
Jenkins is an open-source continuous-integration (CI) and continuous-delivery (CD) server used for project development, deployment, and automation. Software developers use it to build, test, and deploy their software. It is written in Java and provides hundreds of plugins to automate testing and changes in a larger code base.
This guide shows you how to set up Jenkins on Vultr Kubernetes Engine, which provides many benefits over standalone server-based deployment. Kubernetes-based deployment is a very cost-effective solution and also decreases the time needed for development.
Prerequisites
- Deploy a Vultr Ubuntu 20.04 instance to use as a management workstation.
- Deploy a Kubernetes cluster at Vultr with at least three or more nodes with 2GB RAM and 2 CPUs.
- Install kubectl on Vultr Ubuntu management workstation.
You'll perform the rest of the steps in this guide from your management workstation.
Verify Kubernetes Cluster
Before starting, verify the Vultr Kubernetes Cluster using the following command:
kubectl cluster-infoYou will see the Cluster information in the following output:
Kubernetes control plane is running at https://e4737bcd-3971-4624-b896-0181aae56bae.vultr-k8s.com:6443
CoreDNS is running at https://e4737bcd-3971-4624-b896-0181aae56bae.vultr-k8s.com:6443/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns:dns/proxyTo check the active status of all Cluster nodes, run the following command:
kubectl get nodesYou should see that all nodes are in ready status:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
jenkins-cluster-136e69da18fb Ready <none> 3m21s v1.25.4
jenkins-cluster-97b1dd155b22 Ready <none> 3m21s v1.25.4
jenkins-cluster-a329dcb28ac7 Ready <none> 3m21s v1.25.4Install Jenkins on Kubernetes
First, create the Jenkins namespace:
# kubectl create namespace jenkins-namespaceOutput.
namespace/jenkins-namespace createdNext, create a
serviceAccount.yamlfile.# nano serviceAccount.yamlAdd the following configurations to create a service account called
jenkins-accountand binds theclusterRoleto the service account.--- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: jenkins-account rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["*"] verbs: ["*"] --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: jenkins-account namespace: jenkins-namespace --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: jenkins-account roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: jenkins-account subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: jenkins-account namespace: jenkins-namespaceApply the above configuration to Kubernetes Cluster.
# kubectl apply -f serviceAccount.yamlOutput.
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/jenkins-account created serviceaccount/jenkins-account created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/jenkins-account createdCreate a volume configuration file.
# nano volume.yamlAdd the following configuration for persistent volume.
kind: StorageClass apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: jenkins-storage provisioner: kubernetes.io/no-provisioner volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: jenkins-pv-volume labels: type: local spec: storageClassName: jenkins-storage claimRef: name: jenkins-pv-claim namespace: jenkins-namespace capacity: storage: 10Gi accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce local: path: /opt nodeAffinity: required: nodeSelectorTerms: - matchExpressions: - key: kubernetes.io/hostname operator: In values: - jenkins-cluster-136e69da18fb --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: jenkins-pv-claim namespace: jenkins-namespace spec: storageClassName: jenkins-storage accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 3GiNote: Replace the
jenkins-cluster-136e69da18fbwith any of your cluster nodes.If you need to know the hostname of your worker node, run the following command.
# kubectl get nodesThe above configuration will create a
PersistentVolumevolume in a cluster node inside the/optdirectory. You will also need to properly define the worker node name for the Jenkins pod to get scheduled in the specific node.Create a persistent volume on the Kubernetes cluster using the
kubectlcommand.# kubectl create -f volume.yamlOutput.
storageclass.storage.k8s.io/jenkins-storage created persistentvolume/jenkins-pv-volume created persistentvolumeclaim/jenkins-pv-claim createdCreate a
deployment.yamlfile.# nano deployment.yamlAdd the following manifest configuration.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: jenkins namespace: jenkins-namespace spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: jenkins-server template: metadata: labels: app: jenkins-server spec: securityContext: fsGroup: 1000 runAsUser: 1000 serviceAccountName: jenkins-account containers: - name: jenkins image: jenkins/jenkins:lts resources: limits: memory: "2Gi" cpu: "1000m" requests: memory: "500Mi" cpu: "500m" ports: - name: httpport containerPort: 8080 - name: jnlpport containerPort: 50000 livenessProbe: httpGet: path: "/login" port: 8080 initialDelaySeconds: 90 periodSeconds: 10 timeoutSeconds: 5 failureThreshold: 5 readinessProbe: httpGet: path: "/login" port: 8080 initialDelaySeconds: 60 periodSeconds: 10 timeoutSeconds: 5 failureThreshold: 3 volumeMounts: - name: jenkins-data mountPath: /var/jenkins_home volumes: - name: jenkins-data persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: jenkins-pv-claimThe above configuration file will:
- Creates a Jenkins deployment using the latest Jenkins image and opens ports
8080and50000to accept connections from Jenkins workers. - Mounts the persistent volume on the
/var/jenkins_homedirectory to hold Jenkins data. - Define
liveness probesto check the container's health status. - Define
readiness probesto know when a container can start accepting traffic.
- Creates a Jenkins deployment using the latest Jenkins image and opens ports
Apply the above deployment to the Kubernetes cluster.
# kubectl apply -f deployment.yamlOutput.
deployment.apps/jenkins createdWait for some time to pull the Jenkins image and get the Jenkins pod running.
Verify the status of the Jenkins pod.
