Introduction
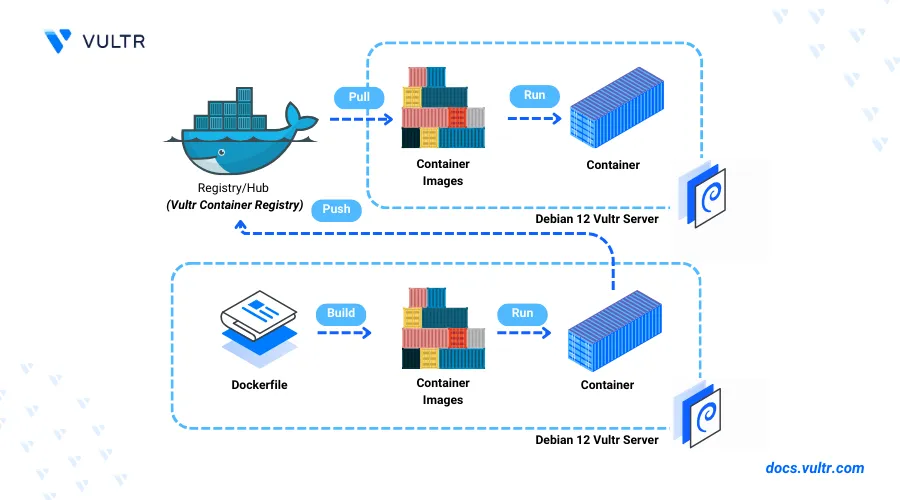
Docker is an open-source platform that enables you to build, package, and deploy applications to multiple platforms or environments using containers. Containers include the necessary dependencies, libraries, code, and runtime that enable your applications to run consistently in multiple environments.
This article explains how to install Docker on Debian 12 and run containerized applications on your server. You will deploy container images and integrate a container registry such as the Vultr Container Registry to store your container images.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- Deploy a Debian 12 instance on Vultr.
- Access to the server using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
- Create a Vultr Container Registry to store your Docker images.
Install Docker
Docker is available in the default package repositories on Debian 12, but the available package versions may not be the latest. Follow the steps below to add the official Docker repository to your Debian package sources and install the latest Docker version on your server.
Update the server's package index.
console$ sudo apt update
Install the necessary dependency packages on your server.
console$ sudo apt install ca-certificates curl
Add the Docker GPG key to your server's keyrings.
console$ sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/debian/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
Add the latest Docker repository information to your APT sources list.
console$ echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/debian $(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
Update the server's package index to apply the new repository changes.
console$ sudo apt update
Install Docker and all necessary add-on packages such as
containerd.ioconsole$ sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io -y
View the installed Docker version on your server.
console$ docker --version
Your output should be similar to the one below.
Docker version 27.0.3, build 7d4bcd8
Manage the Docker System Service
Docker uses the docker system service to manage the daemon runtime and processes on your server. Follow the steps below to manage the Docker system service, enable it to start at system boot, and add your non-root user to the docker group to run CLI commands without sudo privileges.
Enable the Docker service to automatically at system boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable docker
Output:
Synchronizing state of docker.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install. Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable dockerView the Docker service status and verify that it's running on your server.
console$ sudo systemctl status docker
Output:
● docker.service - Docker Application Container Engine Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/docker.service; enable> Active: active (running) since Mon 2024-07-01 18:39:27 UTC> TriggeredBy: ● docker.socket Docs: https://docs.docker.com Main PID: 4050 (dockerd) Tasks: 7 Memory: 32.9M CPU: 483ms CGroup: /system.slice/docker.service └─4050 /usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --containerd=/run>Stop the Docker service.
console$ sudo systemctl stop docker
Output:
Warning: Stopping docker.service, but it can still be activated by: docker.socketRestart the Docker service.
console$ sudo systemctl start docker
Add your non-root user to the
Dockergroup to run Docker CLI commands without sudo privileges. Replacelinuxuserwith your actual username.console$ sudo usermod -aG docker linuxuser
Enable the new user group changes in your active session.
console$ newgrp docker
Deploy Containerized Applications using Docker
Docker runs applications using container images on your server. Follow the steps below to use Docker CLI and pull a sample hello-world container image from the Docker Hub registry to deploy on your server.
