How to Install Podman on Ubuntu 20.04
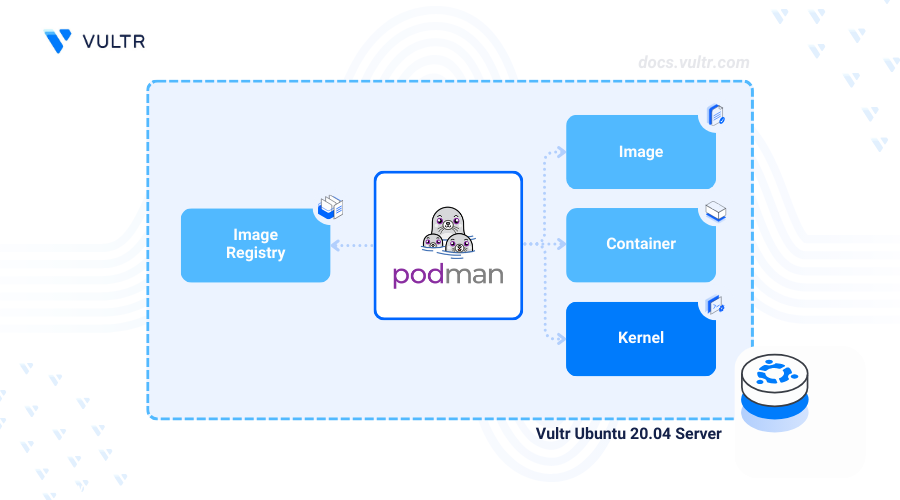
Podman is an open-source tool for managing containers without the need for a background daemon process. It improves the security and reduces resource usage for containerized applications through its daemonless architecture.
This article covers how to install Podman on Ubuntu 20.04 and perform key operations to manage containerized applications.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
Have an Ubuntu 20.04 server.
Create a Container Registry to store your Podman container images. This article uses Vultr Container Registry as an example, but the commands can be adapted to any registry by switching to the appropriate registry-specific variables.
Access the server using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Install Podman
Podman is available in the default package repositories on Ubuntu 20.04. Follow the steps below to install Podman on your server using the APT package manager.
Update the server's package index.
console$ sudo apt update
Load the system release information.
console$ source /etc/os-release
Add the official Podman repository to your server's apt index.
console$ echo "deb https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel:/kubic:/libcontainers:/stable/xUbuntu_${VERSION_ID}/ /" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/devel:kubic:libcontainers:stable.list
Import the repository's GPG key.
console$ curl -fsSL https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/devel:kubic:libcontainers:stable/xUbuntu_${VERSION_ID}/Release.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/libcontainers.gpg > /dev/null
Update the package index again.
console$ sudo apt update
Install Podman.
console$ sudo apt install podman -y
View the installed Podman version on your server.
console$ podman --version
Your output should be similar to the one below.
podman version 3.4.2
Manage the Podman System Service
Podman operates with two system services: podman CLI and podman.socket. The podman CLI allows users to interact directly with Podman to manage containers, images, and pods. Meanwhile, podman.socket is a systemd socket file that provides remote API access for managing Podman, making it suitable for remote control and integration with development tools. You can also run Podman as a system service using podman.socket. Follow the steps below to manage and enable the Podman system service on your server.
Enable the Podman service to automatically start at system boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable podman.socket
Start the Podman service.
console$ sudo systemctl start podman.socket
Stop the Podman service.
console$ sudo systemctl stop podman.socket
Restart the Podman service.
console$ sudo systemctl restart podman.socket
View the Podman service status and verify that it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status podman.socket
Output:
● podman.socket - Podman API Socket Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/podman.socket; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (listening) since Mon 2024-08-26 12:07:01 UTC; 37s ago Triggers: ● podman.service Docs: man:podman-system-service(1) Listen: /run/podman/podman.sock (Stream) CGroup: /system.slice/podman.socket
Deploy Containerized Applications using Podman
Podman utilizes different image sources to pull container images from registries listed in the /etc/containers/registries.conf file. Follow the steps below to deploy an HTTP server application using the Nginx container image from Docker Hub.
Pull the Nginx container image from Docker Hub.
console$ podman pull docker.io/nginx:alpine
Output:
Trying to pull docker.io/library/nginx:alpine... //... Writing manifest to image destination 1ae23480369fa4139f6dec668d7a5a941b56ea174e9cf75e09771988fe621c95List all container images available on the server.
console$ podman images
Verify that the Nginx container image is available in your output.