# kubectl get deployments -n jenkins-namespaceOutput.
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE jenkins 1/1 1 1 94sGet a detail information about Jenkins deployment.
# kubectl describe deployments --namespace=jenkins-namespaceOutput.
Name: jenkins Namespace: jenkins-namespace CreationTimestamp: Tue, 22 Nov 2022 21:03:42 +0530 Labels: <none> Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 1 Selector: app=jenkins-server Replicas: 1 desired | 1 updated | 1 total | 1 available | 0 unavailable StrategyType: RollingUpdate MinReadySeconds: 0 RollingUpdateStrategy: 25% max unavailable, 25% max surge Pod Template: Labels: app=jenkins-server Service Account: jenkins-account Containers: jenkins: Image: jenkins/jenkins:lts Ports: 8080/TCP, 50000/TCP Host Ports: 0/TCP, 0/TCP Limits: cpu: 1 memory: 2Gi Requests: cpu: 500m memory: 500Mi Liveness: http-get http://:8080/login delay=90s timeout=5s period=10s #success=1 #failure=5 Readiness: http-get http://:8080/login delay=60s timeout=5s period=10s #success=1 #failure=3 Environment: <none> Mounts: /var/jenkins_home from jenkins-data (rw) Volumes: jenkins-data: Type: PersistentVolumeClaim (a reference to a PersistentVolumeClaim in the same namespace) ClaimName: jenkins-pv-claim ReadOnly: false Conditions: Type Status Reason ---- ------ ------ Available True MinimumReplicasAvailable Progressing True NewReplicaSetAvailable OldReplicaSets: <none> NewReplicaSet: jenkins-7b95fb694 (1/1 replicas created) Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Normal ScalingReplicaSet 19m deployment-controller Scaled up replica set jenkins-7b95fb694 to 1
Create Kubernetes Service for External Access
At this point, Jenkins is successfully deployed and running on the Kubernetes cluster. However, you can not access Jenkins from the remote machine. In this case, you will need to create a service and bind it to the Jenkins deployment.
First, create a
service.yamlfile using the following command:# nano service.yamlAdd the following configurations to expose port
8080of the Jenkins pod to port32000.apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: jenkins-service namespace: jenkins-namespace annotations: prometheus.io/scrape: 'true' prometheus.io/path: / prometheus.io/port: '8080' spec: selector: app: jenkins-server type: NodePort ports: - port: 8080 targetPort: 8080 nodePort: 32000Next, deploy the service configuration to the Jenkins deployment.
# kubectl apply -f service.yamlOutput.
service/jenkins-service createdVerify the status of the Jenkins service.
# kubectl get services --namespace jenkins-namespaceOutput.
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE jenkins-service NodePort 10.103.86.99 <none> 8080:32000/TCP 6s
Access Jenkins Web Interface
At this point, Jenkins is installed and listens on port 32000 for external access. Now, you will need to retrieve the IP address of the cluster node to access the Jenkins web interface.
First, get a node IP address using the
kubectlcommand.# kubectl get nodes -o wideYou will get the external IP of all nodes in the following output.
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL- VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME jenkins-cluster-7e8eba45f3a6 Ready <none> 23m v1.25.4 10.46.96.6 65.20.79.223 Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster) 4.19.0-22-amd64 containerd://1.6.9 jenkins-cluster-a45a12e27a63 Ready <none> 23m v1.25.4 10.46.96.5 65.20.79.2 Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster) 4.19.0-22-amd64 containerd://1.6.9 jenkins-cluster-cfacc64361f5 Ready <none> 23m v1.25.4 10.46.96.4 65.20.74.173 Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster) 4.19.0-22-amd64 containerd://1.6.9Next, open your web browser and access Jenkins using the URL
http://node-external-ip:32000. You will be asked to provide the initial Admin password.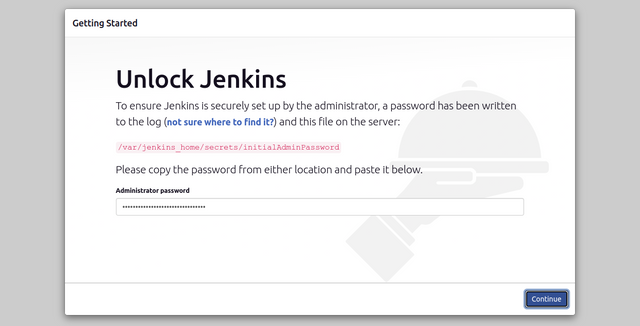
Get Jenkins pod details using the following command.
# kubectl get pods --namespace=jenkins-namespaceOutput.
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE jenkins-7b95fb694-5xqnp 1/1 Running 0 20mCheck the Jenkins pod logs to retrieve the Jenkins Admin password.
# kubectl logs jenkins-7b95fb694-5xqnp --namespace=jenkins-namespaceOutput.
************************************************************* Jenkins initial setup is required. An admin user has been created and a password generated. Please use the following password to proceed to installation: a1f057cba5f6440f863b6e5a57d880fa This may also be found at: /var/jenkins_home/secrets/initialAdminPassword *************************************************************Copy the password from the above output and enter it on the Jenkins initial Admin password screen to proceed with the Jenkins installation.
Conclusion
This guide shows you how to install and configure Jenkins on Vultr Kubernetes Engine. Jenkins is a core component of CI/CD pipelines. It helps you perform very complex operations and increase productivity. For more information, check out the official Jenkins documentation.
No comments yet.