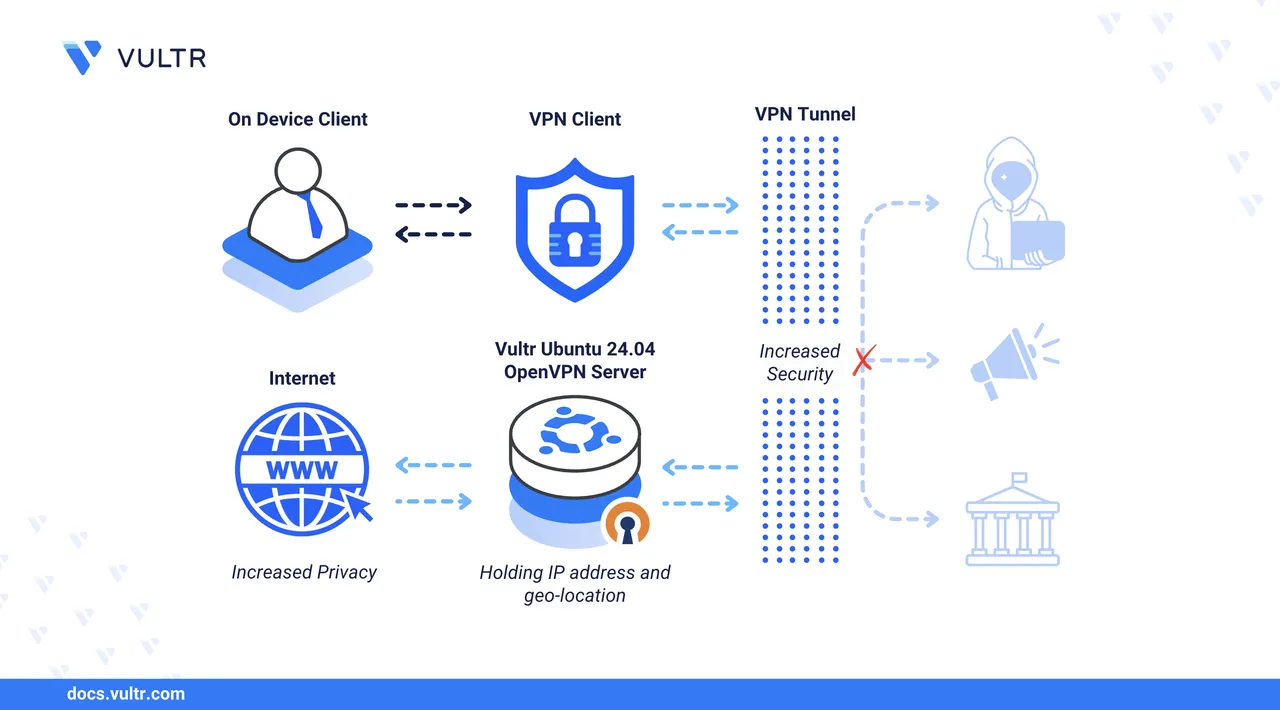
OpenVPN is an open-source, full-featured VPN solution that enables secure site-to-site and point-to-point connections. OpenVPN creates encrypted tunnels using TLS (Transport Layer Security) to secure data transmission over untrusted networks such as the Internet between clients and servers. It supports multiple encryption algorithms, including AES-256, to encrypt traffic and protect network communication from man-in-the-middle and eavesdropping attacks.
This article explains how to install OpenVPN on Ubuntu 24.04 and configure it to create secure end-to-end encrypted connections between the VPN server and client devices.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, you need to:
- Have access to an Ubuntu 24.04 server as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Install OpenVPN
OpenVPN is available in the default package repositories on Ubuntu 24.04. Follow the steps below to update the APT package manager index and install OpenVPN on your server.
Update the APT package index.
console$ sudo apt update
Install OpenVPN.
console$ sudo apt install openvpn -y
Verify the installed OpenVPN version.
console$ openvpn --version
Your output should be similar to the one below.
OpenVPN 2.6.12 x86_64-pc-linux-gnu [SSL (OpenSSL)] [LZO] [LZ4] [EPOLL] [PKCS11] [MH/PKTINFO] [AEAD] [DCO] library versions: OpenSSL 3.0.13 30 Jan 2024, LZO 2.10 DCO version: N/A Originally developed by James Yonan .................................................................OpenVPN
2.6.12is installed based on the above output.
