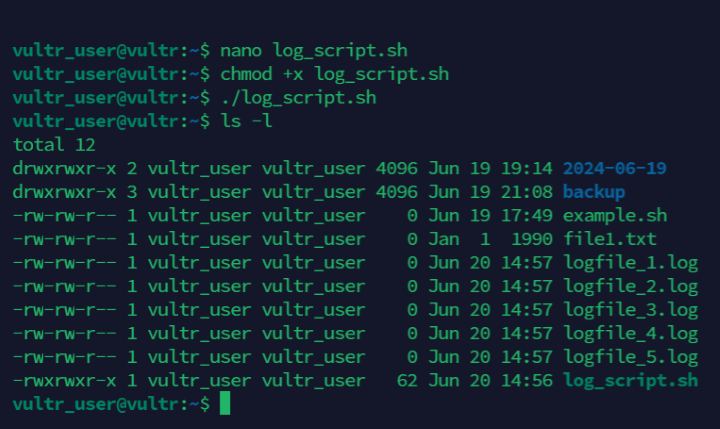
Create log files in a Bash script using
touch.Create a sample script
log_script.shusing a text editor such as Nanoconsole$ nano log_script.sh
Add the following contents to the file.
bash#!/bin/bash for i in {1..5}; do touch "logfile_$i.log" done
Save and close the file.
Enable execute permissions on the file.s
console$ chmod +x log_script.sh
Run the script
console$ bash log_script.sh
The above script creates five empty log files in your working directory using the format
logfile_1.logtologfile_5.log.Output:
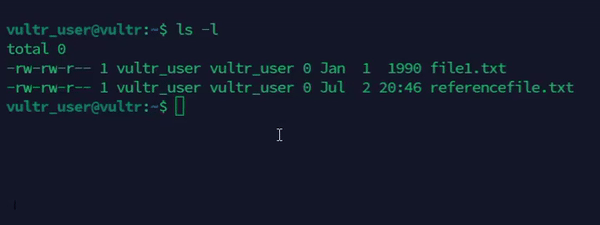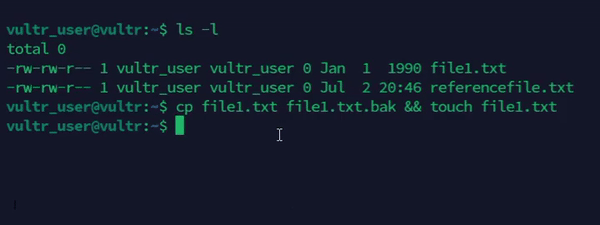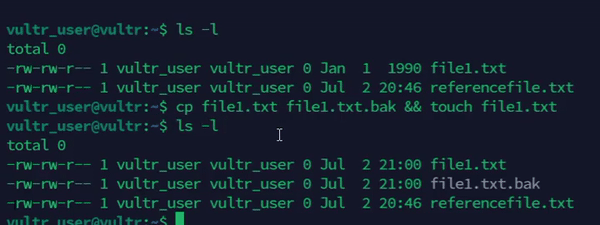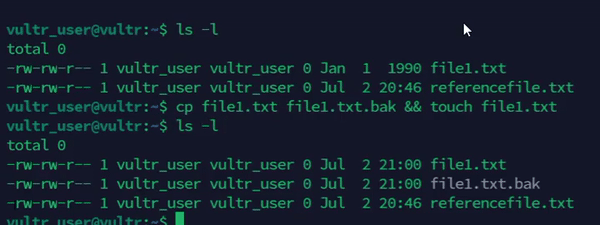
Backup a file before modifying the existing file.
console$ cp file1.txt file1.txt.bak && touch file1.txt
The above command creates a backup of the
file1.txtfile before updating its timestamp.Output:
Create empty files in nested directories.
console$ mkdir -p dir1/dir2 && touch dir1/dir2/file.txt
The above command creates nested directories and an empty file in each directory.
Output:

