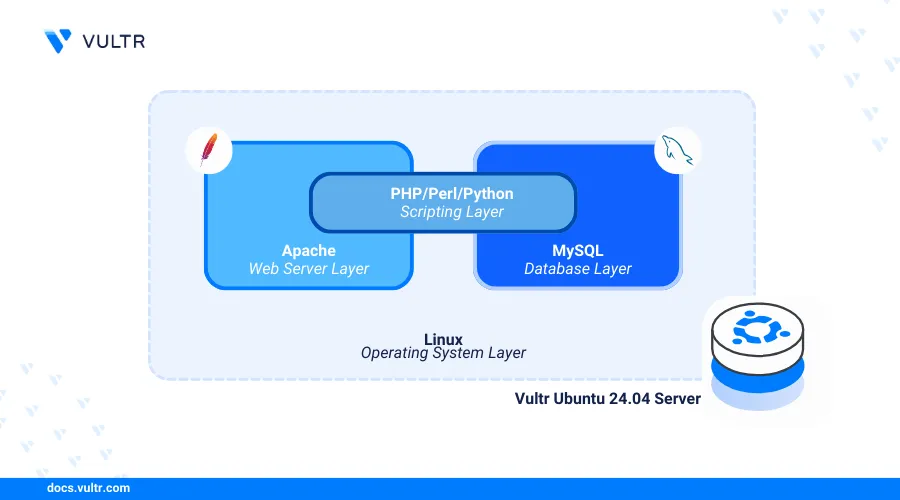
Introduction
Apache, MySQL, and PHP (LAMP stack) is a collection of open-source applications that enable the development and delivery of dynamic web applications on a server. Linux runs as the operating system to deploy the applications, Apache works as the web server, MySQL as the database backend, and PHP processes dynamic web application contents on the server.
This article explains how to install the LAMP stack on Ubuntu 24.04 and configure the server to deliver web applications using the stack.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
Deploy an Ubuntu 24.04 instance on Vultr.
Access the server using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Set up a new A record for your domain that points to the server IP address.
Install Apache
The latest Apache version is available in the default APT repositories on Ubuntu 24.04. Follow the steps below to update the default package index and install the latest Apache web server package on your server.
Update the server's package index.
console$ sudo apt update
Install Apache.
console$ sudo apt install apache2 -y
Start the Apache service.
console$ sudo systemctl start apache2
Enable the Apache service to start automatically at boot time.
console$ sudo systemctl enable apache2
Verify that the Apache server service is running.
console$ sudo systemctl status apache2
Output:
apache2.service - The Apache HTTP Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/apache2.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2024-06-12 06:50:21 UTC; 3 days ago Docs: https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/ Process: 164186 ExecReload=/usr/sbin/apachectl graceful (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 124430 (apache2) Tasks: 8 (limit: 4389) Memory: 18.3M (peak: 44.1M) CPU: 27.485s CGroup: /system.slice/apache2.service ├─124430 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start ├─164195 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start ├─164196 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start ├─164199 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start ├─164201 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k startAllow connections to the HTTP port
80through the default firewall configuration.console$ sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
Access your domain or server IP using a web browser such as Chrome and verify that the default Apache web page displays.
