Introduction
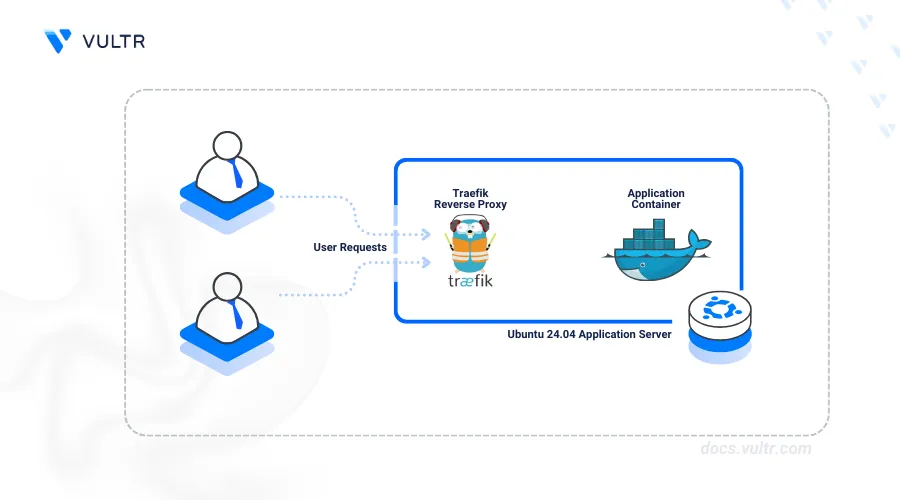
Traefik Proxy is a modern open-source reverse proxy and load balancer for deploying microservices. Traefik Proxy as a reverse proxy uses routing rules to dynamically process TCP, UDP, HTTP, and HTTPS client requests to applications in a containerized environment.
This article explains how to install and set up Traefik proxy as a reverse proxy for Docker containers on Ubuntu. You will access the Traefik web administration dashboard and securely expose containerized applications on your server.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
Deploy a One-Click Docker instance using the Vultr marketplace application.
Set up a new domain A record pointing to the instance's public IP address. For example,
app.example.com.Access the instance using SSH and create a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Add the sudo user to the Docker group. Replace
linuxuserwith your actual user.console# usermod -aG docker linuxuser
Set Up Firewall Rules
The Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) is available and active on Vultr Ubuntu servers by default. Follow the steps below to create new rules to allow Traefik to route incoming HTTP and HTTPS connection requests to applications on your server.
Allow HTTP connections on port
80.console$ sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
Allow HTTPS connections on port
443.console$ sudo ufw allow 443/tcp
View the UFW status and verify that the new connection rules are active.
console$ sudo ufw status
Output:
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- 22/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 80/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 443/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 22/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 443/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
To ensure seamless SSL certificate management, explore how Traefik cert-manager simplifies the process by automating the issuance and renewal of certificates.
Deploy Traefik Using Docker Compose
Traefik uses Docker labels to automatically discover and route traffic to containerized applications. Docker Compose allows you to define and run multi-container applications with multiple labels to define routing paths with Traefik. Follow the steps below to install Traefik using Docker Compose on your server.
View the active Docker Compose version on your server.
console$ docker compose version
Output:
Docker Compose version v2.29.7Create a new
docker-compose.ymlfile.console$ sudo nano docker-compose.yml
Add the following configurations to the file.
yamlservices: traefik: image: "traefik:latest" container_name: "traefik" command: - "--log.level=DEBUG" - "--api.insecure=true" - "--providers.docker=true" - "--entryPoints.web.address=:80" ports: - "80:80" - "8080:8080" volumes: - "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"
Save and close the file.