Create the OpenVPN Server Private Key, Certificate, and TLS Encryption Files
OpenVPN requires a server certificate, private key, and encryption files signed by a trusted certificate authority (CA) to enable VPN tunnel connections. Easy-RSA is a certificate authority management tool for applications like OpenVPN that issue digital certificates, including server certificates and private key pairs. Follow the steps below to install Easy-RSA, create the public key infrastructure (PKI), build a certificate authority, and generate a new server certificate and private key.
Install Easy-RSA.
console$ sudo apt install easy-rsa -y
Navigate to your user's home directory.
console$ cd
Create a new
easy-rsadirectory.console$ mkdir easy-rsa
Link the
/usr/share/easy-rsadirectory toeasy-rsato access the Easy-RSA script and package files.console$ ln -s /usr/share/easy-rsa/* easy-rsa/
List the
easy-rsadirectory and verify the linked files.console$ ls easy-rsa
Output:
easyrsa openssl-easyrsa.cnf vars.example x509-typesChange to the
easy-rsadirectory.console$ cd easy-rsa
Create a new
varsconfiguration using a text editor such asnano.console$ nano vars
Add the following certificate authority configurations to the file.
iniset_var EASYRSA_REQ_COUNTRY "US" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_PROVINCE "Georgia" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_CITY "Atlanta" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_ORG "Vultr Docs" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_EMAIL "linuxuser@example.com" set_var EASYRSA_REQ_OU "Community" set_var EASYRSA_ALGO "ec" set_var EASYRSA_DIGEST "sha512"
Save and close the file.
The above configuration specifies the organizational information for building your CA, including the country, city, administrative email, and unit details.
Initialize the PKI using the
easy-rsascript.console$ ./easyrsa init-pki
Output:
Notice ------ 'init-pki' complete; you may now create a CA or requests. Your newly created PKI dir is: * /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki Using Easy-RSA configuration: * /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/varsBuild the CA to generate the root public certificate and private key pair.
console$ ./easyrsa build-ca
Enter a strong passphrase for signing certificate requests and repeat it when prompted to secure the CA.
... Enter New CA Key Passphrase:Enter a common name for the CA, such as
OpenVPN-CA.... Common Name (eg: your user, host, or server name) [Easy-RSA CA]:Verify the generated
ca.crtCA certificate path.Notice ------ CA creation complete. Your new CA certificate is at: * /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/ca.crt
Generate a new server certificate request. Replace
vpnserverwith your desired server common name.console$ ./easyrsa gen-req vpnserver nopass
Press Enter when prompted to verify the common name.
... If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Common Name (eg: your user, host, or server name) [vpnserver]:Verify the generated public certificate request and private key paths when successful.
Notice ------ Private-Key and Public-Certificate-Request files created. Your files are: * req: /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/reqs/vpnserver.req * key: /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/private/vpnserver.key
Sign the server certificate request using the CA.
console$ ./easyrsa sign-req server vpnserver
Enter
yesand press Enter when prompted to verify the certificate request.Using Easy-RSA 'vars' configuration: * /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/vars ... Type the word 'yes' to continue, or any other input to abort. Confirm request details:Enter your CA passphrase when prompted to sign the server certificate request.
Using configuration from /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/openssl-easyrsa.cnf Enter pass phrase for /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/private/ca.key:Your output should look like the one below when successful.
... Notice ------ Certificate created at: * /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/issued/vpnserver.crt
List the
pki/issueddirectory to verify the generated server certificate.console$ ls pki/issued
Output:
vpnserver.crtGenerate a
ta.keyHMAC signature file to enable TLS verification and authentication on the OpenVPN server.console$ sudo openvpn --genkey secret ta.key
List your working directory files to verify the generated
ta.keyfile.console$ lsOutput:
df.pem easyrsa openssl-easyrsa.cnf pki ta.key vars vars.example x509-typesCreate a strong Diffie-Hellman parameters file to secure key exchange for encrypted OpenVPN sessions.