http://SERVER-IP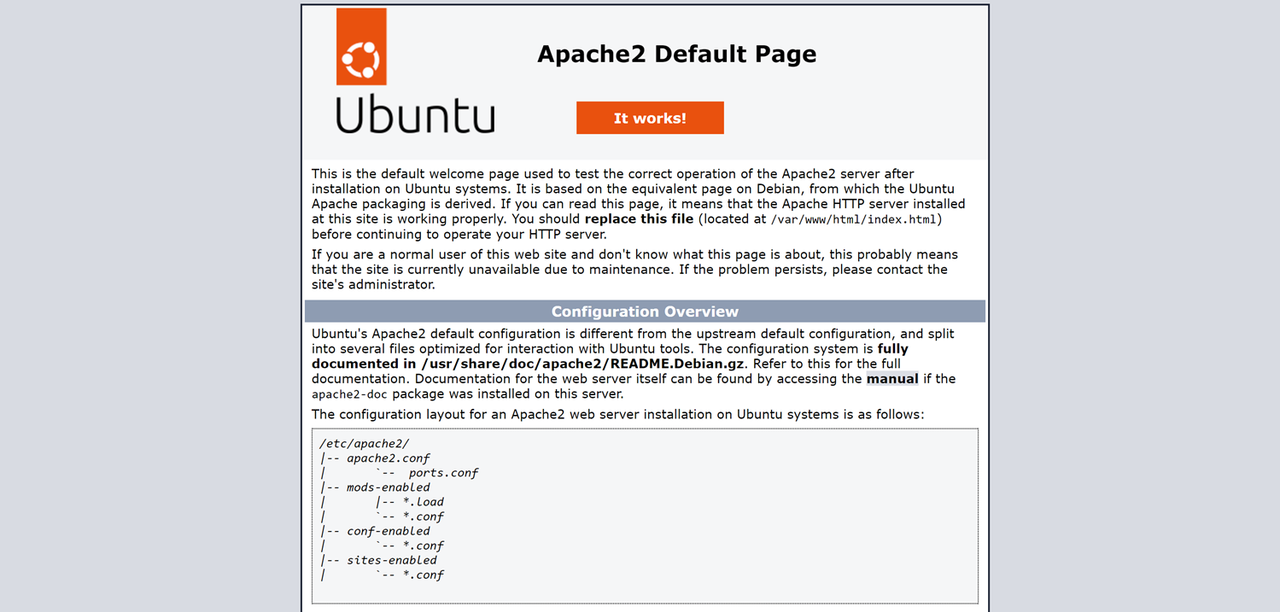
Install MySQL
MySQL works as the database backend within the LAMP stack and you can substitute it with MariaDB depending on your needs. The latest MySQL package is available in the default repositories on Ubuntu 24.04. Follow the steps below to install the latest MySQL version on your server using the default APT package manager.
Install the MySQL database server package.
console$ sudo apt install -y mysql-server
Enable the MySQL service to start automatically at boot time.
console$ sudo systemctl enable mysql
Start the MySQL service.
console$ sudo systemctl start mysql
View the MySQL service status and verify that it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status mysql
Output:
mysql.service - MySQL Community Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/mysql.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2024-06-13 06:54:13 UTC; 2 days ago Process: 144075 ExecStartPre=/usr/share/mysql/mysql-systemd-start pre (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 144083 (mysqld) Status: "Server is operational" Tasks: 38 (limit: 4389) Memory: 369.2M (peak: 382.6M) CPU: 36min 21.658s CGroup: /system.slice/mysql.service └─144083 /usr/sbin/mysqldBased on the
active (running)result in the above output, the MySQL database server is active and running on your server.Run the MySQL secure installation script to disable insecure defaults and enable authentication on your database server.
console$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
Reply to the following MySQL database server options when prompted:
VALIDATE PASSWORD: Enter Y to enable password strength checks on the database server.Password strength policy: Enter 2 to enable multi-character password usage on the server.Remove anonymous users: Enter Y to remove anonymous users from the database server.Disallow root login remotely: Enter Y to disable remote access to therootdatabase user.Remove test database: Enter Y to delete the default MySQL test database on your server.Reload privileges tables now: Enter Y to reload the MySQL privilege tables and apply your configuration changes.
Your output should look like the one below when successful:
Success. All done!Log in to the MySQL console as the
rootuser.console$ sudo mysql
Alter the
rootdatabase user to use a new strong password. ReplaceStrong@@password123with your desired password.sqlmysql > alter user 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Strong@@password123';
Replace
passwordwith a strong password.Flush the MySQL privileges table to apply the new user changes.
sqlmysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Exit the MySQL console.
sqlmysql > EXIT
Log in to the MySQL console again as the
rootuser and enter the password you set earlier when prompted.console$ sudo mysql -u root -p
Create a new sample database
content_database.sqlmysql > CREATE database content_database;
View all databases and verify that the new database is available.