The above configuration creates a new containerized application using the Traefik image that accepts incoming traffic on the HTTP port
80and exposes the web administration dashboard on port8080. Within the configuration:services: Specifies the services to create with specific configuration options.traefik: Creates a newtraefikDocker service.image: Configures thetraefikservice to pull and run the Traefik container image.container_name: Sets the Traefik container image name totraefik.command: Specifies the command line options to execute in thetraefikcontainer image."--log.level=DEBUG": Enables Traefik to run in debug mode and log all runtime errors."--api.insecure=true": Enables HTTP connections to the Traefik dashboard."--providers.docker=true": Enables Traefik to detect and configure routes for Docker containers using labels."--entryPoints.web.address=:80": Sets the HTTP port80as the main entry point to listen for incoming traffic. Traefik requires at least one entry point to define the ports to listen for incoming connection requests.
ports: Includes port mappings to the host. The value80:80binds the Traefik HTTP port80to the host, while8080:8080enables access to the Traefik dashboard.volumes: Mounts specific paths to Traefik. The/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sockvalue mounts the Docker socket as a volume to allow Traefik to monitor and manage Docker services.
Start Traefik in detached mode.
console$ docker compose up -d
View all running Docker containers and verify that the Traefik container status is up.
console$ docker compose ps
Output:
NAME IMAGE COMMAND SERVICE CREATED STATUS PORTS traefik traefik:latest "/entrypoint.sh --lo…" traefik 6 seconds ago Up 6 seconds 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, :::80->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp, :::8080->8080/tcpThe Traefik container is actively running based on the above output.
