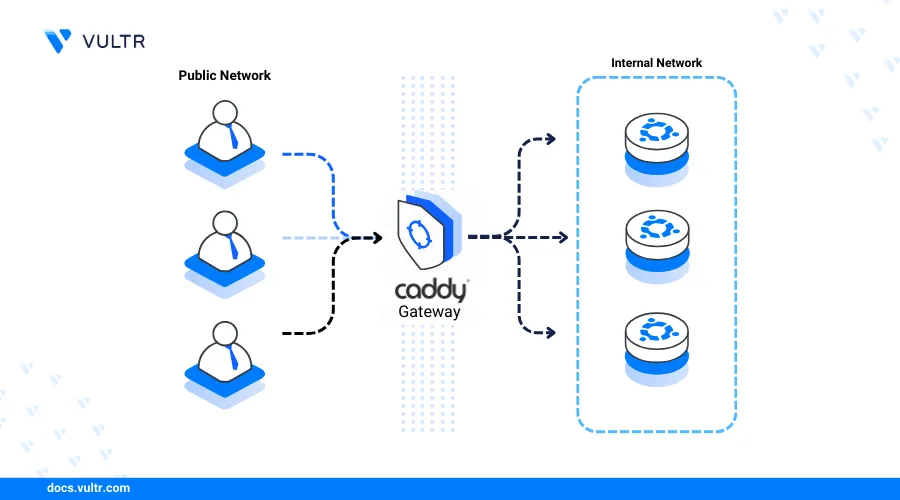
Caddy is an open-source web server that supports both static and modern web applications, with automatic HTTPS enabled for all linked domain names. Written in GO, Caddy provides user-friendly configuration directives, allowing it to function as a web server, reverse proxy, or load balancer to serve web applications on your server.
This article guides you through the process of installing Caddy on Ubuntu 20.04 and securely serving web applications.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
Have an Ubuntu 20.04 server.
Set up a new A record for your domain that points to the server IP address.
Access the server using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Install Caddy
Caddy is not included in the default Ubuntu 20.04 APT repositories. However, it can be installed either from source files or by adding the latest repository information to your server. Follow the steps below to download the latest Caddy repository details and install the application on your server.
Add the latest Caddy GPG Key to your server.
console$ curl -1sLf 'https://dl.cloudsmith.io/public/caddy/stable/gpg.key' | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/caddy-stable-archive-keyring.gpg
Add the Caddy repository to your APT sources.
console$ curl -1sLf 'https://dl.cloudsmith.io/public/caddy/stable/debian.deb.txt' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/caddy-stable.list
Update the server package index.
console$ sudo apt update
Install Caddy.
console$ sudo apt install caddy
View the installed Caddy version to verify that the installation is successful.
console$ caddy -v
Output:
v2.9.1 h1:OEYiZ7DbCzAWVb6TNEkjRcSCRGHVoZsJinoDR/n9oaY=Allow incoming connections to the HTTP port
80through the firewall.console$ sudo ufw allow 80
Restart the firewall to apply changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
Access your server IP to test access to the Caddy web server.
http://SERVER-IPConfirm that the default Caddy webpage displays in your browser.
Manage the Caddy System Service
Enable Caddy to start at boot time.
console$ sudo systemctl enable caddy
Start the Caddy web server.
console$ sudo systemctl start caddy
View the Caddy system service status to verify that the application is running.
console$ sudo systemctl status caddy
Output:
● caddy.service - Caddy Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/caddy.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Sun 2025-04-06 09:20:18 UTC; 4min 10s ago Docs: https://caddyserver.com/docs/ Main PID: 3015 (caddy) Tasks: 9 (limit: 9415) Memory: 10.9M CGroup: /system.slice/caddy.service └─3015 /usr/bin/caddy run --environ --config /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
Create a Caddy Virtual Host
Caddy stores its configuration files in the /etc/caddy directory by default and allows Caddyfile configurations from any location on your server. Follow the steps below to create a new Caddy virtual host to serve web application files from the /var/www/example.com directory on your server.