Pull the
hello-worldcontainer image from Docker Hub.console$ docker pull hello-world
Output:
Using default tag: latest latest: Pulling from library/hello-world c1ec31eb5944: Pull completeView all Docker images on your server and verify that the
hello-worldimage is available.console$ docker images
Output:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest d2c94e258dcb 14 months ago 13.3kBDeploy a new containerized application using the
hello-worldimage.console$ sudo docker run hello-world
Output:
Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.List all Docker processes and verify that your
hello-worldcontainer runs, but exits.console$ sudo docker ps -a
Output:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 4f979e715721 hello-world "/hello" About a minute ago Exited (0) About a minute ago festive_curranRun the following command to stop a running container using its ID. For example,
4f979e715721.console$ sudo docker stop 4f979e715721
Use the
rmoption to delete a container.console$ sudo docker rm 4f979e715721
Login to a Container Registry
A container registry enables the storage, management, and shipping of container images to multiple environments depending on your needs. Docker integrates with registries such as the Vultr Container Registry to build, store, and deploy container images on your server. Follow the steps below to log in and use your Vultr Container Registry with Docker.
Open your Vultr Container Registry's management page using the Vultr Customer Portal to access your registry credentials.
Log in to your Vultr Container Registry using the
docker logincommand. Replace the following example values with your actual registry credentials.console$ sudo docker login https://ewr.vultrcr.com/examplereg -u example-user -p example-vcr-api
Your output should be similar to the one below when successful.
WARNING! Using --password via the CLI is insecure. Use --password-stdin. WARNING! Your password will be stored unencrypted in /home/hum/.docker/config.json. Configure a credential helper to remove this warning. See https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/login/#credential-stores Login SucceededList all Docker images available on your server.
console$ docker images
Output:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest d2c94e258dcb 14 months ago 13.3kBThe
hello-worldimage is available on your server based on the above output, use the image to tag and verify push access to your Vultr Container Registry.Tag the local
hello-worldDocker image with your desired Vultr Container Registry tag. For example,ewr.vultrcr.com/examplereg/hello-world:latest.console$ docker tag hello-world:latest ewr.vultrcr.com/examplereg/hello-world:latest
List all Docker images available on your server.
console$ docker images
Verify that the new tagged image is available similar to the following output.
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest d2c94e258dcb 14 months ago 13.3kB ewr.vultrcr.com/examplereg/hello-world latest d2c94e258dcb 14 months ago 13.3kBPush the tagged image to your Vultr Container Registry.
console$ docker push ewr.vultrcr.com/examplereg/hello-world
Your output should be similar to the one below when successful.
Using default tag: latest The push refers to repository [ewr.vultrcr.com/examplereg/hello-world] ac28800ec8bb: Pushed latest: digest: sha256:d37ada95d47ad12224c205a938129df7a3e52345828b4fa27b03a98825d1e2e7 size: 524Access your Vultr Container Registry's management page, navigate to the Repositories tab and verify that the new Docker image repository is available.
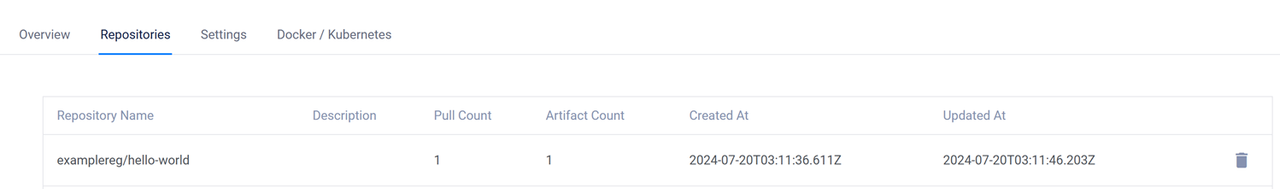
Deploy a new container application using the Docker image from your Vultr Container Registry.
console$ docker run ewr.vultrcr.com/testreg/hello-world
Output:
Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
Conclusion
You have installed Docker on your Debian 12 server and deployed a sample containerized application. Docker enables you to build and deploy multiple applications, bind specific host ports to your container ports, and securely access the containerized applications. For more information and configuration options, visit the official Docker documentation.