Introduction
Llama.cpp is a high-performance inference platform designed for Large Language Models (LLMs) like Llama, Falcon, and Mistral. It provides a streamlined development environment compatible with both CPU and GPU systems. This article explains how to set up and run Llama.cpp in Docker using the Vultr Container Registry.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
Deploy an instance using Vultr's GPU Marketplace App
Access the server using SSH.
Start the Docker service.
console$ sudo systemctl start docker
Add the non-root user to the Docker group. For example,
linuxuser.console$ sudo usermod -aG docker linuxuser
Switch to the user:
console$ su - linuxuser
Set Up the Server
Create a new directory to store your Llama.cpp project files.
console$ mkdir llama-project
Switch to the directory.
console$ cd llama-project
Clone the Llama.cpp project repository using Git.
console$ git clone https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/
List files and verify that a new
llama.cppdirectory is available.console$ lsOutput:
llama.cppSwitch to the
llama.cppproject directory.console$ cd llama.cpp
List all hidden files and verify that a new
.devopsdirectory is available.console$ ls -a
Output:
.. cmake convert.py flake.lock ggml-common.h ggml-metal.h ggml-quantsh .git llama.cpp CMakeLists.txt .devopsThe
.devopsdirectory contains the following Dockerfile resources:main.Dockerfile: Contains the build context for CPU systems.main-cuda.Dockerfile: Contains the build context for GPU systems.
Use the above resources in the next sections to build a CPU or GPU system container image.
Build a Llama.cpp Container Image for CPU Systems
Follow the steps below to build a new Llama.cpp container image using main.Dockerfile that contains the required build context and installs all necessary dependency packages for CPU-based systems.
Copy the
main.Dockerfilefrom the.devopsdirectory to the mainllama.cppproject directory.console$ cp .devops/main.Dockerfile .
Build a new container image using
main.Dockerfilewith all files in the project directory. Replacellama-imagewith your desired image name.console$ docker build -f main.Dockerfile -t llama-image .
View all Docker images on the server and verify that a new
llama-imageis available.console$ docker images
Output:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE llama-image latest f4fcb571a2f7 About a minute ago 80.1MB
Build a Llama.cpp Container Image for GPU Systems
The Llama.cpp main-cuda.Dockerfile resource contains the build context for NVIDIA GPU systems that run the latest CUDA driver packages. Follow the steps below to build a Llama container image compatible with GPU systems.
Copy
main-cuda.Dockerfileto the Llama.cpp project directory.console$ cp .devops/main-cuda.Dockerfile .
Build a new container image
llama-gpu-imageusing themain-cuda.Dockerfilewith all files in the working project directory.console$ docker build -f main-cuda.Dockerfile -t llama-gpu-image .
View all Docker images on the server and verify that the new
llama-gpu-imageis available.console$ docker images
Output:
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE llama-gpu-image latest 40421f1469cf 2 minutes ago 2.08GBTo run the Llama.cpp GPU container image, verify that your target host includes the minimum or higher CUDA version referenced by the
ARG CUDA_VERSION=directive withinmain-cuda.Dockerfile. Run the following command to verify the target CUDA version.console$ cat main-cuda.Dockerfile | grep CUDA_VERSION=
Output:
ARG CUDA_VERSION=12.3.1
Upload the Llama.cpp Container Image to the Vultr Container Registry
Open the Vultr Customer Portal.
Click Products and select Container Registry on the main navigation menu.
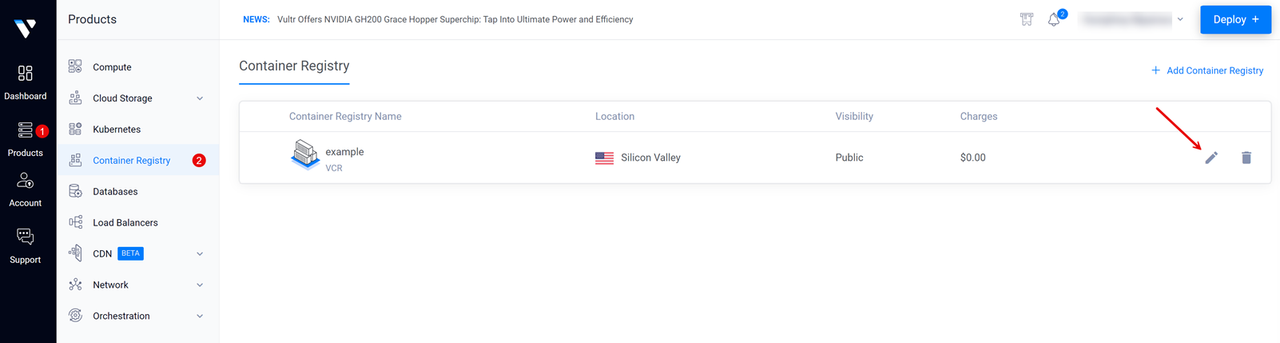
Click your target Vultr Container Registry to open the management panel and view the registry access credentials.