Create the
/var/www/example.comweb application files directory.console$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/example.com
Create a new HTML application file
index.html.console$ sudo nano /var/www/example.com/index.html
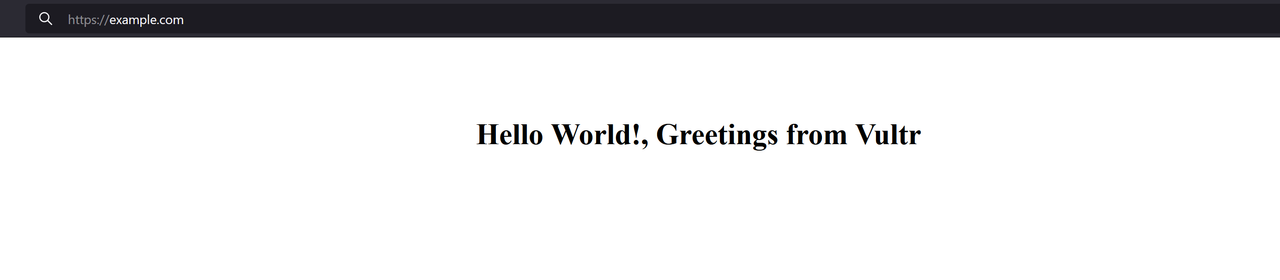
Add the following code to the file.
html<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Greetings from Vultr!</title> </head> <body> <br><br><br> <h1 style="text-align: center;">Hello World! Greetings from Vultr</h1> </body> </html>
Save and close the file.
Switch to the Caddy configuration files directory.
console$ cd /etc/caddy/
Back up the default Caddyfile configuration.
console$ sudo mv Caddyfile Caddyfile.default
Create a new Caddyfile configuration.
console$ sudo nano Caddyfile
Add the following configurations to the file.
iniexample.com { tls admin@example.com root * /var/www/example.com file_server { index index.html } log { output file /var/log/caddy/example.log format console } }
Save and exit the file.
The Caddy configuration above creates a new virtual host for your domain
example.com. Here’s what each part does:example.com: Defines a new virtual host profile using your domain or IP address.tls: Associates an email address with Let's Encrypt for SSL certificate generation requests.root: Specifies the directory containing the web application files for the virtual host.file_server: Enables the file server for serving web application files. Theindexdirective sets the default file to be served when accessing your domain.log: Configures logging for access and error details to a specified file, such as/var/log/caddy/example.log.
Test the Caddy configuration for errors.
console$ sudo caddy validate
Output:
........... 2024/06/1 15:19:11.478 INFO tls.cache.maintenance started background certificate maintenance {"cache": "0xc0000e5300"} 2024/06/1 15:19:11.478 INFO tls.cache.maintenance stopped background certificate maintenance {"cache": "0xc0000e5300"} Valid configurationReload the Caddy web server to apply your configuration changes.
console$ sudo caddy reload
Secure the Caddy Web Server
Caddy automatically enables HTTPS to secure all connections using SSL certificates for virtual host profiles with valid domains on your server. Follow the steps below to secure the Caddy web server by restricting access to the Caddyfile configurations and preventing unauthorized changes by unintended users.
Grant the Caddy user full privileges to the
/etc/caddydirectory.console$ sudo chown -R caddy:caddy /etc/caddy
Grant the Caddy user read and write permissions to the Caddyfile while disabling access for other system users.
console$ sudo chmod 660 /etc/caddy/Caddyfile
Long list the
/etc/caddydirectory to verify the permission changes.console$ ls -l /etc/caddy/
Output:
total 8 -rw-rw---- 1 caddy caddy 168 Jun 2 15:20 Caddyfile -rw-r--r-- 1 caddy caddy 769 Jun 2 12:07 Caddyfle.default
Set Up Firewall Rules
Caddy uses HTTP port 80 and HTTPS port 443, depending on your Caddyfile configurations, to serve files on the server. Follow the steps below to allow access to both Caddy ports through the firewall and enable network connections to the web server.
View the UFW status and verify that it's active.
console$ sudo ufw status
If the status is
inactive, allow the SSH port22and enable UFW.console$ sudo ufw allow 22 && sudo ufw enable
Allow incoming connections to the HTTPS port
443.console$ sudo ufw allow 443
Reload the firewall to apply changes
console$ sudo ufw reload
Access your domain using a browser such as Chrome to verify that Caddy serves your virtual host web application files.
https://example.comIf you receive a connection error, view the Caddy configuration logs to verify the error details.
Conclusion
You have successfully installed the Caddy web server on your Ubuntu 20.04 server and configured a virtual host profile to serve web application files.