Access your server's public IP address using a web browser such as Chrome on port
8080.http://<server-ip>:8080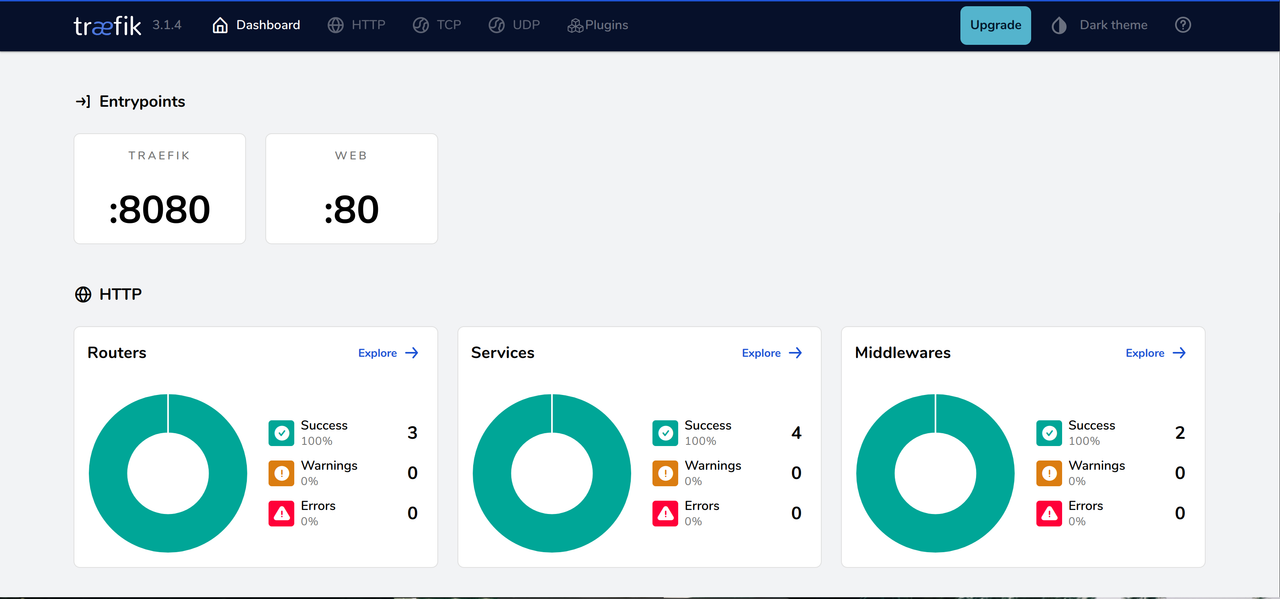
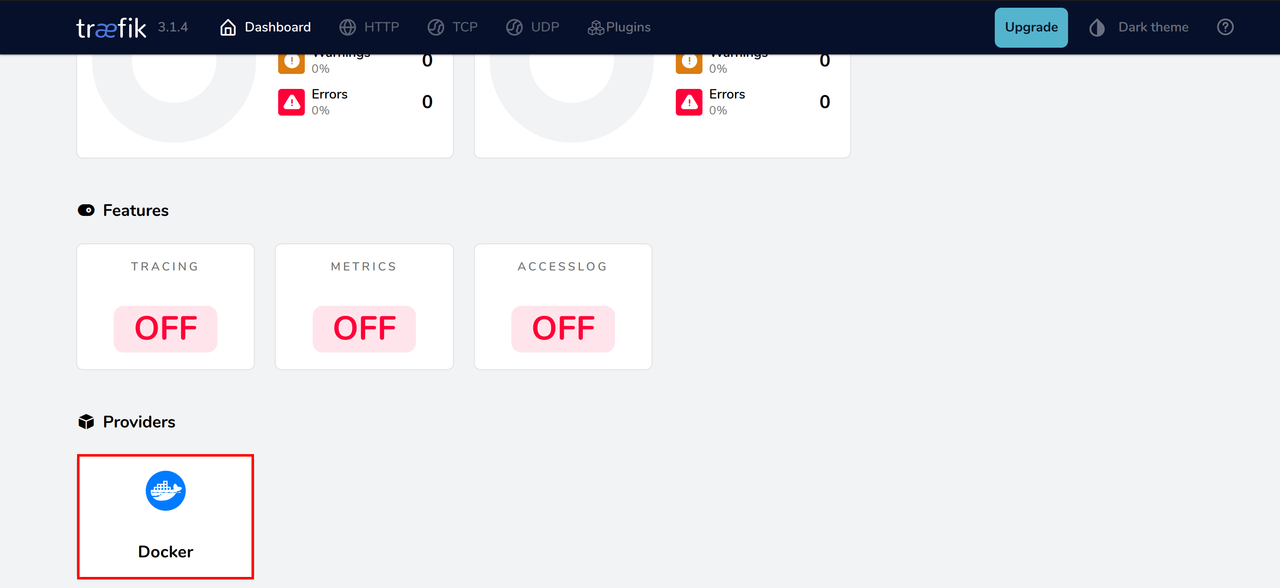
Navigate to the Providers section and verify that Docker is available.
Configure Traefik Proxy as a Reverse Proxy Using Docker Compose
Traefik is actively running and configured to handle HTTP connection requests on port 80. Follow the steps below to create a new sample web server application using the Apache container image to integrate with Traefik and accept connection requests using a domain.
Open the
docker-compose.ymlfile.console$ nano docker-compose.yml
Add the configurations below to the
traefikservice. Replaceapp.example.comwith your actual domain.yamlapache: image: "httpd:latest" container_name: "apache" labels: - traefik.enable=true - traefik.http.routers.apache.rule=Host(`app.example.com`) - traefik.http.routers.apache.entrypoints=web
Save and close the file.
The above configuration creates a new web server application using the Apache container image and accepts incoming connection requests for the
app.example.comdomain and thewebentry point. Within the configuration:apache: Creates a newapacheservice.image: "httpd:latest": Deploys theapacheservice using the Apachehttpdcontainer image.labels: Sets the Docker labels to assign theapacheservice enabling Traefik to dynamically route traffic to the application.traefik.enable=true: Enables Traefik to forward traffic to theapacheservice.traefik.http.routers.apache.rule=Host(`app.example.com`): Sets the domain Traefik uses to listen for incoming connection requests. Specifyapache.localhostinstead ofapache.rule=Hostto use localhost if you don't want to specify a domain.traefik.http.routers.apache.entrypoints=web: Sets thewebentry point Traefik uses to route incoming requests to theapacheservice.
