Introduction
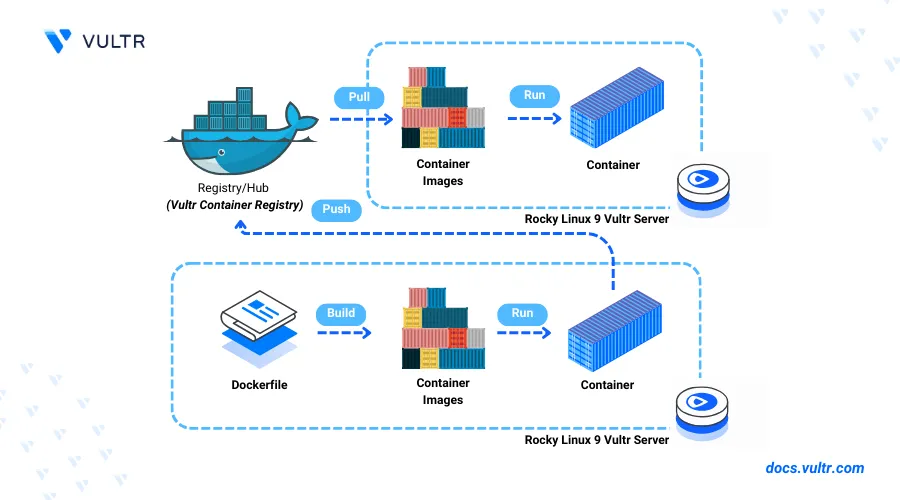
Docker is an open-source platform that enables the creation, packaging, distribution, and deployment of applications using lightweight, portable containers. Each container includes all the necessary runtime dependencies, libraries, application code, and configuration parameters required to run software reliably across multiple environments and on any host system. On Rocky Linux 9, Docker offers a consistent and efficient way to manage containerized applications, making it easier to develop, test, and deploy software in isolated environments.
This article explains how to install Docker on Rocky Linux 9 and run containerized applications on your server. You'll set up the Docker Engine, which allows you to create and manage lightweight, portable containers. For those using other Linux distributions, you can check out our guide on how to install Docker on Ubuntu 24.04, which covers installing the latest Docker packages.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- Deploy a Rocky Linux 9 instance on Vultr.
- Create a Vultr Container Registry to store your Docker images.
- Access your server using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges
- Update the server.
Install Docker on on Rocky Linux 9
Docker is available in the default package repositories on Rocky Linux 9, but the version information may not be the latest. Follow the steps below add the latest repository information and install Docker on your server using the default DNF package manager.
Install the
dnf-utilspackage.console$ sudo dnf install -y dnf-utils
Add the official Docker repository to your package sources.
console$ sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/rhel/docker-ce.repo
Install Docker and all required dependency packages such as
containerd.io.console$ sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
Manage the Docker System Service
The Docker engine uses the docker systemd service to run and manage the daemon processes on your server. Only privileged users can access Docker CLI and manage the containerized application processes. Follow the steps below to manage the Docker system service and enable unprivileged system users to use Docker CLI to manage containerized applications on the server.
Enable the Docker service to automatically start at system boot.
console$ sudo systemctl start docker
Start the Docker service.
console$ sudo systemctl start docker
View the Docker service status and verify that it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status docker
Output:
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; disabled; preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Sat 2024-07-06 00:00:46 UTC; 35s ago TriggeredBy: ● docker.socket Docs: https://docs.docker.com Main PID: 6412 (dockerd) Tasks: 7 Memory: 65.5M CPU: 233ms CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service └─6412 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run/containerd/containerd.sockThe Docker service is active and running on your server based on the
active (running)prompt in the above output.Stop the Docker service.
console$ sudo systemctl stop docker
Restart the Docker service.
console$ sudo systemctl restart docker
Deploy Containerized Applications using Docker
Docker can find and run applications from container image sources such as Docker Hub. Follow the steps below to deploy a sample containerized application using the hello world image from Docker Hub and verify the container processes on your server.
Pull the
crccheck/hello-worldDocker image from Docker Hub.console$ docker pull crccheck/hello-world
List all Docker images available on your server and verify that the new image is available.
console$ docker images
Output:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE crccheck/hello-world latest 24349d78cb62 2 years ago 1.24MBDeploy a new containerized application using the
hello-worldDocker image.console$ docker run -d --name web-test -p 80:8000 crccheck/hello-world
The above command runs a new Docker container with the following configuration:
-d: Starts the container in detached mode as a background process.--name web-test: Assigns the containerized application nameweb-testfor identification and management.-p 80:8000: Maps the localhost port80to the container port8000to enable access the containerized application.crccheck/hello-world: Sets the Docker image to use when creating the container
List all active Docker containers running on your server.