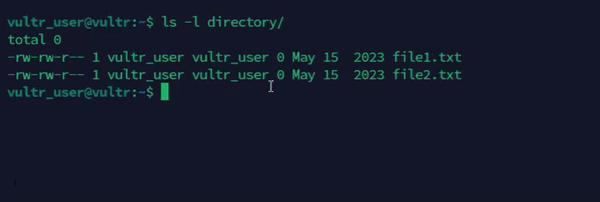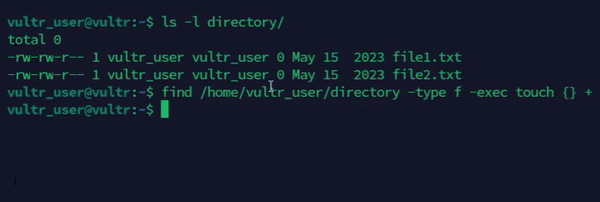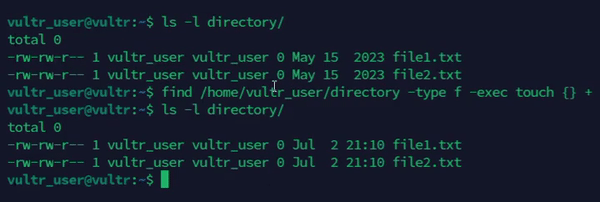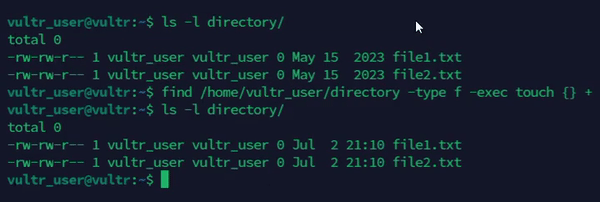
Combine
touchwithfindto recursively update timestamps on multiple files.console$ find /path/to/directory -type f -exec touch {} +
The above command updates the timestamps of all files in a specific directory.
Output:
Create new files using the current system date and a specific extension.
console$ touch "$(date +%Y-%m-%d).txt"
The above command creates a new empty file with the current system date and the
.txtextension.Output:

Use
touchwithxargsfor batch processing.console$ echo -e "file1.txt\nfile2.txt\nfile3.txt" | xargs touch
The above command creates multiple files in your standard input using the
xargsutility.Output:

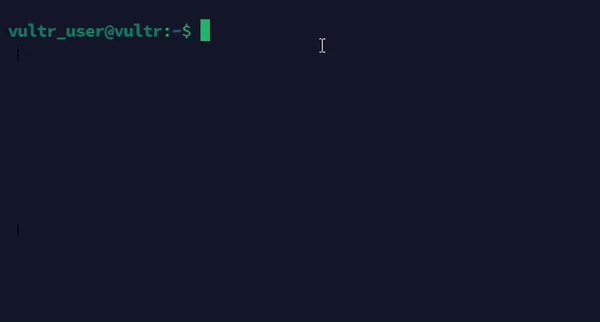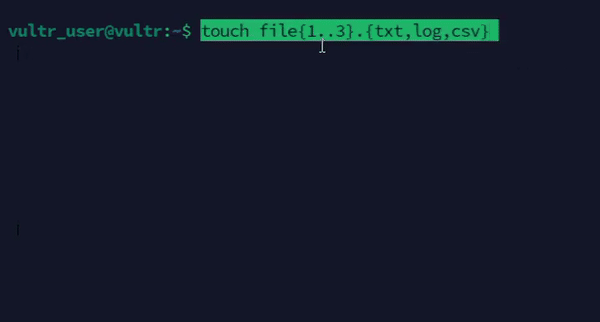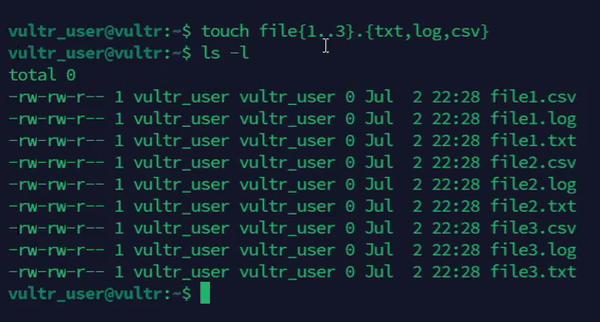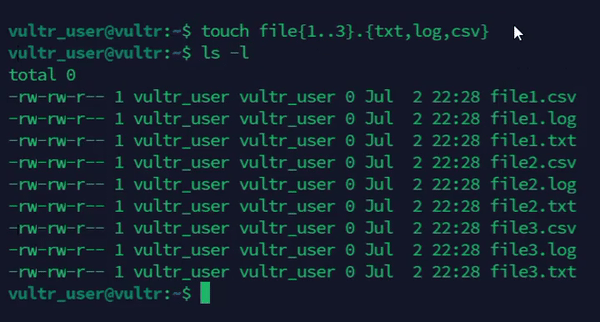
Create a series of empty files with different extensions.
console$ touch file{1..3}.{txt,log,csv}
The above command creates a series of files with different extensions using the brace expansion method.
Output:
Conclusion
You have used the touch command to create and manipulate files in Linux. For more command options, run the man touch command to view the touch manual page.