Introduction
Webmin is a web-based interface for managing Unix-like systems through a browser, eliminating the need to manually edit configuration files from the command line. It allows you to easily perform system administration tasks such as adding users, setting disk quotas, managing software packages, configuring networks, and controlling databases. Webmin is highly extensible, supporting a wide range of open-source tools to enhance server functionality. Installing Webmin on Debian 12, a stable and secure long-term support release, provides a user-friendly and efficient way to manage your server with greater control and flexibility.
This article explains how to install Webmin on Debian 12 and enable access to the web-based graphical interface. If you're working with a different Linux distribution, you might also find these guides helpful: How to Install Webmin on Ubuntu 24.04 and How to Install Webmin on Rocky Linux 9.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- Deploy a Debian 12 instance on Vultr.
- Create a domain name A record pointing to the instance's public IP address. For example,
webmin.example.com. - Access the instance using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
- Update the instance.
Install Webmin on Debian 12
Webmin is not available in the default package repositories on Debian 12. Follow the steps below to download the latest Webmin repository information script and install the application.
Download the latest Webmin repository setup script and save it as
setup-repos.sh.console$ curl -o setup-repos.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/webmin/webmin/master/setup-repos.sh
Run the script using the Bash interpreter.
console$ sudo bash setup-repos.sh
Enter Y and press Enter when prompted to proceed with the repository installation. When successful, your output should be similar to the one below.
Setup repository? (y/N) y Downloading Webmin key .. .. done Installing Webmin key .. .. done Setting up Webmin repository .. .. done Cleaning repository metadata .. .. done Downloading repository metadata .. .. done Webmin package can now be installed using apt-get install --install-recommends webmin command.Update your system's package information index to apply the Webmin repository information.
console$ sudo apt update
Install Webmin and the default recommended packages.
console$ sudo apt install webmin --install-recommends -y
Enable the Webmin service to automatically start at system boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable webmin
Start the Webmin service.
console$ sudo systemctl start webmin
View the Webmin system service status and verify it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status webmin
Output:
● webmin.service - Webmin server daemon Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/webmin.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2024-08-19 14:15:47 EDT; 42s ago Main PID: 4614 (miniserv.pl) Tasks: 1 (limit: 4572) Memory: 125.7M CPU: 2.060s CGroup: /system.slice/webmin.service └─25004614 /usr/bin/perl /usr/share/webmin/miniserv.pl /etc/webmin/miniserv.confWebmin is active and running based on the above output information.
Secure Webmin
Webmin runs on the default TCP port 10000 and serves the web administration control panel using HTTP. Generate trusted SSL certficates to secure network connections to the Webmin interface using HTTPS. Follow the steps below to install the Certbot Let's Encrypt client and enable Webmin to use trusted SSL certificate files.
Allow HTTP traffic on the default port
80to enable Let's Encrypt validations.console$ sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
Restart UFW to apply the new changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
Install the Certbot Let's Encrypt client tool.
console$ sudo apt install certbot -y
Generate a new SSL certificate for your domain. Replace
webmin.example.comwith your domain andwebmin@example.comwith your actual email address.console$ sudo certbot certonly --standalone -d webmin.example.com -m webmin@example.com --agree-tos
Your output should be similar to the one below when successful.
... Successfully received certificate. Certificate is saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/webmin.example.com/fullchain.pem Key is saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/webmin.example.com/privkey.pem ...Certbot stores the SSL certificate and private key files in the
/etc/letsencrypt/live/webmin.example.com/directory based on the above output.Combine the SSL certificate and private key contents into a single file such as
webmin_key_cert.pem.console$ sudo cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/webmin.example.com/fullchain.pem /etc/letsencrypt/live/webmin.example.com/privkey.pem > webmin_key_cert.pem
Move the file to the
/etc/webmin/Webmin data directory.console$ sudo mv webmin_key_cert.pem /etc/webmin/
Open the
/etc/webmin/miniserv.confWebmin configuration file using a text editor likenano.console$ sudo nano /etc/webmin/miniserv.conf
Find the
keyfiledirective and replace the value with yourwebmin_key_cert.pemSSL certificate path.inikeyfile=/etc/webmin/webmin_key_cert.pem
Restart the Webmin service to apply the configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart webmin
Set Up Firewall Rules
Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) is available and active on Vultr Debian instances by default. Follow the steps below to set up new firewall rules and allow network connections to the Webmin interface.
View the UFW status and verify that it's active.
console$ sudo ufw status
Allow network connections to the default Webmin port
10000.console$ sudo ufw allow 10000/tcp
Allow incoming HTTPS connections.
console$ sudo ufw allow https
Deny incoming HTTP connections to disable insecure requests.
console$ sudo ufw deny http
Reload UFW to apply the firewall changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
View the UFW status and verify the new connection rules are available.
console$ sudo ufw status
Output:
Status: active To Action From -- ------ ---- 443 ALLOW Anywhere 80 ALLOW Anywhere 80/tcp DENY Anywhere OpenSSH ALLOW Anywhere 10000/tcp ALLOW Anywhere 443 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 80/tcp (v6) DENY Anywhere (v6) OpenSSH (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) 10000/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Access Webmin
Webmin listens for incoming connection requests on the default port 10000 based on the /etc/webmin/miniserve.conf configuration. Follow the steps below to access the Webmin web administration interface on port 10000.