Your modified
docker-compose.ymlfile should look like the one below.yamlservices: traefik: image: "traefik:latest" container_name: "traefik" command: - "--log.level=DEBUG" - "--api.insecure=true" - "--providers.docker=true" - "--entryPoints.web.address=:80" ports: - "80:80" - "8080:8080" volumes: - "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock" apache: image: "httpd:latest" container_name: "apache" labels: - traefik.enable=true - traefik.http.routers.apache.rule=Host(`app.example.com`) - traefik.http.routers.apache.entrypoints=web
Start the
apacheservice in detached mode.console$ docker compose up -d
Output:
[+] Running 2/2 ✔ Container traefik Running 0.0s ✔ Container apache Started 0.4sView all running Docker containers and verify
apachecontainer is actively running.console$ docker compose ps
Output:
NAME IMAGE COMMAND SERVICE CREATED STATUS PORTS apache httpd:latest "httpd-foreground" apache 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 80/tcp traefik traefik:latest "/entrypoint.sh --lo…" traefik 35 minutes ago Up 34 minutes 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, :::80->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp, :::8080->8080/tcpAccess your domain in a new web browser window using HTTP and verify that the Apache default page displays. Replace
app.example.comwith your actual domain.http://app.example.com
Access your Traefik dashboard, navigate to the HTTP tab, and verify that the
apacheservice route is available.http://SERVER-IP:8080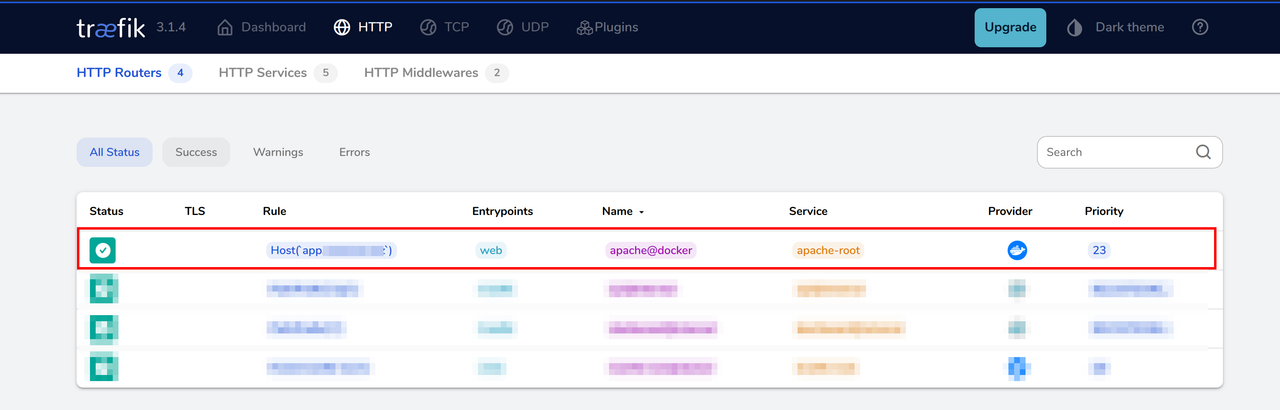
Set up Automatic HTTPS Using Traefik
Traefik uses certificate resolvers to generate and renew trusted SSL certificates from an automatic certificate management environment (ACME) provider. Traefik initializes an ACME challenge to validate your domain and store the generated certificates in an acme.json file. Follow the steps below to set up automatic HTTPS using Traefik and use Let's Encrypt as the ACME to generate trusted SSL certificates for your apache service domain.
