
Introduction
The wc command in Linux is an important tool used to count words, lines, and characters in files or standard input (STDIN). It's also known as word count (wc) and enables the processing of various text operations such as analyzing file sizes, counting lines in documents, or calculating average word lengths.
This article explains how to use the wc command in Linux to manipulate and analyze text data.
wc Command Syntax
Below is the basic wc command syntax:
$ wc [options] [file...]
Within the above command, [file...] specifies one or more files to process. If no files are provided, wc reads from standard input.
wc Command Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
-c |
Count the number of characters. |
-w |
Count the number of words. |
-l |
Count the number of lines. |
-m |
Count the number of characters (same as -c but more POSIX compliant). |
-L |
Display the length of the longest line. |
Practical Examples of the wc Command
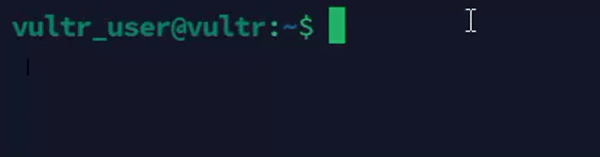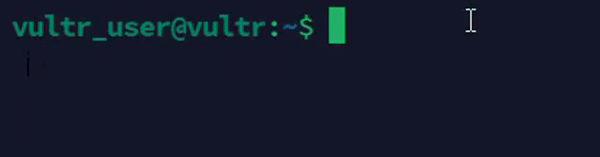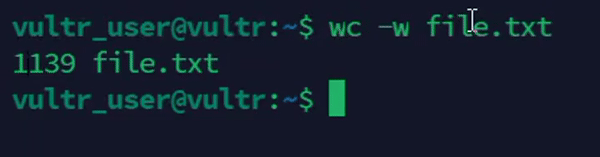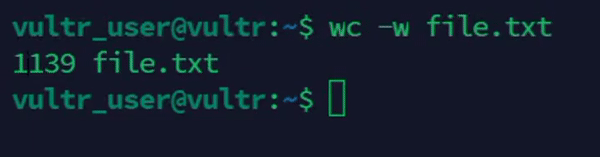
Count the number of words in a file.
console$ wc -w file.txt
The above command counts the number of words in
file.txt.Output:
Count the number of lines in a file.
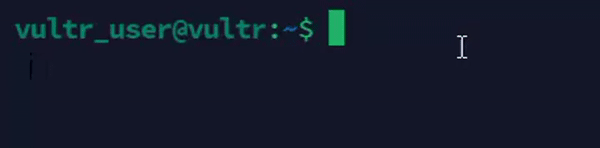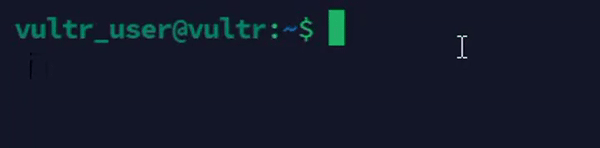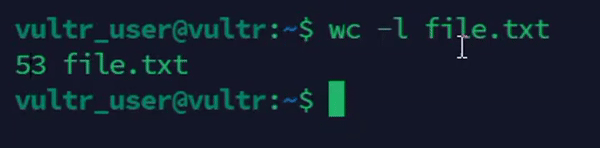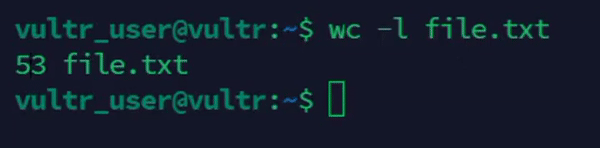
console$ wc -l file.txt
The above command counts the number of lines in the
file.txtfile.Output:
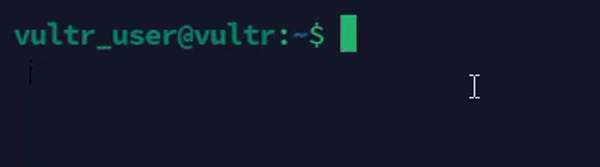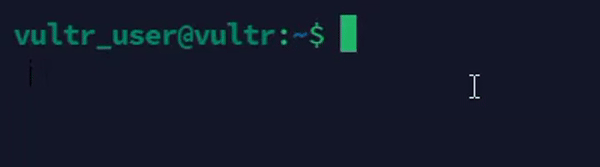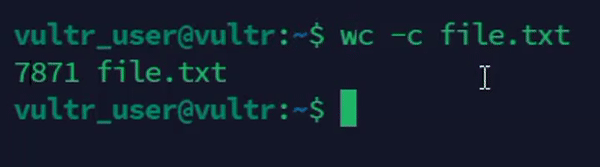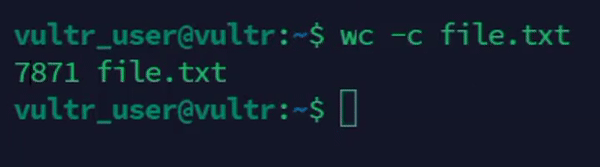
Count the number of characters in a file.
