iRedMail is a free, open-source mail server solution that enables the deployment of a fully functional email system. It integrates components for mail transfer, retrieval, storage, spam filtering, virus scanning, and secure communication, along with a web interface for managing email accounts, domains, and server settings.
This article explains how to install the iRedMail server on Ubuntu 22.04.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
Have an Ubuntu 22.04 server with at least
4 GBRAM.Set up at least
2domain DNS records pointing to the instance's IP address. For example,mail.example.comandexample.com.Access the server using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Open a new support ticket and request the SMTP port
25to be unblocked on your instance.
Install iRedMail
Follow the steps below to configure the hostname for your server, install iRedMail, and configure it.
Open the terminal and run the following command to set the hostname.
console$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname mail.example.com
Open the
/etc/hostsfile.console$ sudo nano /etc/hosts
Update the
127.0.1.1and127.0.0.1entries to include your mail domain to enable correct name resolution on your server.ini# Part of file: /etc/hosts 127.0.1.1 mail.example.com mail
Verify the active server hostname.
console$ hostname -f
Output:
mail.example.comDownload the latest iRedMail release file.
console$ wget https://github.com/iredmail/iRedMail/archive/refs/tags/1.7.3.tar.gz
The above command downloads the iRedMail version
1.7.3release file. Visit the official download page to verify the latest version to install on your server.Extract files from the
tararchive.console$ tar -xvf 1.7.3.tar.gz
Switch to the extracted iRedMail files directory.
console$ cd iRedMail-1.7.3
Update the server package index before running the main script.
console$ sudo apt update
Run the iRedMail installation script.
console$ sudo bash iRedMail.sh
Press Enter when prompted to start the installation wizard. Then, reply to each of the following prompts to install iRedMail on your server.
Default mail storage path: Press Enter to use the default
/var/vmaildirectory.Preferred web server: Keep
Nginxselected and press Enter to enable the web server.Choose backend for mail accounts: Press the Down arrow key and press Space to select MariaDB as the database backend.
LDAP suffix: Press Enter to use the default domain format for the directory tree.
MySQL administrator password: Enter a strong password for the
rootdatabase user.Your first domain name: Enter your domain to use for sending and receiving emails (e.g.,
example.com).Mail domain administrator password: Enter a strong password for the
postmastermail administrator account.Optional components: Select optional components to install and press Enter to apply changes.
Enter Y when prompted to continue and save your iRedMail installation options.
< Question > Continue? [y|N]Enter Y to use firewall offered by iRedMail and allow SSH connections on the default port
22.< Question > Would you like to use firewall rules provided by iRedMail? < Question > File: /etc/nftables.conf, with SSHD ports: 22. [Y|n]Enter Y to allow SSH connections on the default port
22through the firewall.< Question > Restart firewall now (with ssh ports: 22)? [y|N]
Reboot the server to apply the iRedMail installation changes.
console$ sudo systemctl reboot
iRedMail Post Installation
iRedMail requires valid MX, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records for your mail domain to send and receive emails. Log in to your domain registrar and configure the following DNS records to enable email functionality on your iRedMail server.
Create a new MX (Mail Exchange) record with the following details.
- Type:
MX - Name:
@ - Priority:
10 - Value:
mail.example.com
- Type:
Create a new SPF (Sender Policy Framework) record with the following details. Replace
192.0.2.1with your actual server IP address.- Type:
TXT - Name:
@ - Value:
"v=spf1 a mx ip4:192.0.2.1 -all"
- Type:
Create a new DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) record:
Run the following command in your server's terminal to view your domain's DKIM records generated by the
amavisdiRedMail utility.console$ sudo amavisd-new showkeys
Your output should be similar to the one below.