console$ docker ps
Verify that the
web-testcontainer is active running similar to the following output.CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 74609506c374 crccheck/hello-world "/bin/sh -c 'echo \"h…" 6 seconds ago Up 6 seconds (health: starting) 0.0.0.0:80->8000/tcp, :::80->8000/tcp web-testAccess your localhost port
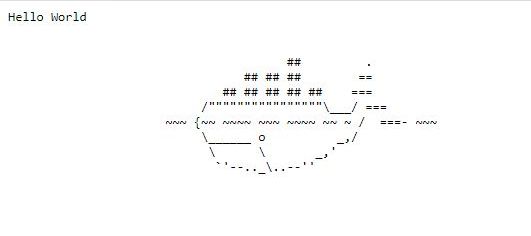
80using thecurlutility and verify that your application responds to user requests.console$ curl 127.0.0.1:80
Output:
Hello WorldAccess your server IP address using a web browser such as Chrome and verify that your application's graphical interface page displays.
http://SERVER-IP:80Output:
Run the following command to stop the Docker container.
console$ docker stop web-test
Log in to a Container Registry
Docker supports private and public container registries such as the Vultr container registry to build, store and deploy container images. Follow the steps below to use Docker with your Vultr Container Registry to deploy containerized applications on the server.
Access your Vultr Container Registry's management page and copy the
docker logincommand in the Example Commands section that contains all necessary credentials.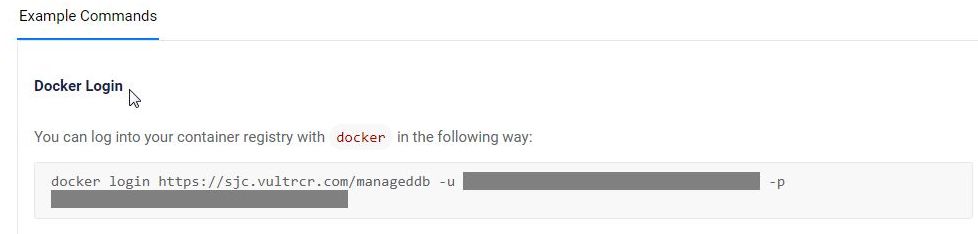
Run the
docker loginin your terminal session to log in to the Vultr Container Registry. Replaceexampleregistry,example-user, andregistry-keywith your actual details.console$ docker login https://sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry -u example-user -p registry-key
Your output should be similar to the one below when successful:
Login SucceededTag the
crccheck/hello-worldDocker image with your desired Vultr Container Registry repository name.console$ docker tag crccheck/hello-world:latest sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry/crccheck/hello-world:latest
List all Docker images and verify that the new tagged image is available.
console$ docker images
Output:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE crccheck/hello-world latest 24349d78cb62 2 years ago 1.24MB sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry/crccheck/hello-world latest 24349d78cb62 2 years ago 1.24MBPush the tagged Docker image to your Vultr Container Registry.
console$ docker push sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry/crccheck/hello-world:latest
Your output should be similar to the one below.
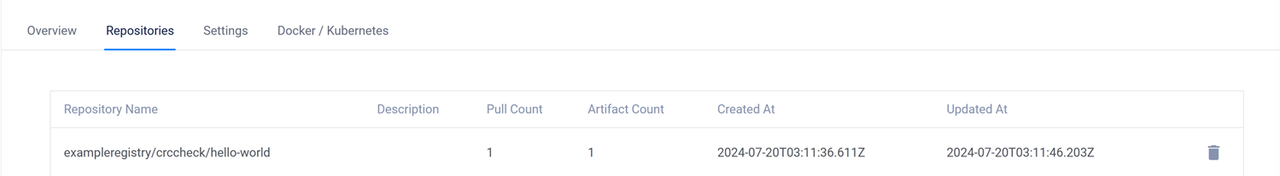
The push refers to repository [sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry/crccheck/hello-world] e35bd73d1b9a: Pushed d94c78be1352: Pushed latest: digest: sha256:0404ca69b522f8629d7d4e9034a7afe0300b713354e8bf12ec9657581cf59400 size: 734Access your Vultr Container Registry's management page, navigate to the Repositories tab and verify that the new Docker image repository is available.
Deploy a new container using your Vultr Container Registry Docker image.
console$ docker run -d --name web-test-vcr -p 80:8000 sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry/crccheck/hello-world:latest
List all active Docker containers running on your server.
console$ docker ps
Verify that the
web-test-vcrcontainer is running similar to the following output.CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 74609506c374 sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry/crccheck/hello-world:latest "/bin/sh -c 'echo \"h…" 6 seconds ago Up 6 seconds (health: starting) 0.0.0.0:80->8000/tcp, :::80->8000/tcp web-test-vcr
Conclusion
You have installed Docker on Rocky Linux 9 and deployed containerized applications on your server. Docker supports multiple container image sources you can use to run containerized applications on your server. For more information and Docker CLI options, visit the Docker reference documentation.