console$ wc -c file.txt
The above command counts the number of characters in the
file.txtfile.Output:
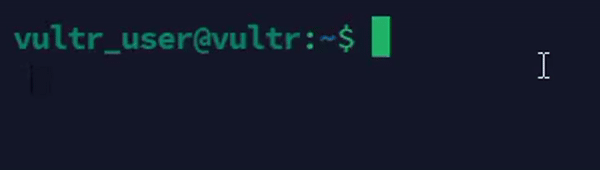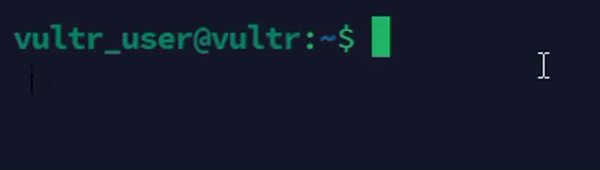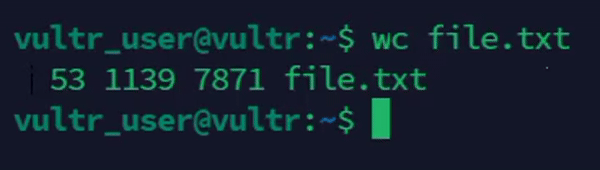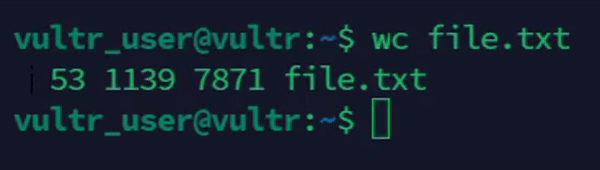
Count words, lines, and characters together.
console$ wc file.txt
The above command displays the count of lines, words, and characters in the
file.txtfile.Output:
Count the number words in multiple files.
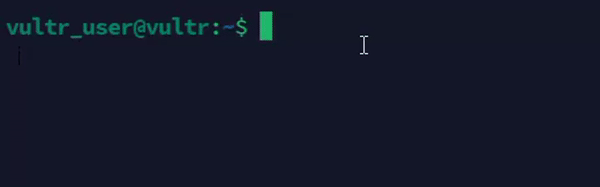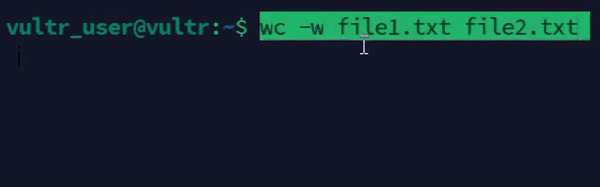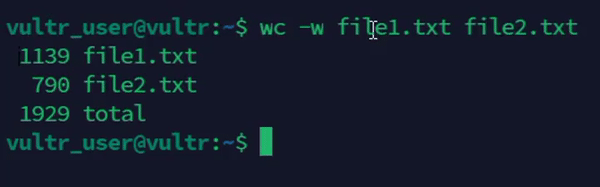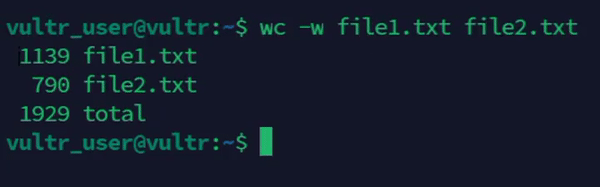
console$ wc -w file1.txt file2.txt
The above command counts the number of words in the specified files
file1.txtandfile2.txt.Output:
Count the number of lines in multiple files.