Copy the Registry URL value, Username, and API Key to use when accessing the registry.
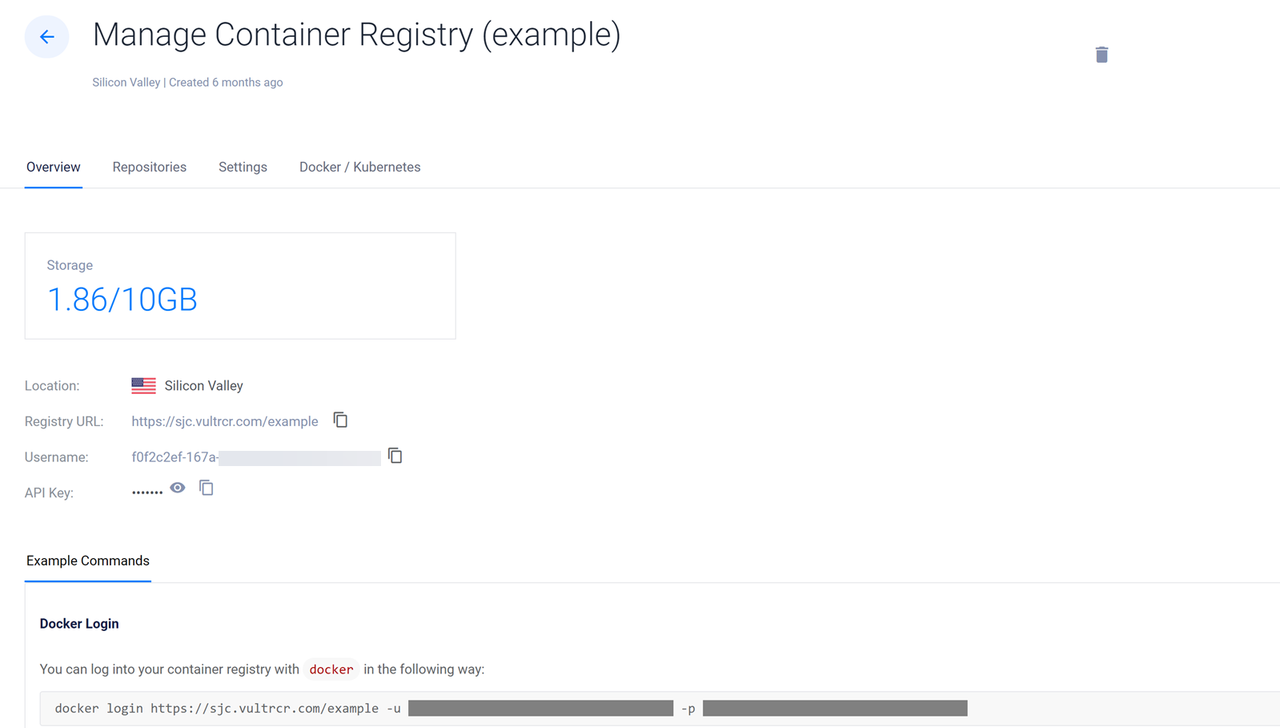
Switch to your server terminal session and log in to your Vultr Container Registry. Replace
exampleregistry,exampleuser,registry-passwordwith your actual registry details.console$ docker login https://sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry -u exampleuser -p registry-password
Tag the Llama.cpp container image with your desired Vultr Container Registry tag. For example,
sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry/llama-gpu-image.console$ docker tag llama-gpu-image sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry/llama-gpu-image
View all Docker images on the server and verify that the new tagged image is available.
console$ docker images
Output:
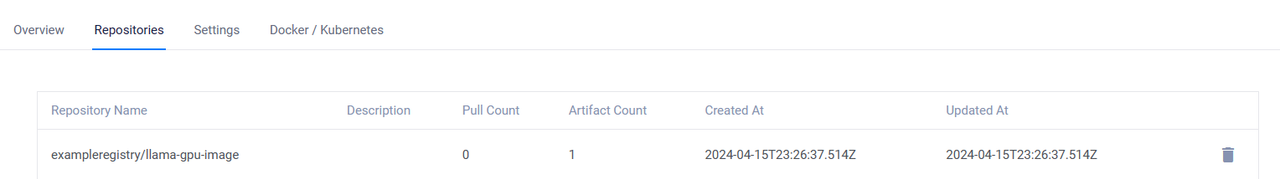
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry/llama-gpu-image latest 40421f1469cf 3 minutes ago 2.08GB llama-gpu-image latest 40421f1469cf 3 minutes ago 2.08GBPush the tagged image to your Vultr Container Registry repository.
console$ docker push sjc.vultrcr.com/exampleregistry/llama-gpu-image
Open your Vultr Container Registry management panel and click Repositories on the top navigation bar to verify that the new repository is available.