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE docker.io/library/nginx alpine 1ae23480369f 6 weeks ago 45.1 MBRun a new containerized application using the Nginx image.
console$ podman run -d --name nginx-server -p 9090:80 docker.io/nginx:alpine
List all running Podman container processes.
console$ podman ps
Output:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 20628c4b7d0f docker.io/library/nginx:alpine nginx -g daemon o... 4 seconds ago Up 4 seconds 0.0.0.0:9090->80/tcp nginx-serverTest access to the container using the host port
9090.console$ curl http://localhost:9090
Output:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> //.....
Log in to Vultr Container Registry
Podman supports custom registries like the Vultr Container Registry to build and store container images. Follow the steps below to create a Python application using FastAPI, build the container image, and push it to your Vultr Container Registry.
Access your Vultr Container Registry's management panel to view the registry's username and API key credentials.
Create a new environment variable to store your Vultr Container Registry name.
console$ export VULTR_CONTAINER_REGISTRY_NAME=<enter the Vultr Container Registry name>
Create another environment variable to store the registry username.
console$ export VULTR_CONTAINER_REGISTRY_USERNAME=<enter the Vultr Container Registry username>
Create a environment variable to store the registry's API key.
console$ export VULTR_CONTAINER_REGISTRY_API_KEY=<enter the Vultr Container Registry API key>
Log in to your Vultr Container Registry using the environment variable values.
console$ sudo podman login sjc.vultrcr.com/$VULTR_CONTAINER_REGISTRY_NAME -u $VULTR_CONTAINER_REGISTRY_USERNAME -p $VULTR_CONTAINER_REGISTRY_API_KEY
Replace
sjc.vultrcr.comwith the URL of the region where your VCR is hosted.Output:
Login Succeeded!Create a new Python application file
app.py.console$ nano app.py
Add the following contents to the file.
pythonfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Response import uvicorn app = FastAPI() @app.get("/") def hello(): return Response(content="Hello from Vultr", media_type="text/plain") if __name__ == "__main__": uvicorn.run(app, host="0.0.0.0", port=5000)
Save and close the file.
The above FastAPI application initializes a new web server on port
5000that displays aHello from Vultrmessage when accessed.Create a new
Dockerfileconfiguration.console$ nano Dockerfile
Add the following contents to the file.
dockerfileFROM python:3.12-slim WORKDIR /app COPY app.py /app RUN pip install fastapi uvicorn EXPOSE 5000 CMD ["python", "app.py"]
Save and close the file.
The above
Dockerfilecreates a Python 3.12 environment, installsfastapianduvicorn, and runs a web server on port5000using theapp.pyfile.Build the container image with all files in your working directory.
console$ podman build -t python-fastapi-app .
Output:
//... Successfully tagged localhost/python-fastapi-app:latest 8f00b7a023da93ce714c41ab817be66913385f8c8583b4c38e59a35e53af0037Tag the container image with your Vultr Container Registry's name.
console$ podman tag python-fastapi-app sjc.vultrcr.com/$VULTR_CONTAINER_REGISTRY_NAME/python-fastapi-app:v1
Replace
sjc.vultrcr.comwith the URL of the region where your VCR is hosted.List all container images on your server and verify that the tagged image is available.
console$ podman images
Output:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE sjc.vultrcr.com/demo/python-fastapi-app v1 8f00b7a023da 30 seconds ago 217 MB localhost/python-fastapi-app latest 8f00b7a023da 30 seconds ago 217 MB docker.io/library/nginx alpine 1ae23480369f 6 weeks ago 45.1 MB docker.io/library/python 3.12-slim 8d6f9eba56c9 11 days ago 135 MBPush the image to your Vultr Container Registry.
console$ podman push sjc.vultrcr.com/$VULTR_CONTAINER_REGISTRY_NAME/python-fastapi-app:v1
Replace
sjc.vultrcr.comwith the URL of the region where your VCR is hosted.Output:
//... Writing manifest to image destinationDeploy a new containerized application using your Vultr Container Registry image.
console$ podman run -d --name demo-app -p 5000:5000 sjc.vultrcr.com/$VULTR_CONTAINER_REGISTRY_NAME/python-fastapi-app:v1
Test access to the application using Curl on the host port
5000.console$ curl http://localhost:5000
Output:
Hello from Vultr
Conclusion
You have successfully installed Podman on your Ubuntu 20.04 server and deployed containerized applications. Podman allows you to build, store, and manage containers on your server.