
Jitsi Meet is a free and open-source video conferencing service solution packed with various premium features, such as superior sound quality, high-grade encryption and privacy, and universal multi-platform availability. With the help of Jitsi Meet, you can easily set up a stunning video conferencing service of your own.
One-Click Jitsi Server
Vultr has preinstalled Jitsi servers ready to launch! Deploy a Jitsi Meet server in your customer portal without any installation steps required. The One-Click Jitsi server supports your custom domain name, a Let's Encrypt SSL certificate, and it's the best way to install Jitsi.
Learn more about our One-Click Jitsi server, or if you prefer to install your server manually, follow the steps below.
Manual Installation
If you prefer to install your server manually, follow the steps below.
Prerequisites
- A fresh Vultr Ubuntu 20.04 LTS x64 server instance. For best results, we recommend a High Frequency Compute instance with at least 2 GB of memory.
- A non-root sudo user. Use Vultr's best practice guide to create a sudo user on Ubuntu.
- A Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) assigned to your server's IP address.
Examples
This tutorial uses examples:
- Server hostname: jitsi
- Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN): jitsi.example.com
- IP address 192.0.2.123
1. Create a Swap Partition
For a machine with 2 GB of memory, a 2 GB (2048 MB) swap partition is recommended to improve system performance. Choose a swap partition size appropriate for your instance.
$ sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile count=2048 bs=1M
$ sudo chmod 600 /swapfile
$ sudo mkswap /swapfile
$ sudo swapon /swapfile
$ echo '/swapfile none swap sw 0 0' | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab
$ free -m2. Set the Hostname and FQDN
You must set the hostname and FQDN before you deploy the Let's Encrypt HTTPS certificate for security. Use the Vultr's Best Practice Guide to configure your server hostname and FQDN. This guide uses the example names jitsi, and jitsi.example.com.
3. Configure Firewall Rules for Jitsi Meet
Jitsi requires OpenSSH, HTTP, and HTTPS traffic, along with inbound UDP traffic on port 10000 through port 20000.
$ sudo ufw allow OpenSSH
$ sudo ufw allow http
$ sudo ufw allow https
$ sudo ufw allow in 10000:20000/udp
$ sudo ufw enable
Command may disrupt existing ssh connections. Proceed with operation (y|n)? yWhen prompted to proceed, type Y and then Enter.
4. Update the system
For security and performance, follow Vultr's best practices guide to update Ubuntu.
5. Install OpenJDK Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 8
Jitsi requires the Java Runtime Environment. Install OpenJDK JRE 8.
$ sudo apt install -y openjdk-8-jre-headlessVerify OpenJDK is installed properly.
$ java -version
openjdk version "1.8.0_252"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_252-8u252-b09-1ubuntu1-b09)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.252-b09, mixed mode)Set the JAVA_HOME environment variable.
$ echo "JAVA_HOME=$(readlink -f /usr/bin/java | sed "s:bin/java::")" | sudo tee -a /etc/profile
$ source /etc/profile6. Install the Nginx Web Server
Jitsi works best with Nginx and will automatically configure Nginx settings if we install it first.
$ sudo apt install -y nginx
$ sudo systemctl start nginx.service
$ sudo systemctl enable nginx.service7. Install Jitsi
Install Jitsi from the official Jitsi repository.
$ wget -qO - https://download.jitsi.org/jitsi-key.gpg.key | sudo apt-key add -
$ echo "deb https://download.jitsi.org stable/" | sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jitsi-stable.list
$ sudo apt update
$ sudo apt install -y jitsi-meetThe installer will request your FQDN. Enter the fully-qualified domain name of your server.
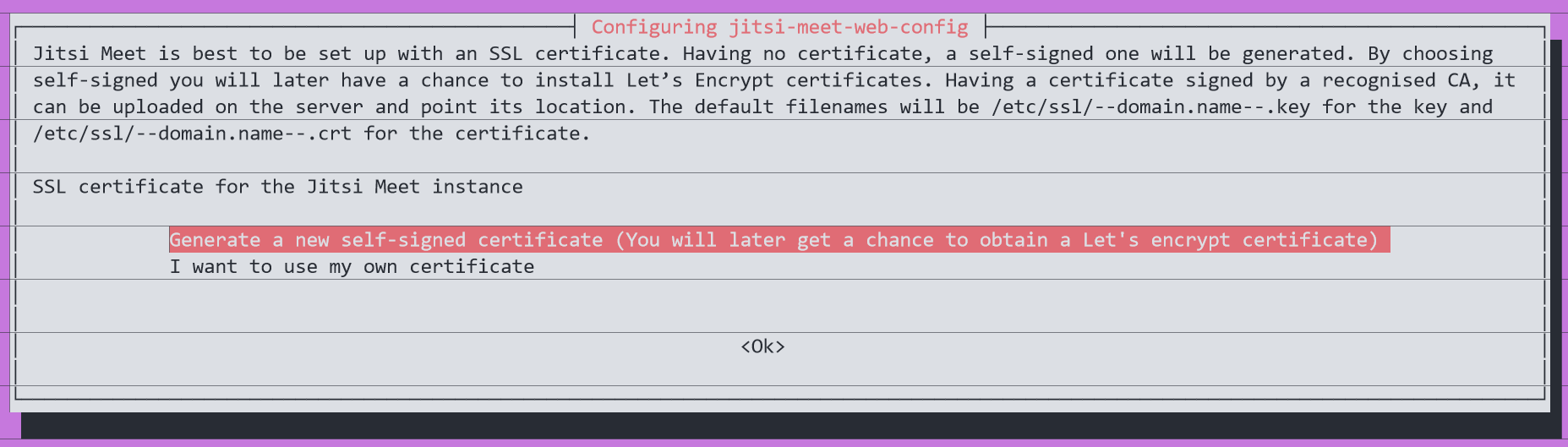
When asked to configure SSL, select Generate a new self-signed certificate.
8. Install Let's Encrypt SSL Certificate
Use the following script to request a Let's Encrypt SSL certificate.
$ sudo /usr/share/jitsi-meet/scripts/install-letsencrypt-cert.shThe script prompts for your email address. Enter your address and press Enter.
Enter your email and press [ENTER]: admin@example.comCorrect the certbot-auto error
You will probably see the following error, because Ubuntu 20.04 has removed the python-virtualenv package.
Package python-virtualenv is not available, but is referred to by another package.
This may mean that the package is missing, has been obsoleted, or
is only available from another source
E: Package 'python-virtualenv' has no installation candidateThis work-around will correct the error.
Install the certbot package from the Ubuntu 20.04 repository.
$ sudo apt install certbotUpdate install-letsencrypt-cert.sh to use certbot instead of certbot-auto.
$ sudo sed -i 's/\.\/certbot-auto/certbot/g' /usr/share/jitsi-meet/scripts/install-letsencrypt-cert.shThe Jitsi script expects certbot in /usr/sbin, and Ubuntu installs it in /usr/bin. Make a symbolic link for the script.
$ sudo ln -s /usr/bin/certbot /usr/sbin/certbotRun the script again.
$ sudo /usr/share/jitsi-meet/scripts/install-letsencrypt-cert.sh
9. Start a Meeting
Navigate to https://jitsi.example.com in your favorite web browser to access your Jitsi Meet Video conferencing service.