; key#1 2048 bits, s=dkim, d=example.com, /var/lib/dkim/example.com.pem dkim._domainkey.example.com. 3600 TXT ( "v=DKIM1; p=" "MIIBIjANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQEFAAOCAQ8AMIIBCgKCAQEAw+56AfGG9pAdkFNiw5nt" "6NifxPCB+2offAblD8ZIXpTg3Z9vT8dy8glDGL/BBdlzfAnX6FxQz1NuKstDLFZc" "MfNo3TiKvEAjrrSet7fdfI79inqeQyKkGqaRn+vn2VK/qnD4hZMESLk2V4Ovpb+H" "47q1AjybY7QDDHp2cIQFJ8oAkUFColAwEHSuW6PpJkQI9A9NfBHFrSQRZG33EYHA" "hAf0sLclA5u+ahaPTkxK5cL76w1kRp668L7qi+SI6fWZpzNnlFDrmfwdEtywvSvS" "4igHoHhncGGqo6bjTlI2cV92aBZ1e2n84MGp1JqjBhQWZjsFDr4tOxrKlE8F4Vhe" "FQIDAQAB")Copy all contents in bracelets
()to use as your DKIM record's data.Create a new
TXTrecord using the generated DKIM information with the following details.- Type:
TXT - Name:
dkim._domainkey - Value:
"<iredmail-dkim-data>"
- Type:
Test your DKIM keys configuration using
amavisdto verify the DNS record.console$ sudo amavisd-new testkeys
Output:
TESTING#1 example.com: dkim._domainkey.example.com => pass
Create a new DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) record with the following details to send aggregate reports to your administrative email
dmarc-reports@example.com.- Type:
TXT - Name:
_dmarc - Value:
"v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@example.com; pct=100"
- Type:
Configure iRedMail to Use Trusted Let's Encrypt SSL Certificates
Follow the steps below to configure iRedMail to use trusted Let's Encrypt SSL certificates on your server.
Install the Certbot Let's Encrypt client tool.
console$ sudo snap install certbot --classic
Generate a new Let's Encrypt SSL certificate for your mail domain. Replace
mail.example.comandhello@example.comwith your actual details.console$ sudo certbot certonly --webroot -w /opt/www/well_known -d mail.example.com -m hello@example.com --agree-tos
Open the default iRedMail virtual host configuration for Nginx.
console$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/00-default-ssl.conf
Add the following directives to the file after
server_name _;. Replace/etc/letsencrypt/live/mail.example.com/with your actual Let's Encrypt directory.inissl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/mail.example.com/fullchain.pem; ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/mail.example.com/privkey.pem;
Save and close the file.
The above configuration directives enable Nginx to use your domain's trusted Let's Encrypt certificates to deliver requests on your server.
Open the
/etc/nginx/templates/ssl.tmplfile.console$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/templates/ssl.tmpl
Find the following configuration directives.
inissl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/iRedMail.crt; ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/iRedMail.key;
Replace the SSL certificate and private key paths with your actual Let's Encrypt details.
inissl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/mail.example.com/fullchain.pem; ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/mail.example.com/privkey.pem;
Save and close the file.
Open the main
Postfixconfiguration file/etc/postfix/main.cf.console$ sudo nano /etc/postfix/main.cf
Find the following TLS settings section.
ini# SSL key, certificate, CA # smtpd_tls_key_file = /etc/ssl/private/iRedMail.key smtpd_tls_cert_file = /etc/ssl/certs/iRedMail.crt smtpd_tls_CAfile = /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt smtpd_tls_CApath = /etc/ssl/certs
Replace the
smtpd_tls_key_fileandsmtpd_tls_cert_filewith your actual Let's Encrypt certificate details.inismtpd_tls_key_file = /etc/letsencrypt/live/mail.example.com/privkey.pem smtpd_tls_cert_file = /etc/letsencrypt/live/mail.example.com/fullchain.pem #smtpd_tls_CAfile = /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt #smtpd_tls_CApath = /etc/ssl/certs
Open the Dovecot configuration file
/etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf.console$ sudo nano /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf
Find the following SSL configuration section.
inissl_cert = </etc/ssl/certs/iRedMail.crt ssl_key = </etc/ssl/private/iRedMail.key
Replace the
ssl_certandssl_keyvalues with your actual Let's Encrypt details.inissl_cert = </etc/letsencrypt/live/mail.example.com/fullchain.pem ssl_key = </etc/letsencrypt/live/mail.example.com/privkey.pem
Save and close the file.
Restart Nginx, Postfix and Dovecot to apply your configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart nginx postfix dovecot
Test the Mail Server
Follow the steps below to test the iRedMail server functionalities.
