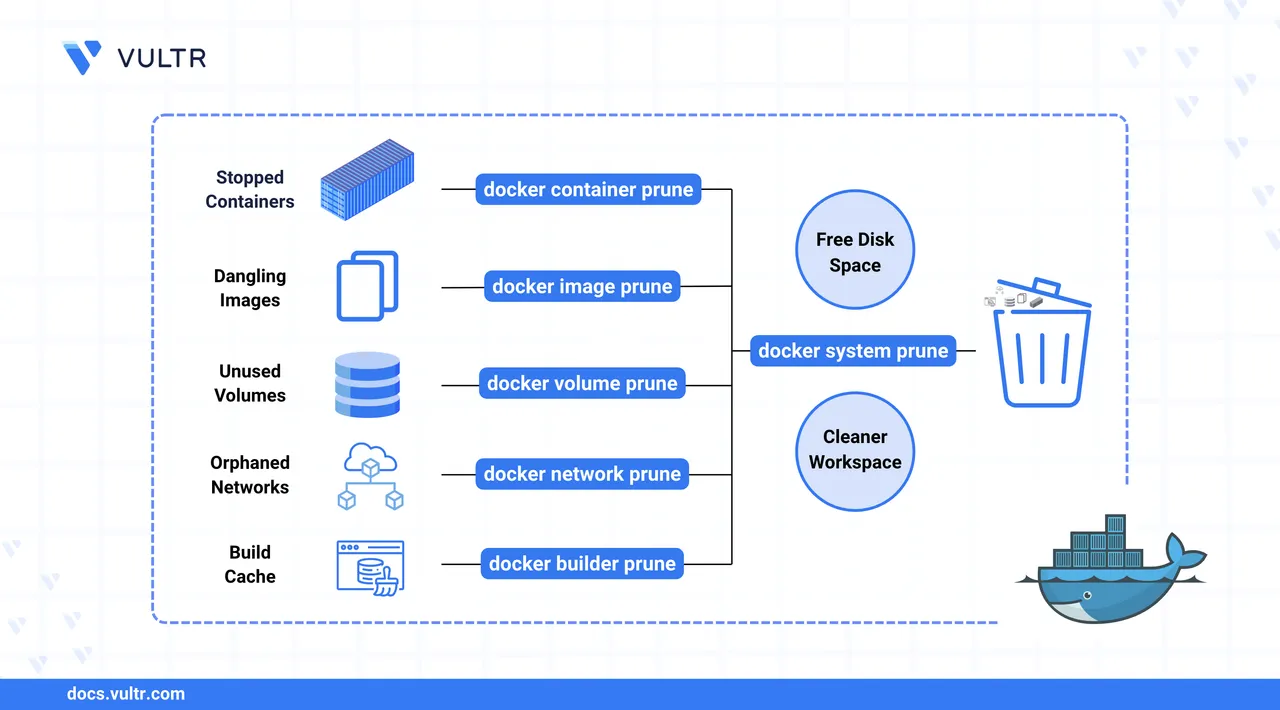
Docker is a widely used containerization platform for building, running, and distributing applications. As you develop and deploy containers over time, Docker can accumulate unused objects like stopped containers, dangling images, unused volumes, and networks. These leftover resources consume disk space and may degrade system performance if not cleaned up.
This article explains how to use the docker prune command family to safely remove unused Docker resources. You’ll learn the differences between docker prune and manual deletion, how to use each prune variant effectively, and best practices to prevent accidental data loss during cleanup.
What Is docker prune?
The docker prune command family helps you remove unused Docker resources like stopped containers, dangling images, unused volumes, networks, and build cache, all in one go. It's faster and less manual than using docker rm or docker rmi.
| Feature | docker rm / rmi |
docker prune |
|---|---|---|
| Removes one item at a time | Yes | No |
| Removes all unused resources at once | No | Yes |
| Requires specific names or IDs | Yes | No |
| Safer for manual deletions | Yes | No |
| Useful for quick cleanup | No | Yes |
Use docker rm when you need precision. Use docker prune when you want to clean everything efficiently.
