How to Install Nginx Web Server on Ubuntu 22.04
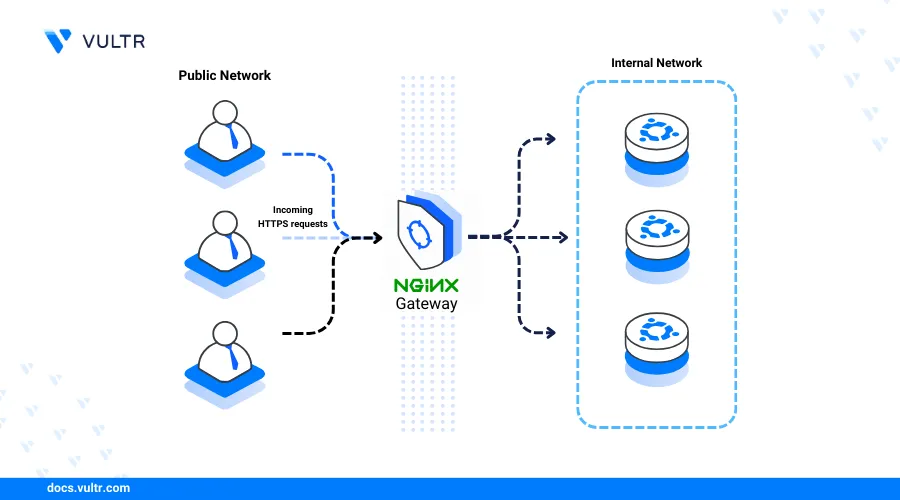
Nginx is an open-source web server that facilitates the delivery of static and dynamic web applications or services. It serves as a web server, load balancer, reverse proxy, or HTTP cache, seamlessly integrating with existing applications to form a stack or deliver web applications through your server's IP address or domain.
This article explains how to install Nginx on Ubuntu 22.04 and set up sample web applications to run efficiently on your server.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
Have an Ubuntu 22.04 server.
Create a domain name A record pointing to the server IP address.
Access the server using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Install Nginx on Ubuntu 22.04
The latest version of Nginx is available in the default APT repositories for Ubuntu 22.04. Follow the steps below to update your server packages and install the Nginx web server.
Update the server package index.
console$ sudo apt update
Install Nginx.
console$ sudo apt install nginx -y
View the installed Nginx version on your server.
console$ nginx -v
Your output should be similar to the one below:
nginx version: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
Manage the Nginx System Service
Nginx utilizes the nginx systemd service profile to manage the web server's runtime and processes on your server. Follow the steps below to enable the Nginx system service and control the web server processes on your system.
Enable the Nginx web server to start automatically at boot time.
console$ sudo systemctl enable nginx
Output:
Synchronizing state of nginx.service with SysV service script with /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install. Executing: /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable nginxStart the Nginx service.
console$ sudo systemctl start nginx
Stop the Nginx service.
console$ sudo systemctl stop nginx
Restart the Nginx service.
console$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Verify the Nginx service status.
console$ sudo systemctl status nginx
Output:
● nginx.service - A high performance web server and a reverse proxy server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Sun 2025-04-06 07:47:16 UTC; 1min 49s ago Docs: man:nginx(8) Process: 3141 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 3142 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 3143 (nginx) Tasks: 5 (limit: 9385) Memory: 4.8M CPU: 30ms CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service ├─3143 "nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on;" ├─3144 "nginx: worker process" ├─3145 "nginx: worker process" ├─3146 "nginx: worker process" └─3147 "nginx: worker process"
Create a new Nginx Virtual Host
Nginx virtual hosts include specific configurations that allow the web server to serve web application files from a designated directory using a specified domain. Follow the steps below to create a sample Nginx virtual host configuration for securely serving web application files on your server.
Create a new Nginx virtual host configuration in the
/etc/nginx/sites-availabledirectory. For example,app.example.com.conf.console$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/app.example.com.conf
Add the following configurations to the file.
iniserver { listen 80; listen [::]:80; server_name app.example.com; root /var/www/app.example.com; index index.html; location / { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } }
Save and close the file.
The above Nginx virtual host configuration listens for incoming connections using your
app.example.comdomain and serves your web application files from the/var/www/app.example.comweb root directory on your server.Test the Nginx configuration for errors.
console$ sudo nginx -t
Link the configuration to the
/etc/nginx/sites-enableddirectory to activate the virtual host on your server.console$ sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/app.example.com.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
Create a new web root directory
/var/www/app.example.comto store your web application files.console$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/app.example.com
Create a new HTML application file within the directory. For example,
index.html.console$ sudo nano /var/www/app.example.com/index.html
Add the following HTML contents to the file.
html<html> <head></head> <body> <h1>Greetings from Vultr</h1> </body> </html>
Save and close the file.
The above HTML application displays a
Greetings from Vultrheading when accessed in a web browser.Restart Nginx to apply the new virtual host configurations on your server.
console$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Access your domain to ensure that Nginx is correctly delivering the web application files from your virtual host configuration. You can use the
curlutility to test access to your domain. For example:console$ curl http://app.example.com
Output:
<html> <head></head> <body> <h1>Greetings from Vultr</h1> </body> </html>
Secure the Nginx Web Server
SSL certificates enable secure communication between a user's browser and the Nginx web server using HTTPS. By default, Nginx listens for incoming connections on the insecure HTTP port 80. Follow the steps below to generate trusted Let's Encrypt SSL certificates and configure Nginx to securely handle HTTPS connection requests.
Install the Certbot Let's Encrypt client package using Snap.
console$ sudo snap install --classic certbot
View the installed Certbot version on your server.
console$ certbot --version
Output:
certbot 3.3.0Allow network connections on the HTTP port
80for Certbot ACME verification.console$ sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
Generate a new SSL certificate for your domain. Replace
app.example.comwith the actual domain in your Nginx virtual host configurations.console$ sudo certbot --nginx -d app.example.com --agree-tos
Set Up Firewall Rules
Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) is enabled by default on Ubuntu 22.04. Follow the steps below to configure the firewall with rules that allow Nginx to listen for incoming HTTP and HTTPS connections on your server.
Allow connections on the HTTPS port
443.console$ sudo ufw allow 443/tcp
View the UFW table and verify that the new connection rules are active.
console$ sudo ufw status
Output:
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- 22/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 80/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 443/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 22/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 443/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Conclusion
In this article, you installed Nginx on your Ubuntu 22.04 server and configured it to serve web applications. Nginx supports multiple virtual hosts for secure application delivery and can be integrated with other applications like MySQL and PHP to enable dynamic web services.