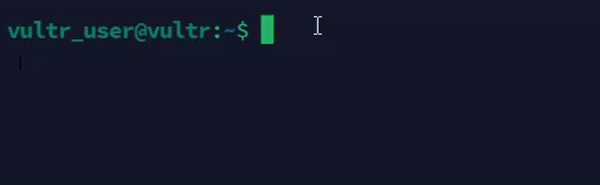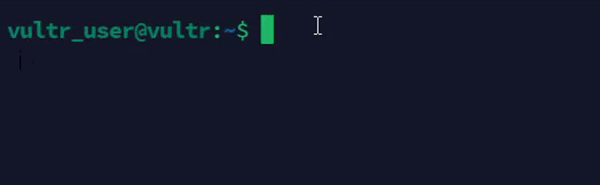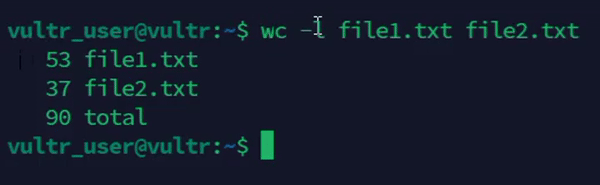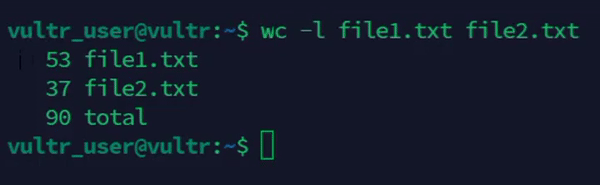
console$ wc -l file1.txt file2.txt
The above command counts the number of lines in both
file1.txtandfile2.txt.Output:
Count the number of characters in multiple files.
console$ wc -c file1.txt file2.txt
The above command counts the number of characters in the specified files
file1.txtandfile2.txt.Output:

Count words from standard input.
console$ echo "Hello world" | wc -w
The above command counts the number of words from standard input provided by the
echocommand.Output:

Count the number of lines from standard input.
console$ echo -e "Line 1\nLine 2\nLine 3" | wc -l
The above command counts the number of lines from standard input.
Output:

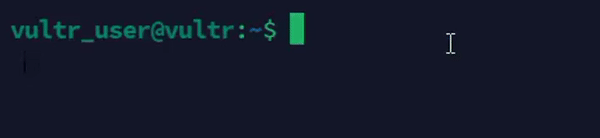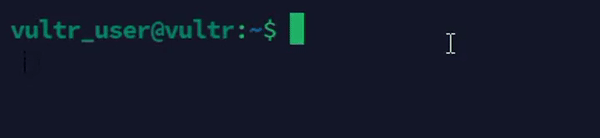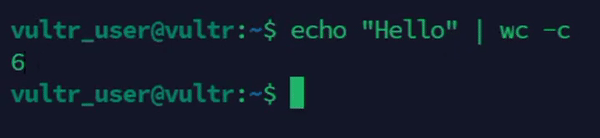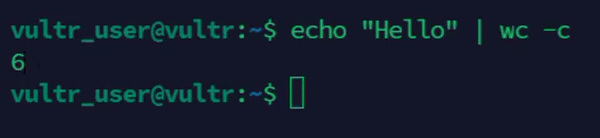
Count characters from standard input.
console$ echo "Hello" | wc -c
The above command counts the number of characters from standard input.
Output:
Advanced Usage Scenarios
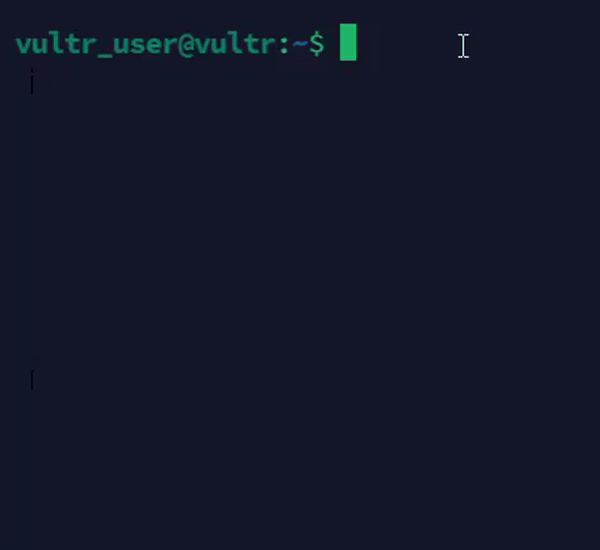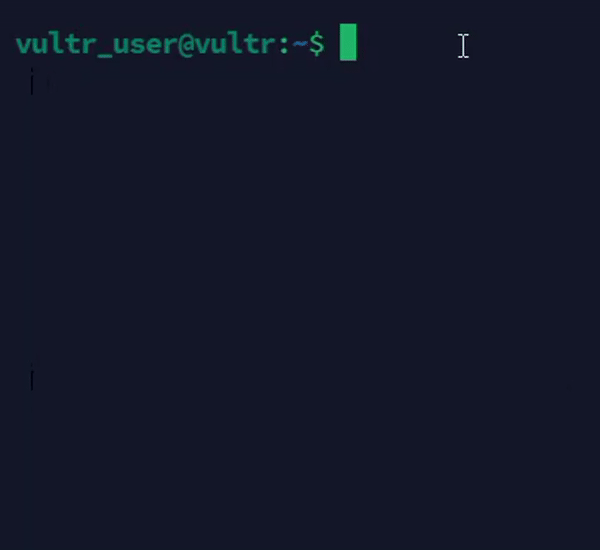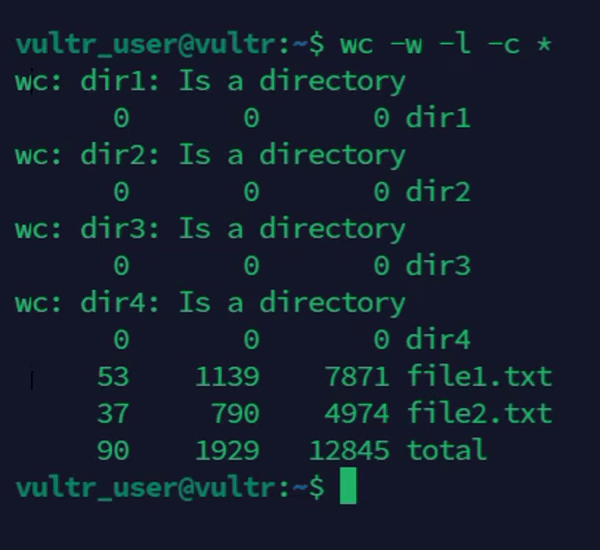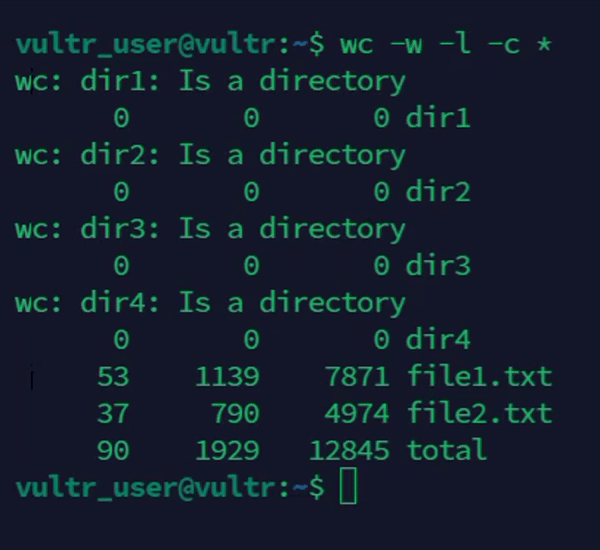
Count words, lines, and characters recursively in directories.
console$ wc -w -l -c *
The above command recursively counts the number of words, lines, and characters in all files within the working directory and subdirectories.
Output:
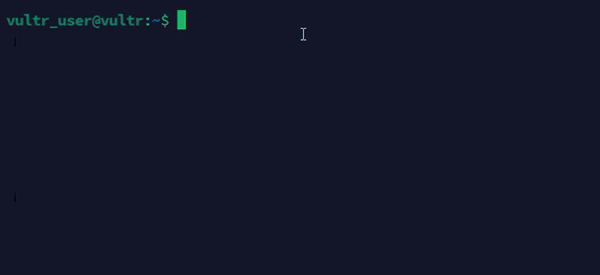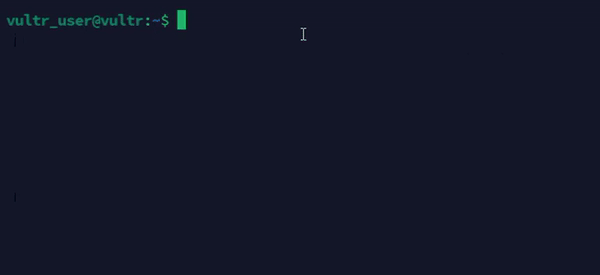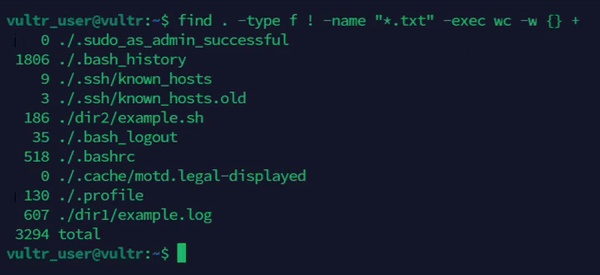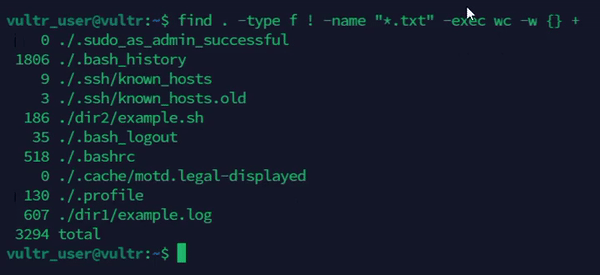
Exclude specific files.