Back up the original
docker-compose.ymlfile.console$ mv docker-compose.yml http-docker-compose.yml
Create a new
docker-compose.ymlfile.console$ nano docker-compose.yml
Add the following configurations to the file. Replace
app.example.comwith your domain andhello@example.comwith your active email address.yamlservices: traefik: image: "traefik:latest" container_name: "traefik" command: - "--log.level=DEBUG" - "--api.insecure=true" - "--providers.docker=true" - "--entryPoints.apachesecure.address=:443" - "--certificatesResolvers.apacheresolver.acme.tlsChallenge=true" - "--certificatesResolvers.apacheresolver.acme.email=hello@example.com" - "--certificatesResolvers.apacheresolver.acme.storage=/letsencrypt/acme.json" ports: - "443:443" - "8080:8080" volumes: - "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock" - "./letsencrypt:/letsencrypt" apache: image: "httpd:latest" container_name: "apache" labels: - traefik.enable=true - traefik.http.routers.apache.rule=Host(`app.example.com`) - traefik.http.routers.apache.entrypoints=apachesecure - traefik.http.routers.apache.tls=true - traefik.http.routers.apache.tls.certresolver=apacheresolver
Save and close the file.
The above configuration enables Traefik to accept only secure HTTPS connection requests using the
apachesecureentry point on port443. Within thetraefikservice configuration:--entryPoints.apachesecure.address=:443: Enables HTTPS connections on port443using theapachesecureentry point.--certificatesResolvers.apacheresolver.acme.tlsChallenge=true: Creates a newapacheresolvercertificate resolver and uses the ACMETLS-ALPN-01challenge as a TLS challenge to generate a new SSL certificate. Traefik uses the Let's Encrypt ACME by default.--certificatesResolvers.apacheresolver.acme.email=hello@example.com: Sets ACME challenge email address .--certificatesResolvers.apacheresolver.acme.storage=/letsencrypt/acme.json: Specifies the path to store the ACME configuration to reuse between container restarts.
Within the
apacheservice configuration:traefik.http.routers.apache.entrypoints=apachesecure: Creates a newapachesecureentry point to handle connection requests.traefik.http.routers.apache.tls=true: Enables secure TLS connections to the service.traefik.http.routers.apache.tls.certresolver=apacheresolver: Creates a newapacheresolvercertificate resolver to generate and manage SSL certificates.
Apply the Docker Compose configuration to modify the
traefikandapacheservice containers.console$ docker compose up traefik apache -d
View all running Docker containers and verify the service status.
console$ docker compose ps
Access your domain using HTTPS in a new web browser window. Then, verify the connection is secure and the default web page displays.
https://app.example.comAccess the Traefik dashboard and verify that the
apachesecureentry point is available on port443.SERVER-IP:8080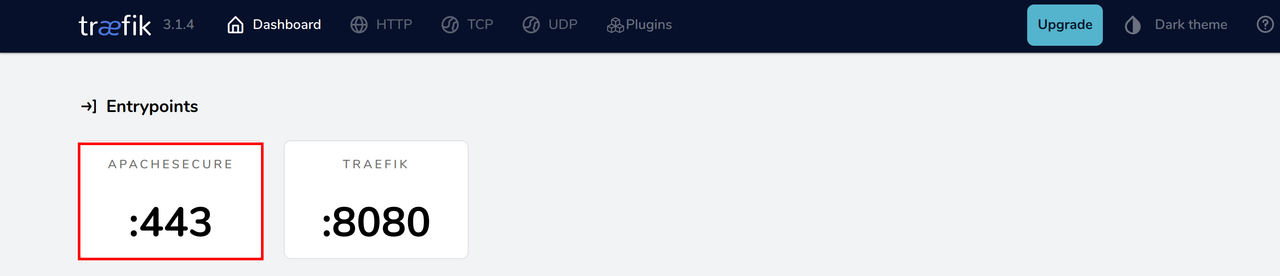
Navigate to the HTTP tab and verify TLS is active on the
apacheservice.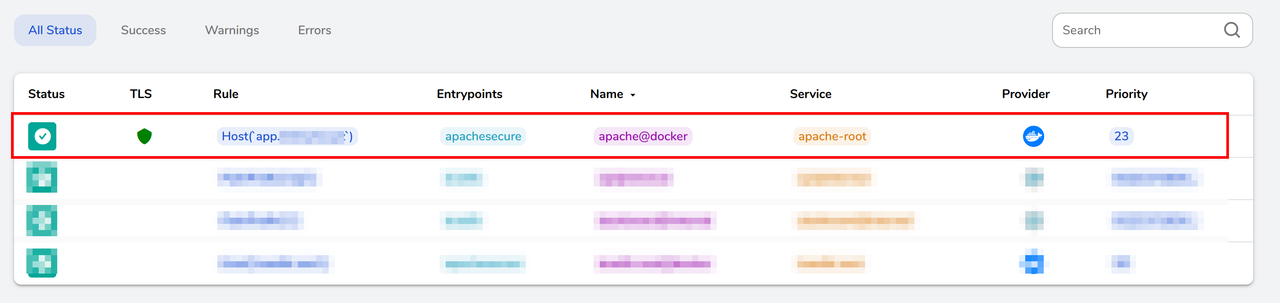
Stop the
traefikandapachecontainer.console$ docker stop traefik apache
Deploy Traefik Using Docker CLI