sqlmysql > SHOW DATABASES;
Output:
+--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | content_database | | mysql | | performance_schema | | sys | +--------------------+ 5 rows in set (0.01 sec)Create a new MySQL user such as
dbadminwith a strong password. ReplaceStrong@@password123with your desired password.sqlmysql > CREATE USER 'dbadmin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Strong@@password123';
Grant the user full privileges to your sample database
content_database.sqlmysql > GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON content_database.* TO 'dbadmin'@'localhost';
Flush the MySQL privileges table to apply changes.
sqlmysql > FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Exit the MySQL shell.
sqlmysql > EXIT
Install PHP and Configure PHP-FPM
PHP is a core LAMP stack component that processes dynamic content and integrates with your MySQL database server to read or create database records. PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) manages the connection to the PHP service and optimizes the application performance using pools of worker processes. Follow the steps below to install the latest PHP version and configure PHP-FPM to enable dynamic web application processes on your server.
Install PHP and the PHP-FPM module.
console$ sudo apt install -y php php-fpm
Install common PHP extensions on your server.
console$ sudo apt install -y php-mysql php-opcache php-cli libapache2-mod-php
The above command installs the following PHP modules:
php-mysql: Enables PHP to connect and interact with the MySQL database server.libapache2-mod-php: Enables the Apache web server to process and run PHP scripts.php-opcache: Enables caching of precompiled PHP scripts in memory for faster execution.php-cli: Enables access to PHP in your server terminal.
View the installed PHP version on your server.
console$ php -v
Output:
PHP 8.3.6 (cli) (built: Jun 13 2024 15:23:20) (NTS) Copyright (c) The PHP Group Zend Engine v4.3.6, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies with Zend OPcache v8.3.6, Copyright (c), by Zend TechnologiesStart the PHP-FPM service based on the installed PHP version on your server. For example,
PHP 8.3.console$ sudo systemctl start php8.3-fpm
Enable PHP-FPM to start at boot time.
console$ sudo systemctl enable php8.3-fpm
View the PHP-FPM service status and verify that it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status php8.3-fpm
Output:
php8.3-fpm.service - The PHP 8.3 FastCGI Process Manager Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/php8.3-fpm.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2024-06-12 06:50:21 UTC; 3 days ago Docs: man:php-fpm8.3(8) Main PID: 124416 (php-fpm8.3) Status: "Processes active: 0, idle: 2, Requests: 15, slow: 0, Traffic: 0req/sec" Tasks: 3 (limit: 4389) Memory: 12.0M (peak: 12.4M) CPU: 31.204s CGroup: /system.slice/php8.3-fpm.service ├─124416 "php-fpm: master process (/etc/php/8.3/fpm/php-fpm.conf)" ├─124419 "php-fpm: pool www" └─124420 "php-fpm: pool www"
Configure PHP-FPM
PHP-FPM ensures optimized performance for PHP applications on your server using pools depending on your server memory. Follow the steps below to configure PHP-FPM to work with the Apache web server and modify the default pool configurations to enable efficient resource management.
Enable the required Apache modules.
console$ sudo a2enmod proxy_fcgi setenvif
The above command enables the following modules on your web server:
proxy_fcgi: Enables Apache to work as a proxy with PHP-FPM.setenvif: Sets the necessary environment variables to enable connections between Apache and PHP-FPM.
Enable the default PHP-FPM configuration.
console$ sudo a2enconf php8.3-fpm
Restart the Apache web server to apply the changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Switch to the PHP-FPM pool configurations directory.
$ sudo cd /etc/php/8.3/fpm/pool.d/Open the default
www.confPHP-FPM pool configuration.console$ sudo nano /etc/php/8.3/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
Verify that the default PHP-FPM pool name
www.ini[www]Find and verify the following directives are set to
www-datato enable PHP-FPM to use the default web server user profile.iniuser = www-data group = www-data listen.owner = www-data listen.group = www-data
Find the following pool configurations and modify them to suite your desired server needs:
pm: Sets the default process manager. The valuedynamicenables PHP child processes to dynamically adjust on your server.pm.start_servers: Defines the number of PHP child processes to create at startup. The default value is2.pm.max_children: Sets the maximum number of PHP child processes that can be active simultaneously. The default value is5.pm.min_spare_servers: Setsthe minimum number of idle PHP child processes. The default value is1.pm.max_spare_servers: Specifies the maximum number of idle PHP child processes. The default value is3.pm.max_requests: Limits the number of requests a PHP child process can handle before it's recycled.