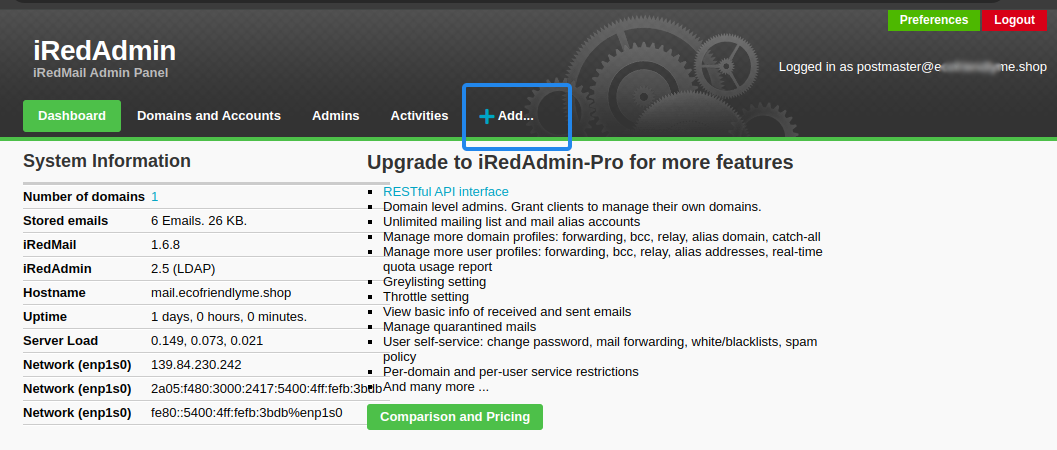
Access iRedMail Administration Console (iRedAdmin) using your domain in a web browser such as Chrome.
https://mail.example.com/iredadminLog in to the iRedMail web administration dashboard using the
postmasteradministrator email and password you set during the installation process.Click the Add drop-down and select User from the list to set up a new email account.
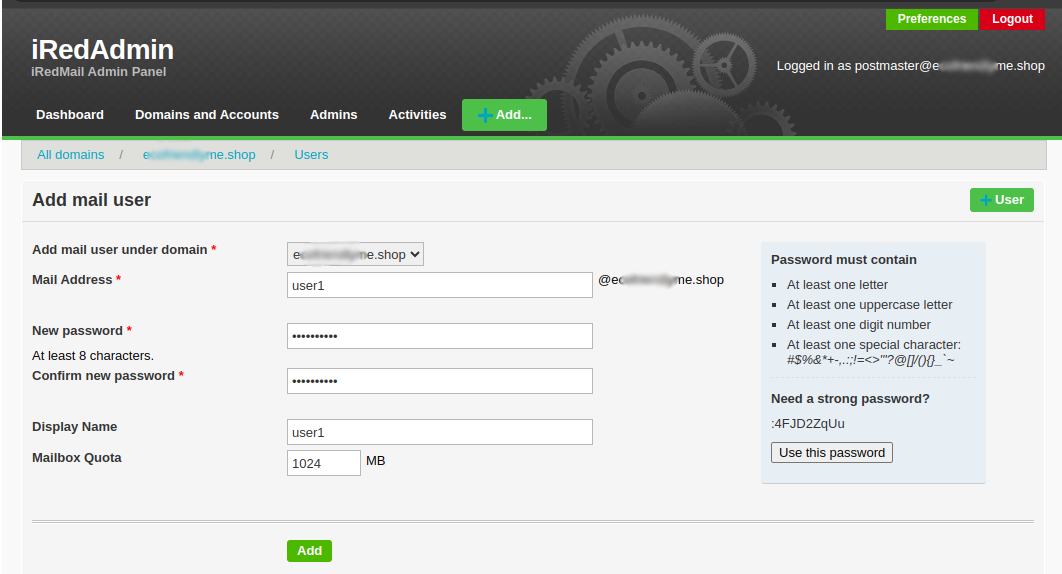
Enter your desired email information and click Add to create the new user.