You can deploy Traefik using Docker CLI to work as a reverse proxy for new or existing Docker containers. A Traefik YAML configuration includes the Docker labels and request routing rules to forward connection requests. Follow the steps below to deploy Traefik using Docker CLI and deploy a sample container using the Nginx image to route connection requests.
Create a new
traefik.ymlfile.console$ sudo nano traefik.yml
Add the following configurations to the file.
yamlentryPoints: web: address: ":80" api: dashboard: true insecure: true log: level: debug providers: docker: exposedByDefault: false endpoint: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
Save and close the file.
Within the above configuration:
entrypoint: Creates a newwebentry point that listens for connections on the HTTP port80.api: Enables the Traefik dashboard.log: Enables debug level logging to include warning and error logs.providers: Sets Docker as the provider and connects using the Docker socket.
Deploy Traefik as a new Docker container, mount the
traefik.ymlfile, and the Docker socket.console$ docker run -d -p 8080:8080 -p 80:80 \ -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \ -v $PWD/traefik.yml:/traefik.yml \ traefik:v3.1
View all running Docker containers and verify that the new Traefik container is running.
console$ docker ps
Deploy a new Nginx container using the
webentry point label. Replaceapp.example.comwith your actual domain.console$ docker run -d \ --label "traefik.enable=true" \ --label 'traefik.http.routers.nginx.rule=Host(`app.example.com`)' \ --label "traefik.http.routers.nginx.entrypoints=web" \ nginx
View the running Docker containers and verify that the Nginx container is running.
console$ docker ps
Output:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 6274442a11a2 nginx "/docker-entrypoint.…" 6 seconds ago Up 4 seconds 80/tcp serene_haslett 4c5c3db6e4e4 traefik:v3.1 "/entrypoint.sh trae…" 52 seconds ago Up 51 seconds 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp, :::80->80/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp, :::8080->8080/tcp nice_boseAccess your domain in a new web browser window and verify that the Nginx web page displays.
http://app.example.comOutput:
Welcome to nginx!Access the Traefik dashboard using your server's public IP address and verify the new
webroute in the HTTP tab.http://SERVER-IP:8080
Enable Automatic HTTPS Using Traefik
Traefik supports automatic HTTPS to secure connections to the exposed container applications. Follow the steps below to create a new entry point for the HTTPS port 443 and enable the Let's Encrypt ACME labels to generate SSL certificates.
Back up the
traefik.ymlfile.console$ mv traefik.yml old-traefik.yml
Create the
traefik.ymlfile again.console$ sudo nano traefik.yml
Add the following configurations to the file. Replace
hello@example.comwith your active email address.yamlentryPoints: websecure: address: ":443" api: dashboard: true insecure: true log: level: debug providers: docker: exposedByDefault: false endpoint: "unix:///var/run/docker.sock" certificatesResolvers: nginxresolver: acme: email: hello@example.com storage: /letsencrypt/acme.json tlsChallenge: true
Save and close the file.