console$ ./easyrsa gen-dh
Output:
Generating DH parameters, 2048 bit long safe prime ..................... DH parameters appear to be ok. Notice ------ DH parameters of size 2048 created at: * /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/dh.pemList the
pkidirectory to verify the generateddh.pemfile.console$ ls pki/
Output:
ca.crt dh.pem .....................Copy the
ca.crt,vpnserver.key,vpnserver.crt,ta.key, anddh.pemfiles to the/etc/openvpndirectory.console$ sudo cp ta.key pki/ca.crt pki/private/vpnserver.key pki/issued/vpnserver.crt pki/dh.pem /etc/openvpn/
Configure OpenVPN
OpenVPN uses server and client configurations in the /etc/openvpn directory to create tunnel interfaces and the respective systemd services. /etc/openvpn contains the server configurations you can manage with the openvpn@ service, while /etc/openvpn/server contains additional configurations manageable with the openvpn-server@ service. Follow the steps below to create a new OpenVPN server configuration in the /etc/openvpn directory to enable a VPN tunnel interface on your server.
Copy the sample
/usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/server.confOpenVPN server configuration template to the/etc/openvpndirectory.console$ sudo cp /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/server.conf /etc/openvpn/
Navigate to the
/etc/openvpndirectory.console$ cd /etc/openvpn
Open the copied
server.conffile.console$ sudo nano server.conf
Optional: Remove
;to uncomment thelocaldirective and replacea.b.c.dwith the server IP address OpenVPN should use to listen for incoming connections. Replace192.0.2.100with your server's actual public IP address.inilocal 192.0.2.100Find the
devdirective and verify the default OpenVPN tunnel type.inidev tuntuncreates routed IP tunnels, whiletapcreates Ethernet tunnels.Find the
ca,cert, andkeyoptions, then replace the defaultca.crt,server.crt, andserver.keyvalues with the actual paths to your certificate authority, server certificate, and server private key files.inica /etc/openvpn/ca.crt cert /etc/openvpn/vpnserver.crt key /etc/openvpn/vpnserver.key
Within the above configuration:
ca: Specifies the certificate authority (CA) path.cert: Specifies the server's public certificate path.key: Specifies the private key used to verify the server's public certificate and establish secure VPN connections.
Find the
dhdirective and replacedh2048.pemwith your actual Diffie-Hellman file path.inidh /etc/openvpn/dh.pemFind the
data-ciphersdirective, remove;to uncomment it to enable OpenVPN to use strong, modern ciphers for encryption, then adddata-ciphers-fallback AES-256-CBCas a fallback.inidata-ciphers AES-256-GCM:AES-128-GCM:?CHACHA20-POLY1305:AES-256-CBC data-ciphers-fallback AES-256-CBC
Add the following
authdirective belowdata-ciphersto specify the HMAC digest algorithm, such asSHA512, for authenticating each packet.iniauth SHA512Find the
serverdirective and specify the VPN subnet to assign client addresses. For example, change the default10.8.0.0subnet to10.10.10.0.iniserver 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0Find the
;push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp"directive and remove;to uncomment it, redirecting all traffic through the VPN.inipush "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp"Find the
dhcp-optiondirectives and replace the default addresses with your preferred DNS servers, such as8.8.8.8and1.1.1.1, to enable faster name resolution, then remove;to uncomment the options.inipush "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.8.8" push "dhcp-option DNS 1.1.1.1"
Find the
tls-authdirective, uncomment it, replaceta.keywith your actual key path, and keep0as the direction.initls-auth /etc/openvpn/ta.key 0 # This file is secretFind the
userandgrouppair, replaceopenvpnwithnobodyandnogrouprespectively to run OpenVPN with reduced privileges, then remove;to uncomment the options.iniuser nobody group nogroup
Save and close the
server.conffile.Your modified
server.conffile should look like the one below.iniport 1194 proto udp dev tun ca /etc/openvpn/ca.crt cert /etc/openvpn/vpnserver.crt key /etc/openvpn/vpnserver.key dh /etc/openvpn/dh.pem data-ciphers AES-256-GCM:AES-128-GCM:?CHACHA20-POLY1305:AES-256-CBC data-ciphers-fallback AES-256-CBC auth SHA512 topology subnet server 10.10.10.0 255.255.255.0 ifconfig-pool-persist /var/log/openvpn/ipp.txt push "redirect-gateway def1 bypass-dhcp" push "dhcp-option DNS 8.8.8.8" push "dhcp-option DNS 1.1.1.1" keepalive 10 120 tls-auth /etc/openvpn/ta.key 0 user nobody group nogroup persist-key persist-tun status /var/log/openvpn/openvpn-status.log verb 3 explicit-exit-notify 1
Test the OpenVPN server configuration and verify it runs without errors.
console$ sudo openvpn --config /etc/openvpn/server.conf
Your output should be similar to the one below when the configuration test is successful.