console$ find . -type f ! -name "*.txt" -exec wc -w {} +
The above command uses the
findcommand to locate all files except.txtfiles and counts the number of words in each file.Output:
Count the number of words in a specific column of a CSV file.
console$ cut -d ',' -f 3 data.csv | wc -w
The above command extracts the third column of a comma-separated values (CSV) file using the
cututility and counts the number of words in the column.Output:

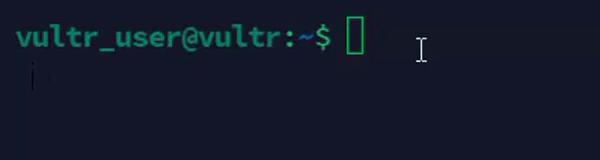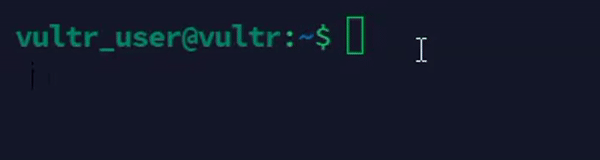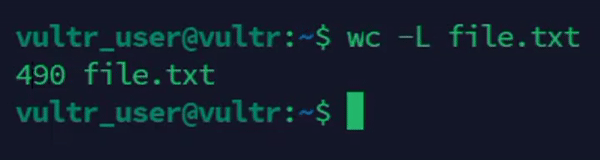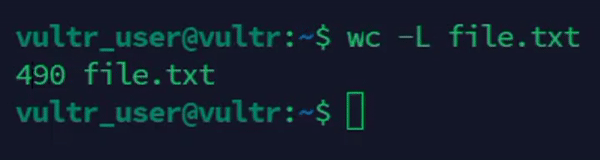
Count the length of the longest line in a file.
console$ wc -L file.txt
The above command displays the length of the longest line in the
file.txtfile.Output:
Combine
wcwithgrepto count specific patterns.console$ grep -o "pattern" file.txt | wc -l
The above command counts the occurrences of a specific pattern in the
file.txtfile usinggrepto match the pattern andwcto count the number of output lines.Output:

Combine
wcwithfindto count lines in multiple directories.console$ find /path/to/directories -type f -exec wc -l {} +
The above command counts the number of lines in all files within multiple directories specified by the
findcommand.Output:

Count all non-empty lines in a file.
console$ grep -cve '^\s*$' file.txt
The above command counts the number of non-empty lines in the
file.txtfile usinggrepto exclude empty lines and count them.Output:

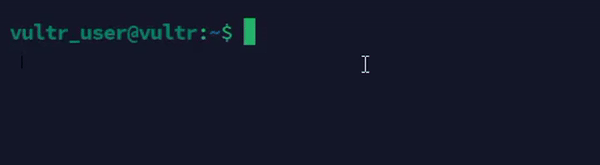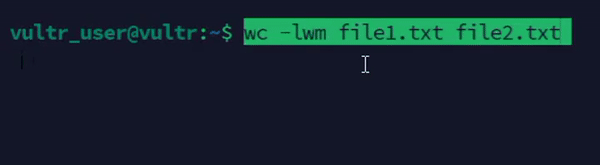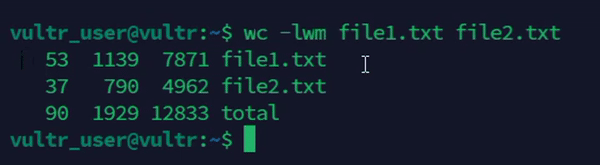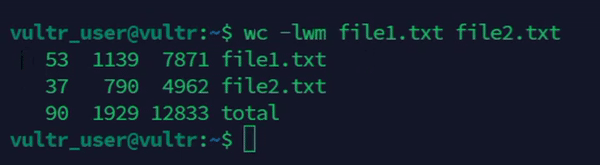
Generate a summary report using
wc.console$ wc -lwm file1.txt file2.txt
The above command generates a summary report showing the number of lines, words, and characters in the files
file1.txtandfile2.txt.Output:
Conclusion
You have used the wc command to perform basic and complex count processing operations. For more options, run the man wc command to view the wc manual page.