Within the above configuration:
websecure: Creates a new entry point.nginxresolver: Sets the certificate resolver name to use with Let's Encrypt as the ACME./letsencrypt/acme.json: Uses theacme.jsonfile in the host data directory or creates the Let's Encrypt directory if unavailable.
Stop the active Traefik container. Replace
traefik-container-idwith your actual Traefik container ID.console$ docker stop <traefik-container-id> -f
Stop the Nginx container. Replace
nginx-container-idwith your actual Nginx container ID.console$ docker stop <nginx-container-id> -f
Deploy Traefik, map the HTTPS port
443to the host, and mount theletsencryptdirectory.console$ docker run -d -p 8080:8080 -p 443:443 \ -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock \ -v $PWD/traefik.yml:/traefik.yml \ -v $PWD/letsencrypt:/letsencrypt \ traefik:v3.1
View all running Docker containers and verify that Traefik is running.
console$ docker ps
Deploy a new Nginx container using the
websecureentry point and thenginxresolvercertificate resolver. Replaceapp.example.comwith your actual domain.console$ docker run -d \ --label "traefik.enable=true" \ --label 'traefik.http.routers.nginx.rule=Host(`app.example.com`)' \ --label "traefik.http.routers.nginx.entrypoints=websecure" \ --label "traefik.http.routers.nginx.tls.certresolver=nginxresolver" \ nginx
Access your domain in a new web browser window using HTTPS.
https://app.example.comVerify that the default Nginx web page displays.
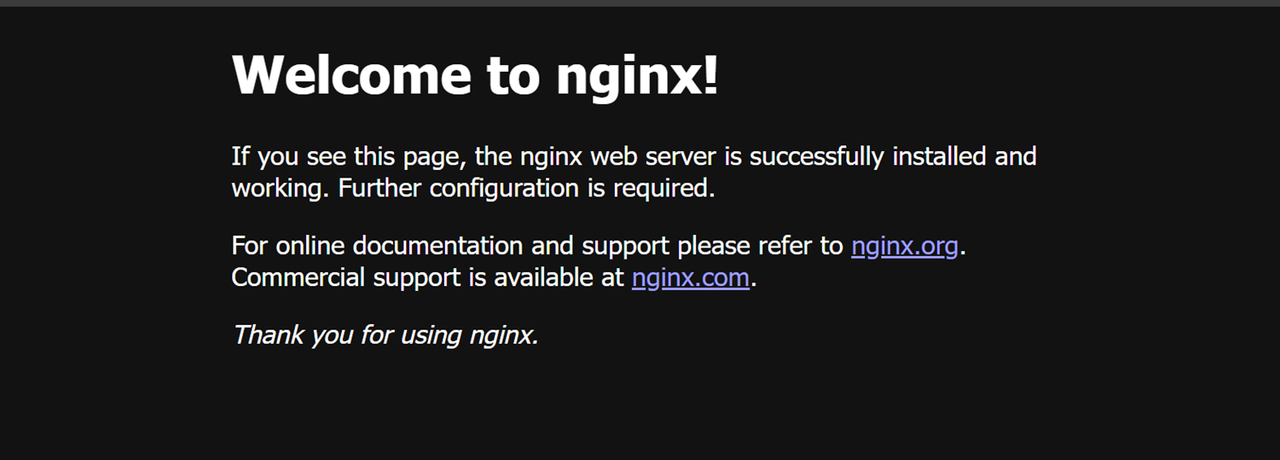
Conclusion
You have deployed Traefik Proxy using Docker Compose and Docker CLI as a reverse proxy to route traffic to container applications. You set up sample web server containers using the Apache and Nginx images to handle connection requests using Traefik. You can also use Traefik as a load balancer or API gateway to securely expose Docker container applications. For more information and Docker labels, visit the Traefik documentation.