Add the
/mailpath to your domain in new web browser window to access the Roundcube Webmail interface and manage your email accounts.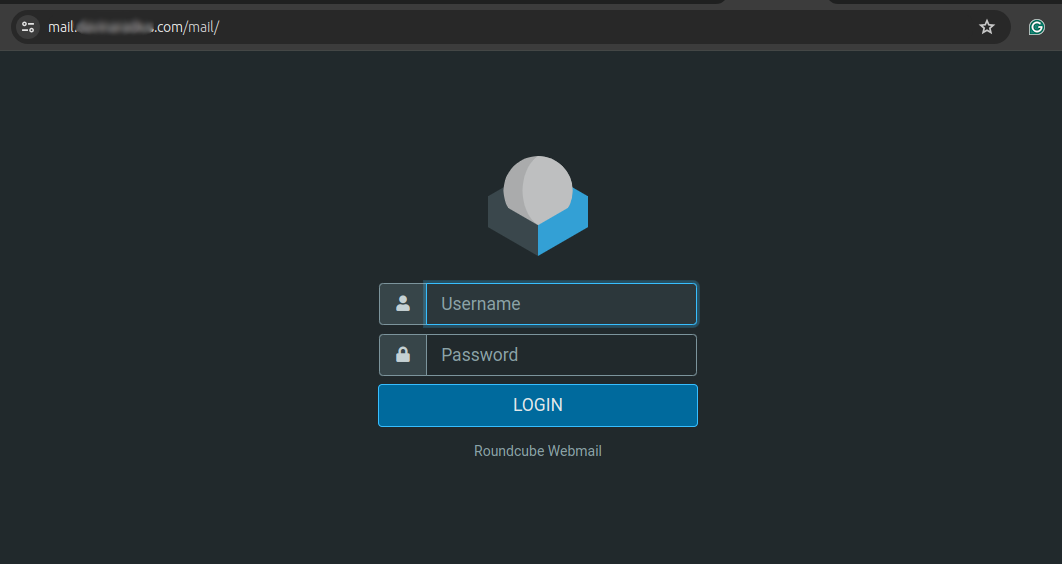
Enter your Postmaster user and password you set to log in to its web mail interface.
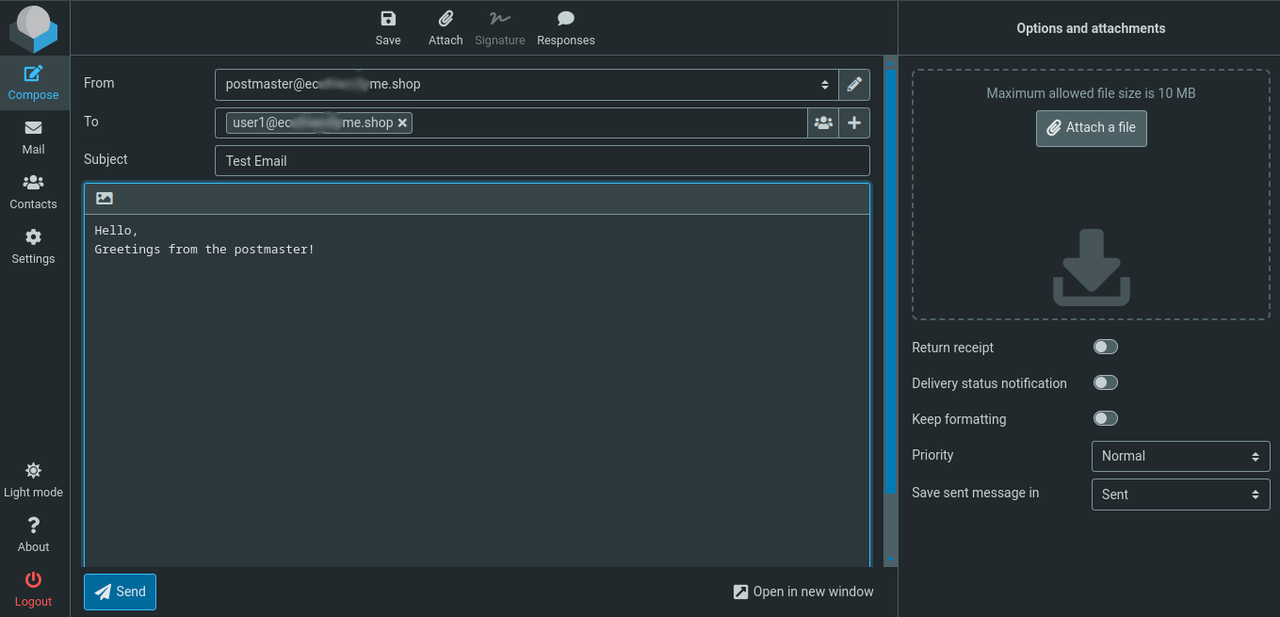
Click Compose to create a new test email to your new user's email. For example,
user1@example.com.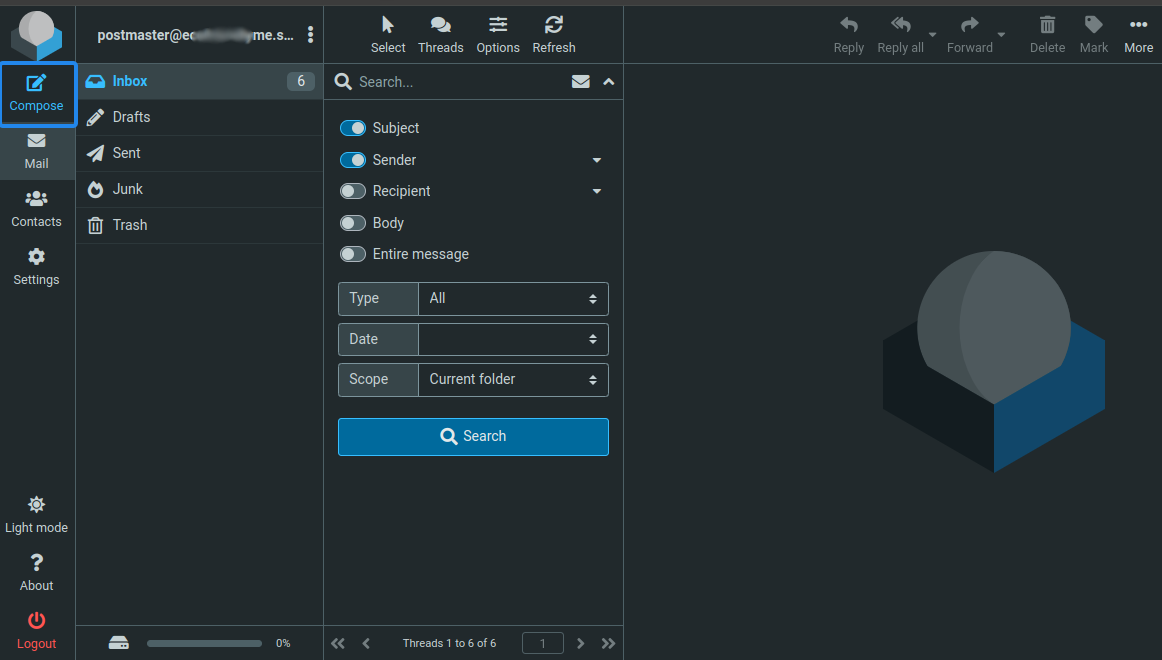