Save and close the file.
Restart the PHP-FPM service to apply your configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart php8.3-fpm
Configure Apache with PHP-FPM
The Apache web server uses the mod_proxy_fcgi module to communicate with PHP-FPM using the service UNIX socket or the default TCP port 9000 depending on your pool configuration. In the following steps, set up a new Apache virtual host configuration and connect to the PHP-FPM service using the UNIX socket.
Remove the default Apache virtual host configuration files.
console$ sudo rm -rf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default.conf && sudo rm -rf /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
Create a new Apache virtual host configuration file. For example,
app.example.com.conf.console$ sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/app.example.com.conf
Add the following configurations to the file. Replace
app.example.comwith your actual domain.ini<VirtualHost *:80> ServerAdmin webmaster@app.example.com ServerName wapp.example.com DocumentRoot /var/www/app.example.com <Directory /var/www/app.example.com> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks AllowOverride All Require all granted </Directory> <FilesMatch \.php$> SetHandler "proxy:unix:/var/run/php/php8.3-fpm.sock|fcgi://localhost/" </FilesMatch> ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/app.example.com_error.log CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/app.example.com_access.log combined </VirtualHost>
Save and close the file.
The above configuration creates a new Apache virtual host that listens for incoming connections on the default HTTP port
80and serves web contents using yourapp.example.comdomain. Then, all PHP file requests are forwarded to the PHP-FPM process using the/var/run/php/php8.3-fpm.sockUNIX socket. Within the configuration:<VirtualHost *:80>: Enables the virtual host profile to listen for connections on port80.<Directory /var/www/app.example.com>: Sets the web root directory to deliver web application files.<FilesMatch \.php$>: Forwards all PHP file requests to the PHP-FPM socket/var/run/php/php8.3-fpm.sockusing the FastCGI protocol.ErrorLog,CustomLog: Enable custom paths to store the virtual host error and access logs respectively.
Enable the new Apache virtual host configuration.
console$ sudo a2ensite app.example.com.conf
Test the Apache configuration for syntax errors.
console$ sudo apache2ctl configtest
Output:
Syntax OKCreate the virtual host web root directory
/var/www/app.example.comdefined in your configuration.console$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/app.example.com
Create a new sample PHP file
info.php.console$ sudo nano /var/www/html/info.php
Add the following contents to the file.
php<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Save and close the file.
The above application code displays information about the PHP version and installed modules on your server when accessed in a web browser.
Restart Apache to apply your configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Access your domain using a web browser such as Chrome and append the