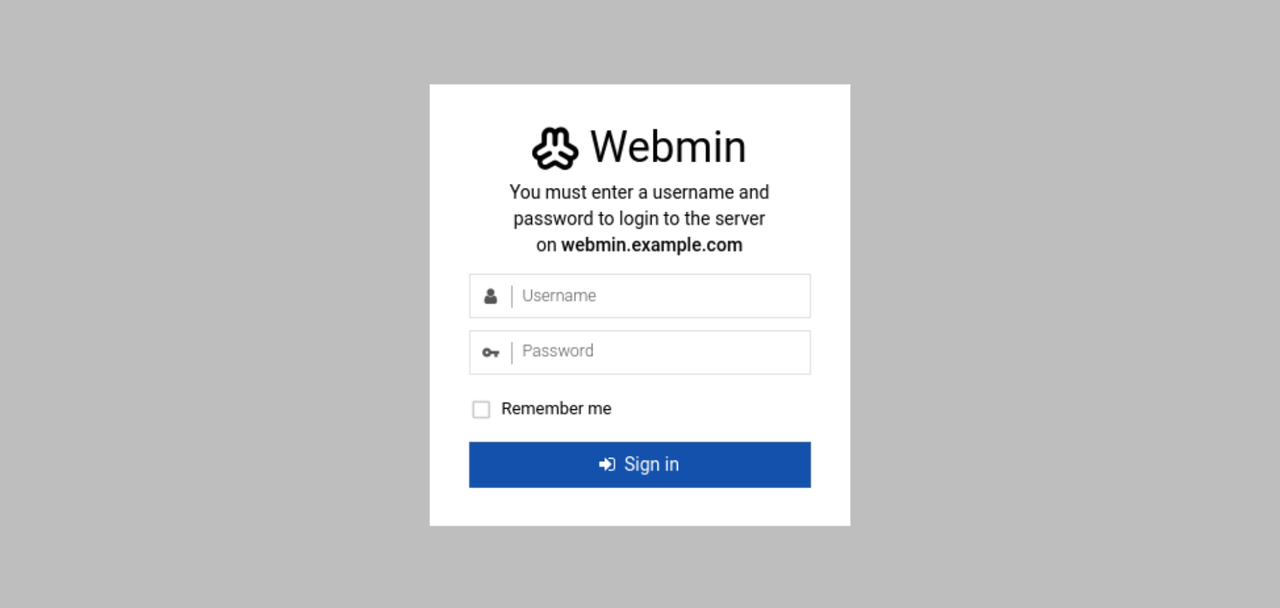
Access your domain on port
10000using a web browser such as Chrome.https://webmin.example.com:10000Enter your non-root sudo user credentials when prompted to log in to the Webmin interface.
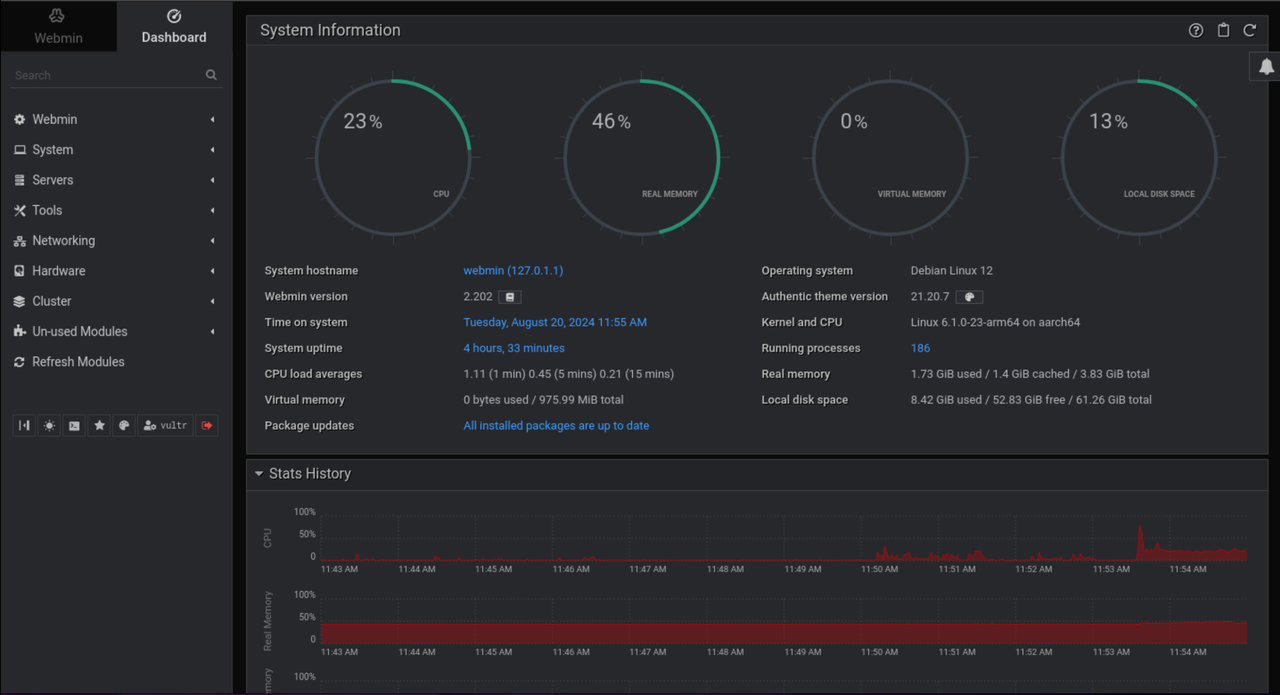
Click Dashboard on the main navigation menu to access the system information summary.
Conclusion
You have installed Webmin on a Debian 12 and secured the control panel interface with trusted Let's Encrypt SSL certificates. Webmin lets you use a GUI to manage and monitor your system applications and services. For more information, please visit the Webmin documentation.