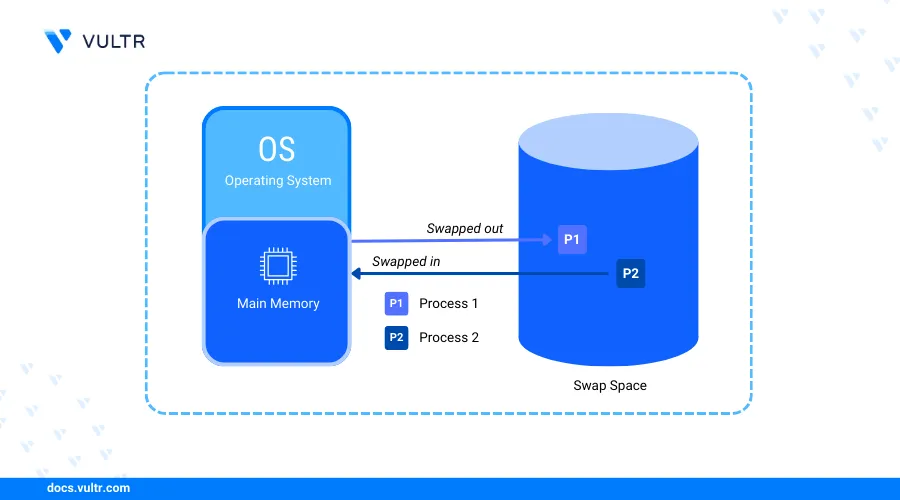
Introduction
Swap space extends the capacity of your system's memory to improve performance when the RAM is full. During a memory shortage, your server stores inactive processes to the swap memory to run your system smoothly. Swapping processes prevents system shutdowns and crashes, especially when running multiple applications.
This article explains how to add a swap memory on FreeBSD 14.0.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- Deploy a FreeBSD 14.0 Cloud Compute instance on Vultr.
- Access the instance using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
- Attach a Vultr Block Storage volume to the FreeBSD 14.0 instance. You'll use this storage as a swap memory.
Check Existing Swap Memory
Before adding a swap memory, verify if there is any existing swap memory on the system by running the following command.
$ swapinfo
Output:
Device 1K-blocks Used Avail CapacityThe above command displays an empty swap information.
Create Swap Memory
You can create swap memory using:
- A Swapfile
- A Vultr Block Storage volume
Swapfile
Create a new swap file.
console$ sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile bs=1M count=2048
The above command creates a new Swapfile with 2 GB (
bs=1M count=2048).Create a new memory block device that points to the file.
console$ sudo mdconfig -a -t vnode -f /swapfile -u 0
Output:
2048+0 records in 2048+0 records out 2147483648 bytes transferred in 0.884273 secs (2428530534 bytes/sec)The above command creates a memory block device associated with the
/swapfilefile and assigns it to the/dev/md0device.Enable the memory block device as a swap.
console$ sudo swapon /dev/md0
The above command activates the Swapfile's block device as swap memory.
Vultr Block Storage
Vultr Block Storage devices attached to your server use the vtbd naming scheme where the first block device is vtbd1 and any additional devices use incremented values such as vtbd2 for a second device. Follow the steps below to create swap memory using the Vultr Block Storage device attached to your server.
Initialize the block storage device attached to your server with a GPT partition table.
console$ sudo gpart create -s GPT vtbd1
Output:
vtbd1 createdAdd a new
swap0partition to the device and use the partition as a swap space.console$ sudo gpart add -t freebsd-swap -l swap0 vtbd1
Output:
vtbd1p1 addedFormat and enable the swap partition:
console$ sudo swapon /dev/vtbd1p1
Configure the File System Table (fstab) for Automatic Mounting
Automatic mounting enables the server to mount the swap memory at boot. Follow the steps below to enable automatic mounting of your swap memory created from a Swapfile or a Vultr Block Storage device.
Enable Automatic Mounting for a Swapfile
Modify the /etc/fstab file to include your Swapfile's block device.
$ echo "/dev/md0 none swap sw 0 0" | sudo tee -a /etc/fstab
Output:
/dev/md0 none swap sw 0 0Enable Automatic Mounting For Vultr Block Storage
Modify the /etc/fstab file to include your Vultr Block Storage device path.
$ sudo echo "/dev/vtbd1p1 none swap sw 0 0" | tee -a /etc/fstab
Output:
/dev/vtbd1p1 none swap sw 0 0Test the Swap Memory
Follow the steps below to ensure the swap memory is actively swapping processes.
View the available swap space.
console$ swapinfoOutput:
Device 1K-blocks Used Avail Capacity /dev/md0 2097152 0 2097152 0%View the swap memory usage using the
toputility.console$ topOutput:
last pid: 1362; load averages: 0.12, 0.12, 0.10 up 0+00:53:25 17:45:17 24 processes: 1 running, 23 sleeping CPU: 0.0% user, 0.0% nice, 0.6% system, 0.0% interrupt, 99.4% idle Mem: 11M Active, 1868M Inact, 326M Wired, 206M Buf, 5708M Free Swap: 2048M Total, 2048M Free PID USERNAME THR PRI NICE SIZE RES STATE C TIME WCPU COMMAND ...Swap memory actively swaps processes and includes
2048free memory based on the abovetopoutput.
Remove Swap Memory
Follow the steps below when detaching swap memory from your server.
Remove Swapfile
Disable the swap device.
console$ sudo swapoff /dev/md0
Delete the memory block device.
console$ sudo mdconfig -d -u 0
Delete the swap file.
console$ sudo rm /swapfile
Remove the entry from
/etc/fstabto disable automatic mounting.console$ sudo sed -i '' '/\/dev\/md0/d' /etc/fstab
Remove Block Storage
Disable the swap partition.
console$ sudo swapoff /dev/vtbd1p1
Remove the swap partition entry from
/etc/fstab.console$ sudo sed -i '' '/\/dev\/vtbd1p1/d' /etc/fstab
Conclusion
In this article, you have added a swap memory on a FreeBSD 14.0 to allow your system to swap processes. You've learned to use a Swapfile or a Vultr Block Storage volume to extend your system's memory. For more information, visit the FreeBSD swap documentation.