/info.phppath to verify that your PHP application information displays.http://app.example.com/info.php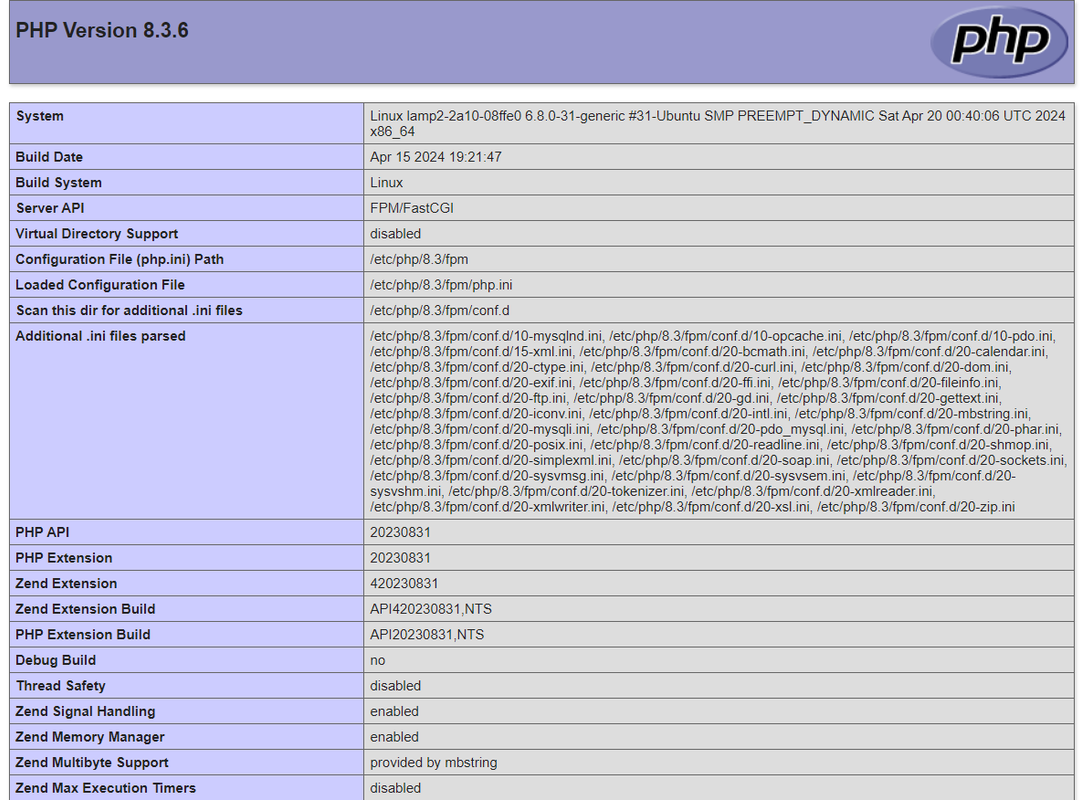
Secure the server
Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) is available and active on Vultr Ubuntu 24.04 servers by default. The Apache web server delivers dynamic web applications on your server using the default HTTP port 80 while other LAMP stack components use internal TCP ports such as the MySQL port 3306 and the PHP-FPM port 9000. Follow the sections below to configure the default firewall to allow connections to the default web server port 80 and set up trusted SSL certificates to enable HTTPS connections on port 443.
Configure the Firewall
View the default firewall status and verify that it's active.
console$ sudo ufw status
Output:
consoleStatus: activeView the available UFW application profiles and verify that the Apache profile is available.
console$ sudo ufw app list
Output:
Apache Apache Full Apache Secure OpenSSHAllow the
Apache Fullprofile to enable HTTP and HTTPS connections on the server.console$ sudo ufw allow "Apache Full"
Reload the firewall rules to apply changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
View the UFW status and verify that the Apache connection rules are available in the firewall table.
console$ sudo ufw status
Output:
To Action From -- ------ ---- 1022/tcp ALLOW Anywhere Apache Full ALLOW Anywhere 1022/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6) Apache Full (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Generate Trusted Let's Encrypt SSL Certificates
Install the Certbot Let's Encrypt client tool using Snap.
console$ sudo snap install certbot --classic
Request a new SSL certificate for your domain. Replace
app.example.comwith your actual domain andadmin@example.comwith your email.console$ sudo certbot --apache -d app.example.com -m admin@example.com --agree-tos
Output:
Requesting a certificate for app.example.com Successfully received certificate. Certificate is saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/app.example.com/fullchain.pem Key is saved at: /etc/letsencrypt/live/app.example.com/privkey.pem This certificate expires on 2024-10-14. These files will be updated when the certificate renews. Certbot has set up a scheduled task to automatically renew this certificate in the background. Deploying certificate Successfully deployed certificate for app.example.com to /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default-le-ssl.conf Congratulations! You have successfully enabled HTTPS on https://app.example.comTest the Certbot automatic SSL certificate renewal process.
console$ sudo certbot renew --dry-run
Restart the Apache web server to apply your SSL configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Test the LAMP Stack Installation
Follow the steps below to set up a new sample table in your existing content_database MySQL database to connect with your PHP application and display the message Hello World! Greetings from Vultr when accessed in a web browser.