Click Send to send the test email and verify that it's successful.
Click Logout in the bottom left to exit the Roundcube Webmail interface.
Log in to Roundcube using the new email account you created earlier to access emails sent from the
postmasteraccount.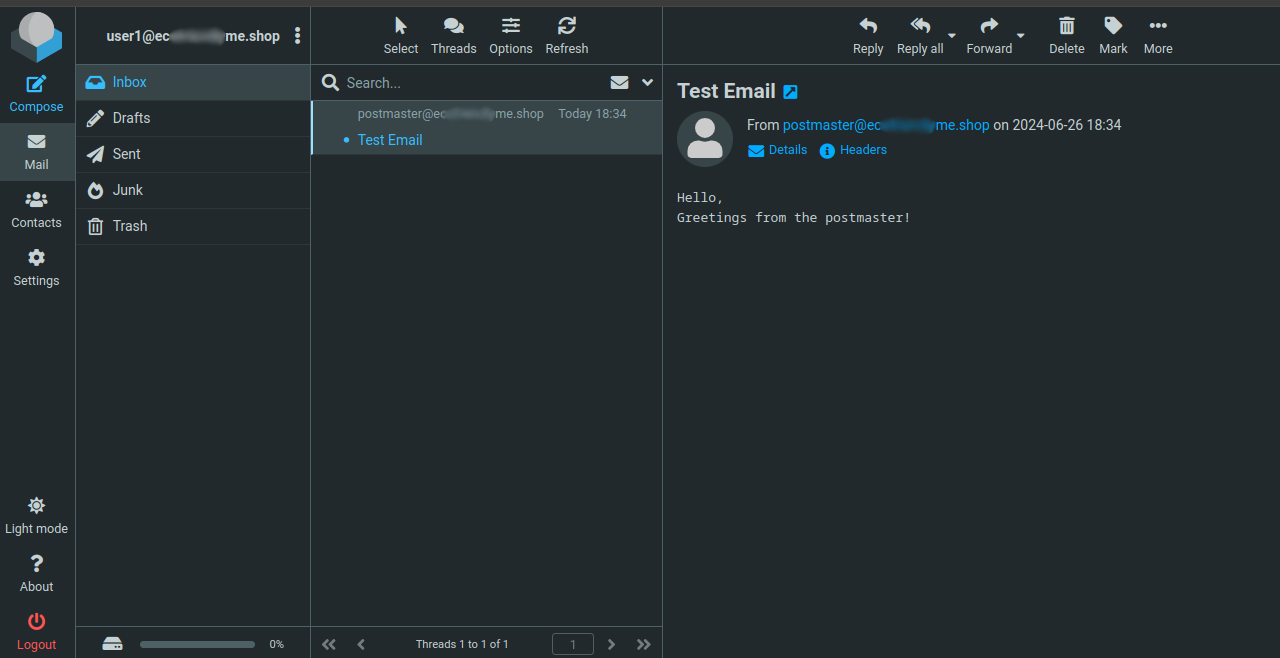
Click the
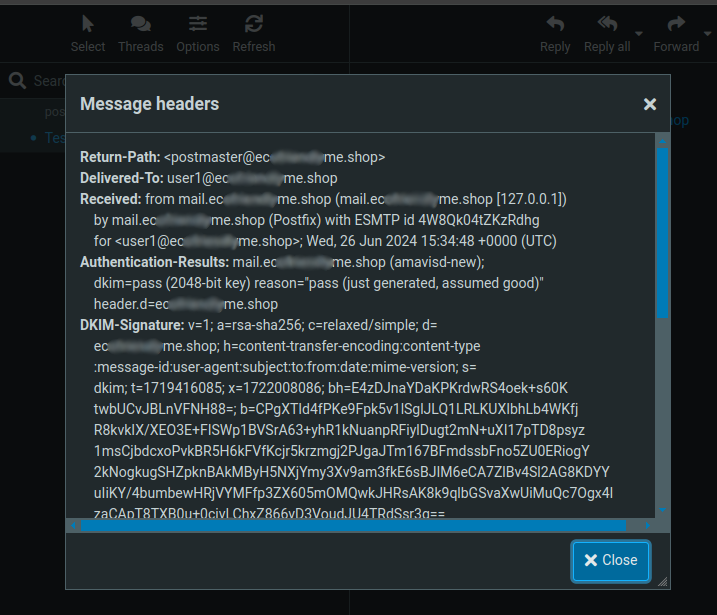
headerlink within Headers.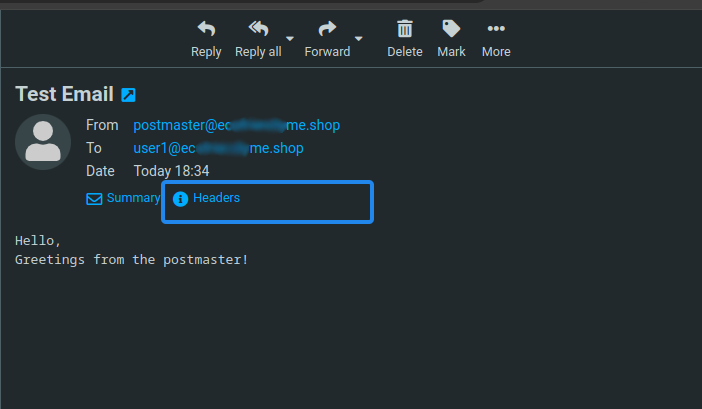
Verify your domain's DKIM values sent to all mail domains.
Conclusion
In this article, you installed iRedMail on an Ubuntu 22.04 server and secured email access using valid SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records. iRedMail supports multiple email domains, allowing you to set up a secure mail server for sending and receiving emails. For more information, visit the iRedMail documentation.