... 2025-07-10 22:21:00 IFCONFIG POOL IPv4: base=10.10.10.2 size=253 2025-07-10 22:21:00 IFCONFIG POOL LIST 2025-07-10 22:21:00 Initialization Sequence Completed- Press Ctrl + C to stop the configuration test.
Enable IP Forwarding
Follow the steps below to enable IP forwarding on the server, allowing OpenVPN clients to access the Internet through the VPN.
Open the
/etc/sysctl.conffile to enable IP forwarding on the server.console$ sudo nano /etc/sysctl.conf
Find the
# net.ipv4.ip_forward=1directive and remove#to uncomment it.ininet.ipv4.ip_forward=1
Save and close the file.
The above
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1configuration enables IP forwarding, allowing OpenVPN clients to route traffic through the VPN.Apply the
/etc/sysctl.confconfiguration changes.console$ sudo sysctl -p
Output:
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1Run the following command to verify the public network interface on your server.
console$ ip route | grep default
Note the public interface name like
enp1s0in your output, similar to the one below.default via 192.0.2.1 dev enp1s0 proto dhcp src 192.0.2.100 metric 100Check the UFW status and verify that it's installed.
console$ sudo ufw status
Run the following command to install UFW and allow SSH traffic if it's not installed.
console$ sudo apt install ufw -y && sudo ufw allow ssh
Open the
/etc/ufw/before.rulesfile to enable NAT through the firewall.console$ sudo nano /etc/ufw/before.rules
Add the following
POSTROUTINGpolicy configuration before the*filtersection. Replaceenp1s0with your actual public interface name.ini*nat :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] -A POSTROUTING -s 10.10.10.0/24 -o enp1s0 -j MASQUERADE COMMIT
Save and close the file.
The above firewall configuration modifies the default
POSTROUTINGpolicy in thenattable to masquerade all traffic from the10.10.10.0/24VPN subnet through the server'senp1s0public network interface.Open the
/etc/ufw/sysctl.conffile to enable IP forwarding through UFW.console$ sudo nano /etc/ufw/sysctl.conf
Find the
#net/ipv4/ip_forward=1directive and remove#to uncomment it.ininet/ipv4/ip_forward=1
Save and close the file.
The above
net/ipv4/ip_forward=1configuration enables IP forwarding through the firewall to route packets between the OpenVPNtuninterface and other interfaces on the server.Open the
/etc/default/ufwfile to allow forwarded packets through UFW.console$ sudo nano /etc/default/ufw
Find the
DEFAULT_FORWARD_POLICYdirective and change the default value fromDROPtoACCEPT.iniDEFAULT_FORWARD_POLICY="ACCEPT"
Save and close the file.
The above configuration enables UFW to allow forwarded packets through the firewall.
Reload UFW to apply the firewall configuration changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
Secure the OpenVPN Server
Follow the steps below to allow connections to the OpenVPN server through the default firewall configuration.
Allow incoming connections to the
tun0OpenVPN interface.console$ sudo ufw allow in on tun0
Allow outgoing connections from the
tun0interface.console$ sudo ufw allow out on tun0
Allow network connections to the
1194OpenVPN server port.console$ sudo ufw allow 1194/udp
Reload UFW to apply the firewall configuration changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
Check the UFW status to verify the active firewall rules.
console$ sudo ufw status
Output:
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- 22/tcp ALLOW Anywhere Anywhere on tun0 ALLOW Anywhere 1194/udp ALLOW Anywhere 22/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) Anywhere (v6) on tun0 ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 1194/udp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) Anywhere ALLOW OUT Anywhere on tun0 Anywhere (v6) ALLOW OUT Anywhere (v6) on tun0
Manage the OpenVPN Server
OpenVPN uses systemd to manage the VPN interfaces based on the server configurations in the /etc/openvpn directory. Follow the steps below to manage the OpenVPN service based on your server configuration and verify the VPN tunnel interface details.
Enable the OpenVPN service to start automatically at boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable openvpn@server.service
Output:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/openvpn@server.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/openvpn@.service.Start the OpenVPN service.
console$ sudo systemctl start openvpn@server.service
View the OpenVPN service status and verify that it runs without errors.
console$ sudo systemctl status openvpn@server.service
Output:
● openvpn@server.service - OpenVPN connection to server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/openvpn@.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2025-07-10 22:27:07 UTC; 6s ago ...Verify that the
tun0OpenVPN interface is active and correctly configured on the server.console$ ip addr show dev tun0
Output:
4: tun0: <POINTOPOINT,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc fq state UNKNOWN group default qlen 500 link/none inet 10.10.10.1/24 scope global tun0 valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever inet6 fe80::42ab:ad8b:dd59:baf4/64 scope link stable-privacy valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Create a Client Certificate and Private Key Pair
OpenVPN requires a valid client certificate and private key pair to connect to the VPN server. Follow the steps below to create a new client certificate and private key to use in your VPN client configuration.
Create a new
keysdirectory in/etc/openvpn/clientto store the client encryption keys.console$ sudo mkdir -p /etc/openvpn/client/keys
Navigate to the
easy-rsadirectory.console$ cd ~/easy-rsa
Generate a new certificate request using the
easyrsascript. Replacevpnclient1with your desired client name.console$ ./easyrsa gen-req vpnclient1 nopass
Press Enter when prompted to verify your client's common name.
... Common Name (eg: your user, host, or server name) [vpnclient1]:Verify the generated private key and public certificate request paths in your output similar to the one below.
Notice ------ Private-Key and Public-Certificate-Request files created. Your files are: * req: /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/reqs/vpnclient1.req * key: /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/private/vpnclient1.key
Import the signing request to generate a new client certificate.
console$ ./easyrsa sign-req client vpnclient1
Enter
yesand press Enter when prompted to verify the client's common name to sign the certificate.You are about to sign the following certificate: ... subject= commonName = vpnclient1 Type the word 'yes' to continue, or any other input to abort. Confirm request details:Enter your CA passphrase to sign the certificate.
Using configuration from /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/openssl-easyrsa.cnf Enter pass phrase for /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/private/ca.key:Verify the generated client certificate path in your output similar to the one below.
... Notice ------ Certificate created at: * /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/issued/vpnclient1.crt
Copy the
vpnclient1.crtclient certificate to the/etc/openvpn/client/keysdirectory.console$ sudo cp pki/issued/vpnclient1.crt /etc/openvpn/client/keys
Move the
vpnclient1.keyprivate key to the/etc/openvpn/client/keysdirectory.console$ sudo cp pki/private/vpnclient1.key /etc/openvpn/client/keys
Create OpenVPN Client Configuration Files
Follow the steps below to create a new client configuration to connect to the OpenVPN server.
Copy the sample
/usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/client.confOpenVPN client configuration to/etc/openvpn/client.console$ sudo cp /usr/share/doc/openvpn/examples/sample-config-files/client.conf /etc/openvpn/client
Navigate to the
/etc/openvpn/clientdirectory.console$ cd /etc/openvpn/client
Rename the
client.confconfiguration tovpnclient1.ovpn.console$ sudo mv client.conf vpnclient1.ovpn
Choose the OpenVPN client configuration format based on:
ovpn: For client configurations compatible with GUI OpenVPN clients for Windows, macOS, Android, or IOS devices.conf: For client configurations compatible with scripts and CLI tools like systemd. Depending on your configuration, you can start the client configuration using a systemd service likeopenvpn-client@vpnclient.service.
Open the
vpnclient1.ovpnconfiguration.console$ sudo nano vpnclient1.ovpn
Verify the following directives:
client: OpenVPN configuration type.proto udp: Client protocol. Value should match the server's configuration.
Find the
remotedirective and replacemy-server-1 1194with your OpenVPN server's IP address and port. Replace192.0.2.100with your actual server IP.iniremote 192.0.2.100 1194Find the
ca,cert, andkeyoptions, then add#before each option to comment them.ini#ca ca.crt #cert client.crt #key client.key
Find the
data-ciphersdirective, remove;to uncomment it, and verify that the cryptographic values match the OpenVPN server configuration.inidata-ciphers AES-256-GCM:AES-128-GCM:?CHACHA20-POLY1305:AES-256-CBC
Add the following
authdirective on a new line to match the OpenVPN server configuration.iniauth SHA512Save and close the
vpnclient1.ovpnfile.Your modified
vpnclient1.ovpnfile should look like the one below.iniclient dev tun proto udp remote 192.0.2.100 1194 resolv-retry infinite nobind persist-key persist-tun remote-cert-tls server data-ciphers AES-256-GCM:AES-128-GCM:CHACHA20-POLY1305:AES-256-CBC auth SHA512 verb 3
Run the following command to append values from the
ca.crt,vpnclient.crt,vpnclient.key, andta.keyfiles tovpnclient1.ovpn.console$ sudo bash -c 'cat <<EOF >> vpnclient1.ovpn <ca> $(< /etc/openvpn/ca.crt) </ca> <cert> $(< keys/vpnclient1.crt) </cert> <key> $(< keys/vpnclient1.key) </key> <tls-auth> $(< /etc/openvpn/ta.key) </tls-auth> key-direction 1 EOF'
View the
vpnclient1.ovpnfile and verify your configuration's appendedca,certificate,private key, andtlsvalues.console$ cat vpnclient1.ovpn
Copy the
vpnclient1.ovpnconfiguration to your user's home directory.console$ cp vpnclient1.ovpn ~/vpnclient1.ovpn
Follow the steps below to revoke OpenVPN clients.
Navigate to the
easy-rsadirectory.console$ cd ~/easy-rsa
Run the following command to revoke a client certificate.
console$ ./easyrsa revoke <client-name>
Verify the client certificate details, enter
yesand press <kbd class="key">Enter</kbd> when prompted to revoke the client certificate.Reason: None given Type the word 'yes' to continue, or any other input to abort. Continue with revocation:Enter your CA's passphrase when prompted to revoke the client.
Generate a
crl.pemcertificate revocation list that includes all revoked clients.console$ ./easyrsa gen-crl
Enter your CA passphrase when prompted and verify the generated
crl.pempath.Using configuration from /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/openssl-easyrsa.cnf Enter pass phrase for /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/private/ca.key: Notice ------ An updated CRL has been created: * /home/linuxuser/easy-rsa/pki/crl.pem
Copy the
crl.pemfile from thepkidirectory to/etc/openvpn.console$ sudo cp pki/crl.pem /etc/openvpn/server/
Open the OpenVPN server configuration.
console$ sudo nano /etc/openvpn/server.conf
Add the following
crl-verifydirective at the end of the file.inicrl-verify /etc/openvpn/server/crl.pemSave and close the file.
The above
crl-verifyconfiguration enables the OpenVPN server to load thecrl.pemand deny all listed clients from connecting to the VPN server.Restart the OpenVPN service to apply the server configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart openvpn@server.service
Check the OpenVPN service status.
console$ sudo systemctl status openvpn@server.service
Test the OpenVPN Server
Follow the steps below to test the VPN server using the OpenVPN Connect application for GUI devices.
Download and install OpenVPN Connect for your device from the official website. For example, OpenVPN Connect for Windows.
Open a new terminal session on your local workstation.
Change the working directory to your user's home directory.
console$ cd
Connect to the OpenVPN server using SFTP. Replace
linuxuserwith your actual user.console$ sftp linuxuser@SERVER-IP
List the directory files and verify that the
vpnclient1.ovpnclient configuration is available.consolesftp> lsDownload the
vpnclient1.ovpnfile to your local workstation.consolesftp> get vpnclient1.ovpnOutput:
Fetching /home/linuxuser/vpnclient1.ovpn to vpnclient1.ovpn vpnclient1.ovpn 100% 8281 539.1KB/s 00:00Launch OpenVPN Connect from your applications menu.
Click UPLOAD FILE on the Get Connected page.
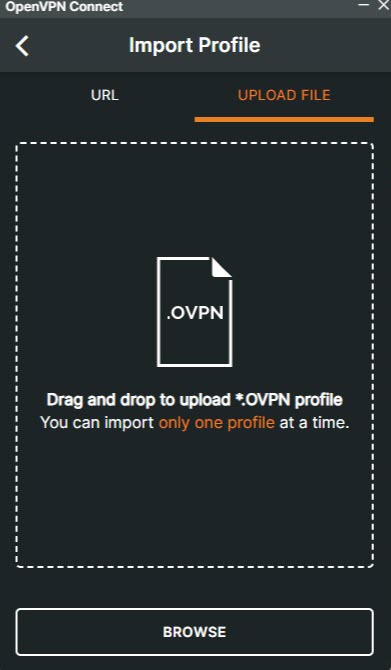
Click Browse to find and open the downloaded
vpnclient1.ovpnclient configuration in your filesystem.Verify that the Server Hostname matches your OpenVPN IP and click Connect.
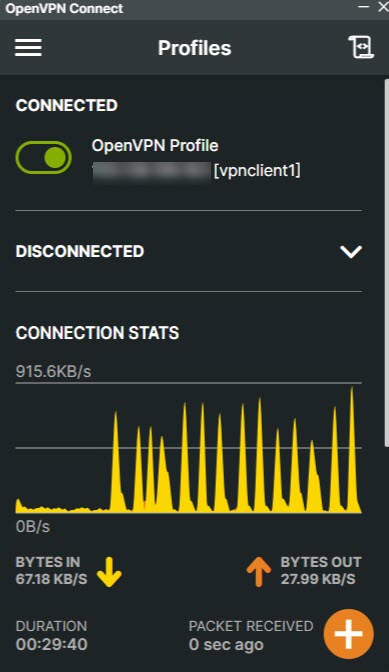
Verify that your OpenVPN profile changes to Connected and monitor the connection statistics.
Run the following command in your terminal and verify that the VPN server IP is your OpenVPN server's active public IP address.
console$ curl ifconfig.me
Test the connection to any network attached to the VPN server or the Internet using a domain like
google.comto verify that it is successful.console$ ping google.com
Output:
Pinging google.com [172.217.170.174] with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 172.217.170.174: bytes=32 time=26ms TTL=108 Reply from 172.217.170.174: bytes=32 time=28ms TTL=108 Reply from 172.217.170.174: bytes=32 time=36ms TTL=108 Reply from 172.217.170.174: bytes=32 time=29ms TTL=108 Ping statistics for 172.217.170.174: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 26ms, Maximum = 36ms, Average = 29ms
Troubleshooting
OpenVPN may return connection errors depending on your server and client configurations. Follow the steps below to troubleshoot common OpenVPN errors.
Follow the steps below to fix the Connection Timeout error displayed in your OpenVPN Connect application.
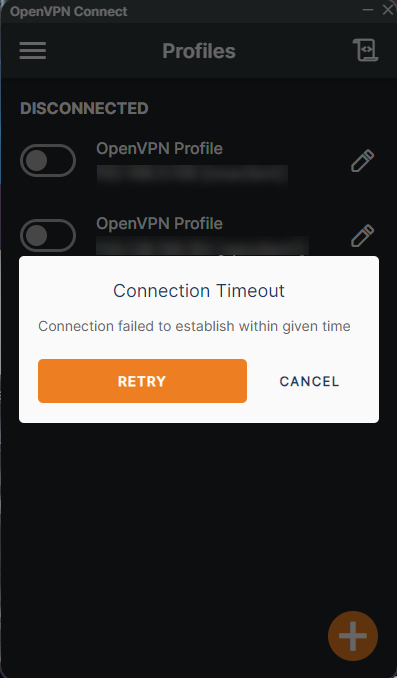
Open the OpenVPN client configuration file using your desired text editor, such as VS Code.
console$ code vpnclient1.ovpn
Verify that the
remoteconfiguration points to your OpenVPN server's public IP address and port.iniremote 192.0.2.100 1194Check the server's UFW status and verify that the OpenVPN port is allowed through the firewall.
console$ sudo ufw status
Allow the OpenVPN server port if it's missing in your firewall table.
console$ sudo ufw allow 1194/tcp
Reload UFW to apply the firewall configuration changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
Connect to the OpenVPN server again and verify the connection is success.