Log in to the MySQL console using the sample database user
dbadminyou created earlier.console$ mysql -u dbadmin -p
Enter the
dbadminuser password when prompted to access the MySQL console.Switch to the sample database
content_database.sqlmysql> USE content_database;
Create a new sample table
messageswith two columns,content_idandcontentto store your data.sqlmysql > CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS messages ( content_id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, content VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL );
The above SQL query creates a new table with the following specifications:
content_id: Contains numeric values and automatically increments unique data on each new row.content: Holds mixed content data with up to255characters.
Insert new data to the
messagestable. For example, add a newHello World! Greetings from Vultrstring to thecontentcolumn.sqlmysql > INSERT INTO messages (content) VALUES ('Hello World! Greetings from Vultr');
View all table data to verify that the new string is added to the column.
sqlmysql > SELECT * from messages;
Output:
+----+------------------------------------------+ | content_id | content | +------------+-----------------------------------+ | 1 | Hello World! Greetings from Vultr | +------------+-----------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)Exit the MySQL console.
sqlmysql > EXIT
Create a new sample PHP application file
setup.phpin your web root directory/var/www/html/app.example.com.console$ sudo nano /var/www/html/setup.php
Add the following contents to the file.
php<?php $hostname = "localhost"; $username = "dbadmin"; $password = "Strong@@password123"; $dbname = "content_database"; // Establish Connection $conn = new mysqli($hostname, $username, $password, $dbname); // Check connection if ($conn->connect_error) { die("Connection Failed." . $conn->connect_error); } $sql = "SELECT content FROM messages"; $result = $conn->query($sql); if ($result->num_rows > 0) { $row = $result->fetch_assoc(); echo ""<h2 style='color: blue; text-align: center; margin-bottom: 15px;'>" . htmlspecialchars($row["content"]) . "</h2>"; } else { echo "<h1>No records found.</h1>"; } $conn->close();
Save and close the file.
The above PHP application code connects to the MySQL database
content_databaseand displays data from thecontentcolumn in themessagestable when accessed. When the MySQL database does not contain any records, aNo records foundmessage displays orConnection Failed.when the connection to the database server fails.Grant the Apache user
www-datafull privileges to your web root directory.console$ chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/app.example.com/
Access your domain using the
/setup.phppath in your web browser to verify that your PHP application displays theHello World! Greetings from Vultrstring content from your MySQL database.https://app.example.com/setup.php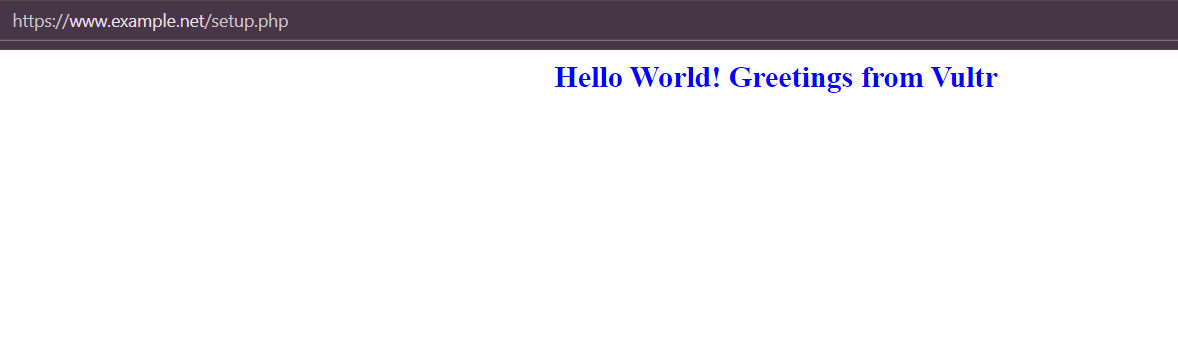
Conclusion
You have installed and configured Apache, MySQL, and PHP (LAMP stack) on your Ubuntu 24.04 server. In addition, you created sample dynamic applications to test access between all LAMP stack components and securely run the applications on your server. For more information and configuration options about each component, visit the following official documentation resources: