SonarQube is an open-source platform used to continuously inspect code quality and manage code quality. It detects bugs, vulnerabilities, and tracks code quality through static analysis with detailed reports. SonarQube supports multiple programming languages and improves code quality, maintainability, and security by offering actionable insights with two editions, community and enterprise.
This article explains how to Install SonarQube on Ubuntu 24.04. You will install SonarQube and use it to inspect code quality with example projects on your workstation.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, you need to:
- Have access to an Ubuntu 24.04 instance as a non-root sudo user.
Set Up a PostgreSQL Database for SonarQube
SonarQube requires a PostgreSQL database to store data. PostgreSQL is available in the default package repositories on Ubuntu. Follow the steps below to install PostgreSQL and create a new database to use with SonarQube.
Install the PostgreSQL if it's not installed on your Ubuntu 24.04 workstation.
console$ sudo apt install -y postgresql-common postgresql -y
Enable the PostgreSQL database server to automatically start at boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable postgresql
Output:
Synchronizing state of postgresql.service with SysV service script with /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install. Executing: /usr/lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable postgresqlStart the PostgreSQL database server.
console$ sudo systemctl start postgresql
Log in to the PostgreSQL database server as the
postgresuser.console$ sudo -u postgres psql
Create a new
sonaruserPostgreSQL role with a strong password to use with SonarQube. Replaceyour_passwordwith your desired password.psqlpostgres=# CREATE ROLE sonaruser WITH LOGIN ENCRYPTED PASSWORD 'your_password';
Create a new
sonarqubedatabase.psqlpostgres=# CREATE DATABASE sonarqube;
Grant the
sonaruserrole full privileges to thesonarqubedatabase.psqlpostgres=# GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON DATABASE sonarqube TO sonaruser;
Switch to the
sonarqubedatabase.psqlpostgres=# \c sonarqube
Output:
You are now connected to database "sonarqube" as user "postgres".Grant the
sonaruserrole full privileges to the public schema.psqlpostgres=# GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON SCHEMA public TO sonaruser;
Exit the PostgreSQL database console.
psqlpostgres=# \q
Install SonarQube
SonarQube is not available in the default package repositories on Ubuntu 24.04 and requires OpenJDK 17 to run. Follow the steps below to download the latest SonarQube release file and install SonarQube.
Update the server's APT package index.
console$ sudo apt update
Install OpenJDK 17.
console$ sudo apt install openjdk-17-jdk -y
Install Unzip to extract files from the SonarQube archive.
console$ sudo apt install unzip
Verify the installed
javaversion.console$ java -version
Your output should be similar to the one below:
openjdk version "17.0.14" 2025-01-21 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 17.0.14+7-Ubuntu-124.04) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 17.0.14+7-Ubuntu-124.04, mixed mode, sharing)Visit the SonarQube releases page and verify the latest version to download. For example,
sonarqube-25.2.0.102705.zip.Download the latest SonarQube archive.
console$ sudo wget https://binaries.sonarsource.com/Distribution/sonarqube/sonarqube-25.2.0.102705.zip
Extract files from the downloaded archive using Unzip.
console$ unzip sonarqube-25.2.0.102705.zip
Move the extracted files to a systemwide directory such as
/opt.console$ sudo mv sonarqube-25.2.0.102705/ /opt/sonarqube
Create a dedicated
sonarqubesystem user without login privileges and a home directory.console$ sudo adduser --system --no-create-home --group --disabled-login sonarqube
Grant the
sonarqubeuser full privileges to the/opt/sonarqubedirectory.console$ sudo chown -R sonarqube:sonarqube /opt/sonarqube
Install SonarScanner CLI
SonarQube uses code scanners depending on the target programming language to scan and analyze code quality. SonarScanner CLI is the default scanner if no specific scanner is specified on your system. Follow the steps below to install the SonarScanner CLI to analyze code on your workstation.
Visit the SonarScanner CLI page and verify the latest version to download. For example, run the following command to download the SonarScanner CLI version
7.0.1console$ wget https://binaries.sonarsource.com/Distribution/sonar-scanner-cli/sonar-scanner-cli-7.0.1.4817-linux-x64.zip
Extract files from the archive depending on the downloaded version.
console$ unzip sonar-scanner-cli-7.0.1.4817-linux-x64.zip
Move the extracted directory to
/opt/sonarscanner.console$ sudo mv sonar-scanner-7.0.1.4817-linux-x64/ /opt/sonarscanner
Open the
sonar-scanner.propertiesconfiguration file.console$ sudo nano /opt/sonarscanner/conf/sonar-scanner.properties
Find the following
sonar.host.urldirective and change the defaulthttps://mycompany.com/sonarqubevalue to127.0.0.1.ini... sonar.host.url=127.0.0.1 ...
Save and close the file.
The above Sonar Host directive specifies the SonarQube server URL to use while performing code scans.
Enable execute permissions on the
sonar-scannerbinary.console$ sudo chmod +x /opt/sonarscanner/bin/sonar-scanner
Link the
sonar-scannerbinary to the/usr/local/bindirectory to enable it as a system-wide command.console$ sudo ln -s /opt/sonarscanner/bin/sonar-scanner /usr/local/bin/sonar-scanner
View the installed SonarScanner version.
console$ sonar-scanner -v
Your output should be similar to the one below.
........ 13:33:31.946 INFO SonarScanner CLI 7.0.1.4817 13:33:31.950 INFO Java 17.0.13 Eclipse Adoptium (64-bit) 13:33:31.951 INFO Linux 6.8.0-51-generic amd64
Configure SonarQube
SonarQube requires specific configurations for optimal performance, including database connections, Java runtime options, system resource limits, and user permissions. Follow the steps below to configure SonarQube to run on your server.
Open the main
sonar.propertiesSonarqube configuration file.console$ sudo nano /opt/sonarqube/conf/sonar.properties
Add the following configurations at the end of the file. Replace
sonaruserandyour_passwordwith actual PostgreSQL database user details.inisonar.jdbc.username=sonaruser sonar.jdbc.password=your_password sonar.jdbc.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/sonarqube sonar.web.javaAdditionalOpts=-server sonar.web.host=0.0.0.0 sonar.web.port=9000
Save and close the file.
The above custom configuration directives enable SonarQube to access the PostgreSQL database, and listen for connections on the TCP port
9000from all network addresses0.0.0.0.Open the
sysctl.configconfiguration file to modify the system memory limits.console$ sudo nano /etc/sysctl.conf
Add the following directives at the end of the file.
inivm.max_map_count=524288 fs.file-max=131072
Save and close the file.
Within the above configuration:
vm.max_map_count=524288: Increases the number of memory maps Elasticsearch can use, allowing it to handle large datasets.fs.file-max=131072: Increases the maximum number of files Elasticsearch can open, allowing it to run efficiently.
SonarQube uses Elasticsearch to store indices in a memory-mapped file system. Adjusting the system limits for virtual memory mapping and file handling ensures better stability and performance for SonarQube.
Create a new
/etc/security/limits.d/99-sonarqube.conffile to create a resource limits configuration for SonarQube.console$ sudo nano /etc/security/limits.d/99-sonarqube.conf
Add the following directives to increase the file descriptor and process limits for SonarQube.
inisonarqube - nofile 131072 sonarqube - nproc 8192
Save and close the file.
Within the configuration:
nofile=131072: Increases the number of open file descriptors, allowing SonarQube to handle large workloads.nproc=8192: Raises the process limit to prevent failures under high concurrency.
Allow network connections to the SonarQube port
9000.console$ sudo ufw allow 9000/tcp
- Run the following command to install UFW and allow SSH connections if it's unavailable.
console$ sudo apt install ufw -y && sudo ufw allow 22/tcp
Reload UFW to apply the firewall configurations.
console$ sudo ufw reload
View the UFW status and verify that below are the only active firewall rules.
console$ sudo ufw status
Your output should be similar to the one below:
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- 22/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 9000/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 22/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 9000/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Set Up SonarQube as a System Service
Follow the steps below to set up a new system service for SonarQube to manage the application processes on your server.
Create a new
sonarqube.servicefile.console$ sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/sonarqube.service
Add the following configurations to the file.
ini[Unit] Description=SonarQube service After=syslog.target network.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/opt/sonarqube/bin/linux-x86-64/sonar.sh start ExecStop=/opt/sonarqube/bin/linux-x86-64/sonar.sh stop User=sonarqube Group=sonarqube PermissionsStartOnly=true Restart=always StandardOutput=syslog LimitNOFILE=131072 LimitNPROC=8192 TimeoutStartSec=5 SuccessExitStatus=143 [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file.
The above configuration creates a new SonarQube system service to monitor and manage the application processes.
Reload systemd to apply the service changes.
console$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
Enable SonarQube to start at boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable sonarqube
Start the SonarQube service.
console$ sudo systemctl start sonarqube
View the SonarQube service status and verify that it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status sonarqube
Your output should be similar to the one below:
● sonarqube.service - SonarQube service Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/sonarqube.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2024-12-26 14:12:47 WAT; 2h 54min ago Process: 1085 ExecStart=/opt/sonarqube/bin/linux-x86-64/sonar.sh start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 1108 (java)Restart the server to apply the SonarQube installation changes.
console$ sudo reboot now
Access SonarQube
SonarQube includes a graphical web-based interface for managing code quality, projects, issues, and security. Follow the steps below to access the SonarQube web interface, update the default administrator password and create a dedicated user for code scanning.
Access the SonarQube port
9000using your server IP or domain name.Log in to SonarQube with the following credentials when prompted.
- Username:
admin - Password:
admin
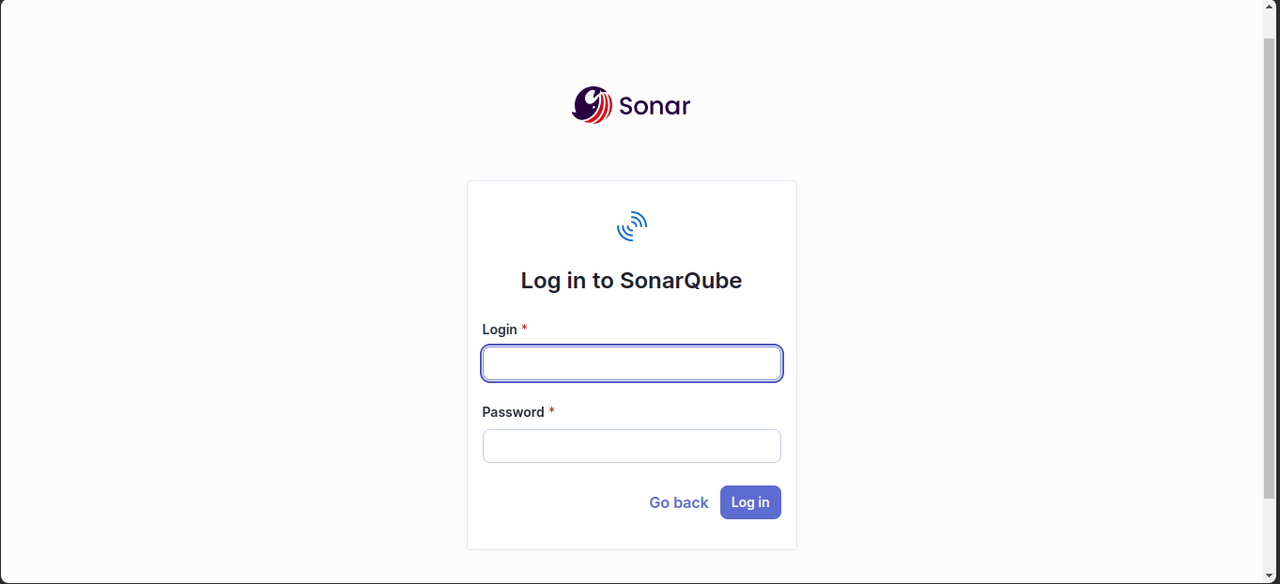
- Change the default administrator password when prompted.
- Username:
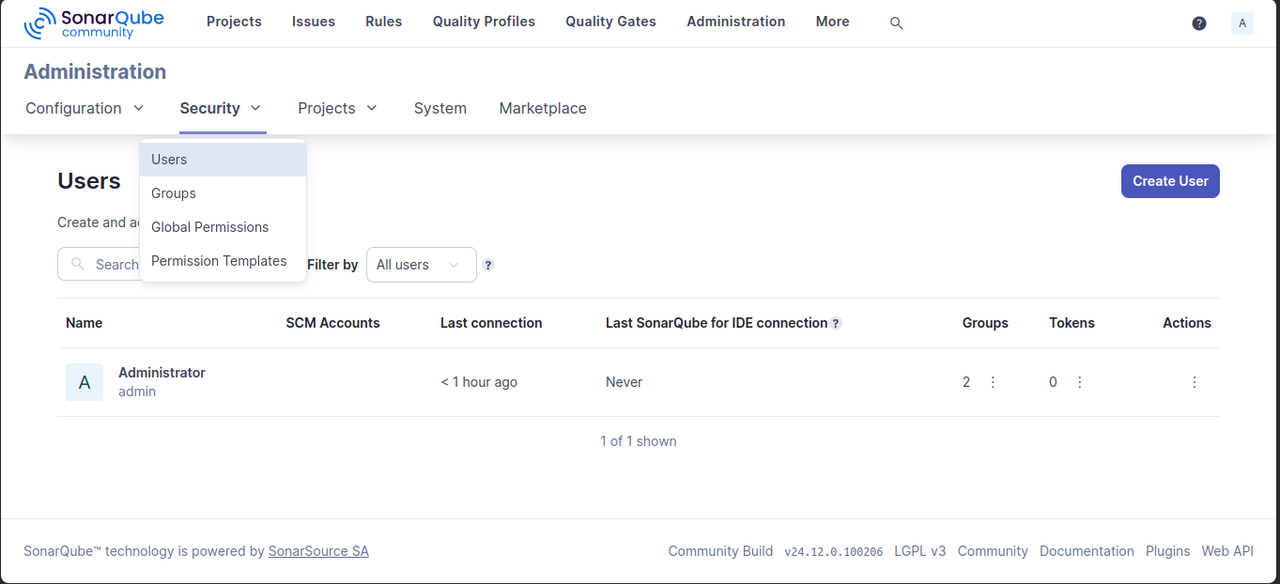
Click Administration within the SonarQube interface, select Security from the list of options, and click the Users dropdown option.
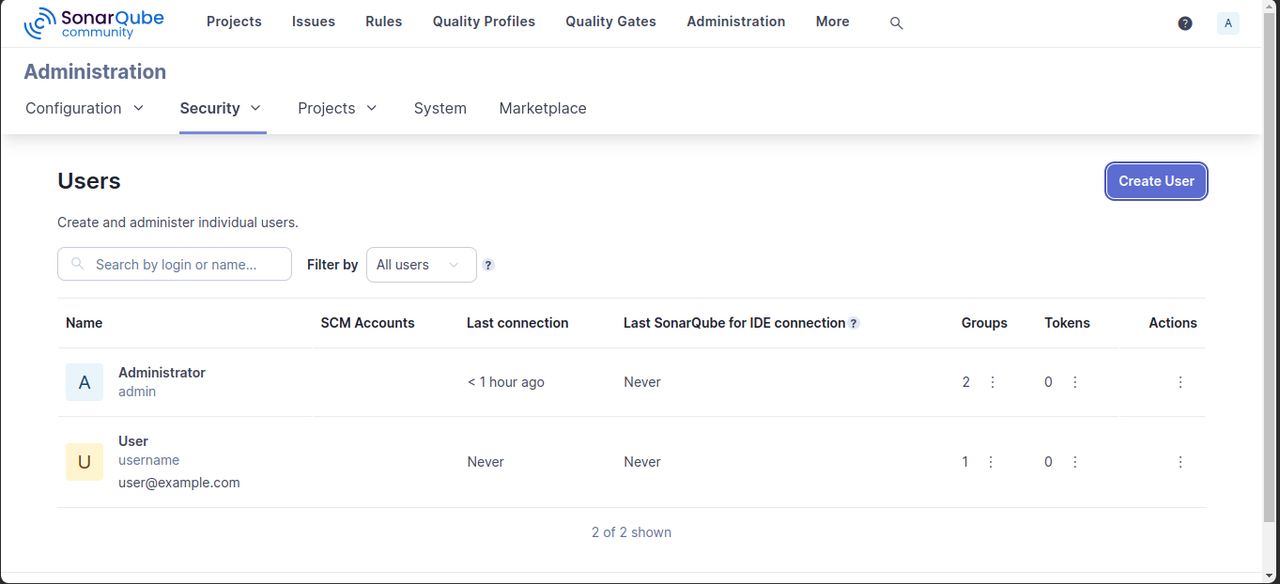
Click Create User to add a new user for code scanning.
Click the options symbol in the Tokens column within the new user's row to generate a token.
Enter the token name, select its expiry period, and click Generate.
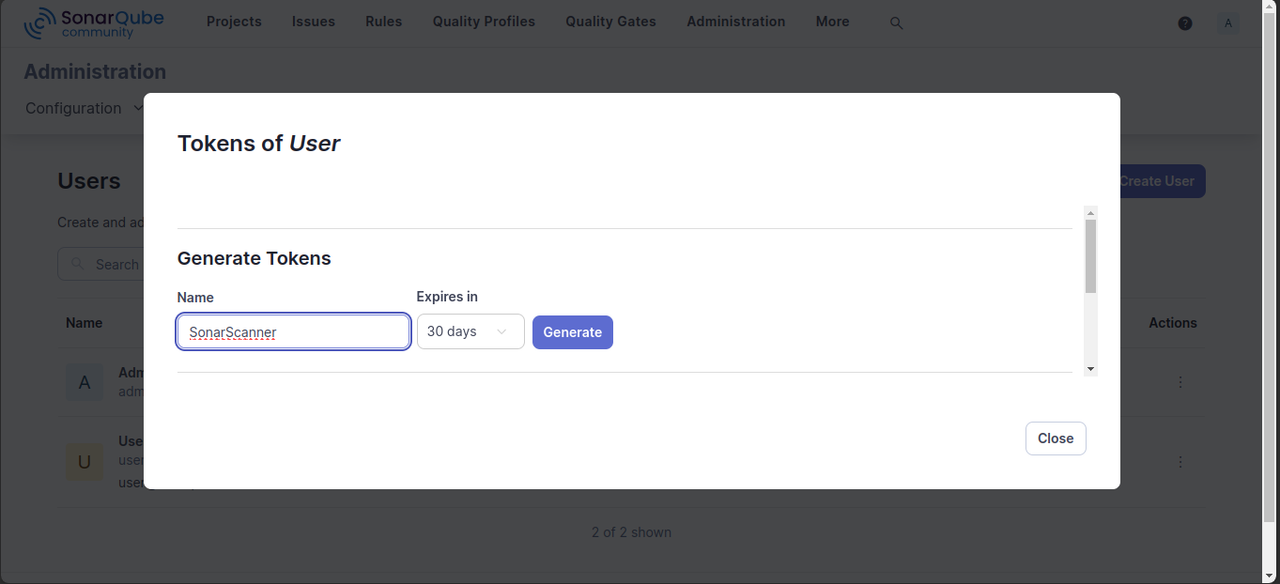
Copy the generated token in your output to use it with code scanning.
Scan SonarQube Example Projects
Follow the steps below to test the default SonarQube scanner using an example project.
Switch to your user's home directory.
console$ cd
Create a new sample
sonar-example-testproject directory.console$ mkdir sonar-example-test
Switch to the
sonar-example-testdirectory.console$ cd sonar-example-test
Download the SonarQube example project archive.
console$ wget https://github.com/SonarSource/sonar-scanning-examples/archive/master.zip
Extract files from the downloaded archive.
console$ unzip master.zip
Switch to the examples directory.
console$ cd sonar-scanning-examples-master
Switch to the example
sonar-scannerdirectory.console$ cd sonar-scanner
Scan the code in the entire directory using SonarScanner. Replace
user-sonar_tokenwith the user token you generated earlier.console$ sonar-scanner -D sonar.token=user-sonar_token
Your output should be similar to the one below:
INFO Analysis total time: 22.116 s INFO SonarScanner Engine completed successfully INFO EXECUTION SUCCESS INFO Total time: 26.095sVisit the SonarQube dashboard to view the scan results and the entire project report.
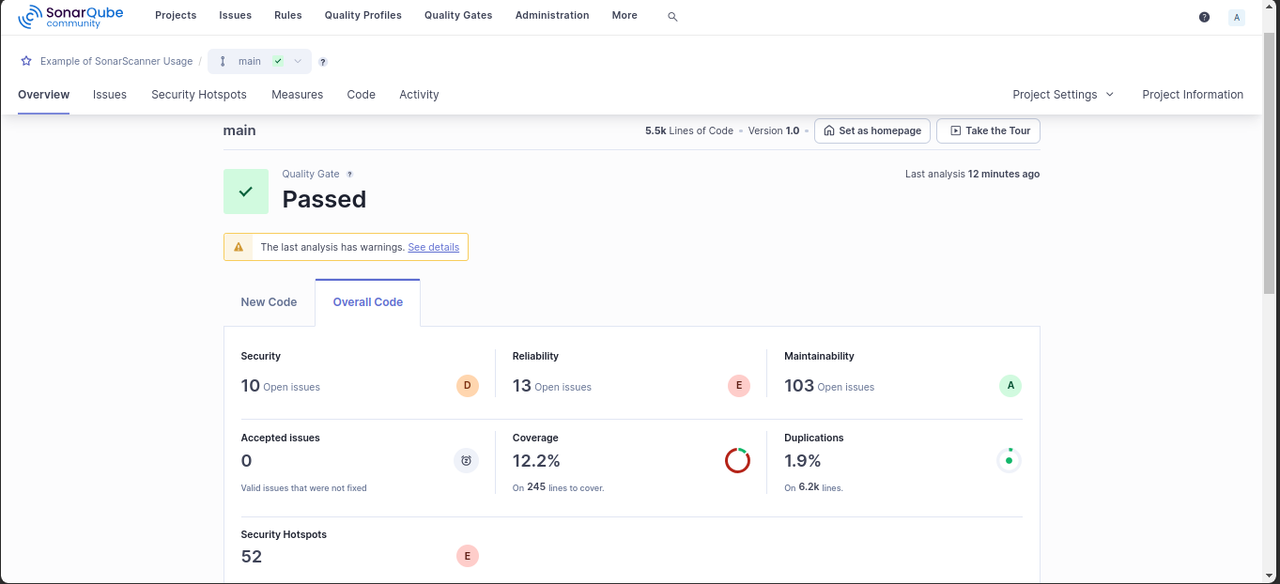
Scan Multiple Projects
Follow the steps below to set up your custom code projects to scan using SonarQube on your workstation.
Navigate to your existing project's root directory. For example,
myproject.console$ cd myproject
Create a new
sonar-project.propertiesconfiguration.console$ nano sonar-project.properties
Add the following configurations to the file to define your project settings. Replace the example values with your actual project values.
ini# Unique identifier for the project sonar.projectKey=MyProject:Key1 # Display name in SonarQube UI sonar.projectName=First Project # Version number being analyzed sonar.projectVersion=1.0 # Brief description of the project sonar.projectDescription=My First Project # Code directory to analyze sonar.sources=src
Save and close the file.
The above project configuration specifies your project settings and a target directory with the code to scan.
Run the SonarScanner CLI to scan the code in your project and access its report in the SonarQube web dashboard.
console$ sonar-scanner -D sonar.token=<sonar_token>
Conclusion
You have installed and configured SonarQube on an Ubuntu 24.04 workstation. You can install Nginx as a reverse proxy to securely forward all incoming connection requests to the SonarQube port 9000. In addition, you can use the SonarScanner CLI to perform test scans on multiple projects on your workstation and generate detailed reports in the SonarQube web dashboard. For more information and configuration samples, visit the SonarQube Documentation.