Follow the steps below to fix the Authentication/Decrypt packet error displayed in the OpenVPN server logs.
Jul 06 02:04:17 Openserver ovpn-server[1767]: Authenticate/Decrypt packet error: packet HMAC authentication failed
Jul 06 02:04:17 Openserver ovpn-server[1767]: TLS Error: incoming packet authentication failed from [AF_INET]192.0.2.200:59864
Jul 06 02:04:18 Openserver ovpn-server[1767]: Authenticate/Decrypt packet error: packet HMAC authentication failed
Jul 06 02:04:18 Openserver ovpn-server[1767]: TLS Error: incoming packet authentication failed from [AF_INET]192.0.2.200:59864Check the OpenVPN server logs and verify additional information about the TLS client connection error.
console$ sudo journalctl -xeu openvpn-server@server.service
View the OpenVPN server
ta.keyfile and note the TLS values in your output.console$ sudo cat /etc/openvpn/ta.key
Your output should look like the one below.
ini<tls-auth> # # 2048 bit OpenVPN static key # -----BEGIN OpenVPN Static key V1----- 1ba01f852d75016a3fd1b3b88aef9609 d52f7dd4e7858f0a219f5b9ec65b37c1 efe9458fe0e06b2ae4d1f9fee3aee929 959bd0e9e260588023fed611d803a769 108dfd5157dd95f6a627c486361e7c6d 753d65f6c25fd2278a44a872e5178f0f 58b2fddb9f3b223dc0ebc0ff95e4a58e a2cc037f8ebaad2f56bd2cafc07a57ae 04e637dfda193c37a91833eeebd664b4 60e9d6a04a86f0407ad7ca6e458d5573 9163933ecc29b567d26f5b70789fe2f5 d523f0ab7c667929a1023d5098d517f3 17f7b227a8eafaf9804fcf2713d753c7 ff35d5c36e035a123ac68a49bc67473d fba57989354045fe4305a705d5effa3d 36d447f62b9ef46e2aec61562c2900eb -----END OpenVPN Static key V1----- </tls-auth>
Open the
server.confOpenVPN server configuration.console$ sudo nano /etc/openvpn/server.conf
Verify your configuration's
data-ciphersandauthvalues.inidata-ciphers AES-256-GCM:AES-128-GCM:?CHACHA20-POLY1305:AES-256-CBC auth SHA512
Close the file.
Open the OpenVPN client configuration file.
console$ nano /etc/openvpn/client/vpnclient1.ovpn
Compare the
tls-authvalues and verify that they match your OpenVPN server'sta.keyfile.ini<tls-auth> # # 2048 bit OpenVPN static key # -----BEGIN OpenVPN Static key V1----- 1ba01f852d75016a3fd1b3b88aef9609 d52f7dd4e7858f0a219f5b9ec65b37c1 efe9458fe0e06b2ae4d1f9fee3aee929 959bd0e9e260588023fed611d803a769 108dfd5157dd95f6a627c486361e7c6d 753d65f6c25fd2278a44a872e5178f0f 58b2fddb9f3b223dc0ebc0ff95e4a58e a2cc037f8ebaad2f56bd2cafc07a57ae 04e637dfda193c37a91833eeebd664b4 60e9d6a04a86f0407ad7ca6e458d5573 9163933ecc29b567d26f5b70789fe2f5 d523f0ab7c667929a1023d5098d517f3 17f7b227a8eafaf9804fcf2713d753c7 ff35d5c36e035a123ac68a49bc67473d fba57989354045fe4305a705d5effa3d 36d447f62b9ef46e2aec61562c2900eb -----END OpenVPN Static key V1----- </tls-auth>
Verify that the
key-directionconfiguration is set to1.inikey-direction 1Verify that the
data-ciphersandauthvalues match the OpenVPN server configuration.inidata-ciphers AES-256-GCM:AES-128-GCM:?CHACHA20-POLY1305:AES-256-CBC auth SHA512
Transfer the OpenVPN client configuration to your client device and test the connection again.

Conclusion
You have installed OpenVPN on Ubuntu 24.04, configured the server, and connected a VPN client. You can use OpenVPN to connect multiple clients using different VPN tunnels and server configurations with unique port numbers. For more information, visit the OpenVPN documentation.