The Short Answer Version
# Remove all unused containers, networks, images, and build cache
$ docker system prune
# Remove only stopped containers
$ docker container prune
# Remove dangling (untagged and unused) images
$ docker image prune
# Remove volumes not used by any container
$ docker volume prune
# Remove networks not connected to any container
$ docker network prune
# Remove Docker build cache
$ docker builder pruneCommon Options for docker prune
Most docker prune commands support the following options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
--force |
Skip confirmation prompts. Use carefully to avoid accidental deletions. |
--filter |
Filter resources by criteria such as age. Example: --filter "until=24h" removes items older than 24 hours. |
--all |
(For images) Remove all unused images, not just dangling ones. |
Use filters to avoid removing recently created resources during cleanup.
Clean All Docker Resources with docker system prune
Use this command to remove all unused containers, networks, dangling images, and build cache.
Command Syntax
docker system prune [OPTIONS]Command Demonstration
Clean up all unused Docker resources interactively.
console$ docker system prune
Clean up all unused resources without confirmation.
console$ docker system prune --force
Clean up unused resources older than 48 hours.
console$ docker system prune --filter "until=48h"
When to Use
- After heavy development or container churn
- When disk space is limited
- When no stopped containers or unused images are needed
Clean Docker Containers with docker container prune
Use this command to remove only stopped containers. Running containers are not affected.
Command Syntax
docker container prune [OPTIONS]Command Demonstration
Remove all stopped containers.
console$ docker container prune
Remove all stopped containers without confirmation.
console$ docker container prune --force
Remove stopped containers older than 24 hours.
console$ docker container prune --filter "until=24h"
When to Use
- After running short-lived containers during testing or development
- When stopped containers pile up over time
- To free up space without affecting running containers
Clean Docker Images with docker image prune
This command removes unused Docker images. By default, it only removes dangling images — images that are untagged and not referenced by any containers.
Command Syntax
docker image prune [OPTIONS]Command Demonstration
Remove all dangling images.
console$ docker image prune
Remove all unused images (not just dangling ones).
console$ docker image prune --all
Remove unused images older than 72 hours.
console$ docker image prune --all --filter "until=72h"
When to Use
- After building or pulling many temporary images
- When running out of disk space due to image layers
- To clean up old application builds not referenced by containers
Clean Docker Volumes with docker volume prune
This command removes volumes that are not referenced by any containers. Active or attached volumes are not affected.
Command Syntax
docker volume prune [OPTIONS]Command Demonstration
Remove all unused volumes interactively.
console$ docker volume prune
Remove all unused volumes without confirmation.
console$ docker volume prune --force
When to Use
- After deleting containers that previously used persistent volumes
- When temporary or test volumes accumulate over time
- To recover disk space tied to orphaned data
Clean Docker Networks with docker network prune
Use this command to remove Docker networks that are not connected to any running or stopped containers.
Command Syntax
docker network prune [OPTIONS]Command Demonstration
Remove all unused networks interactively.
console$ docker network prune
Remove all unused networks without confirmation.
console$ docker network prune --force
When to Use
- After removing containers created with
docker-compose - When testing multi-container applications
- To clean up orphaned or auto-generated bridge networks
Clean Docker Build Cache with docker builder prune
This command removes the build cache created during image builds. By default, it only removes dangling (unused) cache layers.
Command Syntax
docker builder prune [OPTIONS]Command Demonstration
Remove dangling build cache interactively.
console$ docker builder prune
Remove all unused build cache without confirmation.
console$ docker builder prune --all --force
When to Use
- After frequent image builds during development
- When low on disk space
- To clean up intermediate cache layers that are no longer referenced
Troubleshooting Docker Prune Issues
Cause: Docker only removes unused resources. If a container or volume is still referenced, it won't be pruned.
Solution:
Stop the container.
console$ docker container stop <container_id>
Remove the container.
console$ docker container rm <container_id>
Run prune again.
console$ docker system prune
Cause: The volume is still attached to a container.
Solution:
List all volumes.
console$ docker volume ls
Inspect the volume to see where it's used.
console$ docker volume inspect <volume_name>
Remove the attached container.
console$ docker container rm <container_id>
Then prune volumes.
console$ docker volume prune
Cause: Some resources are still referenced or were not covered by the last prune command.
Solution:
Check disk usage summary.
console$ docker system df
Run targeted prune commands.
console$ docker image prune
console$ docker volume prune
Run a full cleanup (if safe to do so).
console$ docker system prune --all
Conclusion
In this article, you learned how to clean up unused Docker resources using the docker prune command family. You explored how to remove stopped containers, dangling images, unused volumes and networks, and build cache safely and efficiently. These commands help maintain a clean development environment and reduce disk usage.