How to Install Nginx, MySQL, PHP (LEMP Stack) on Debian 12
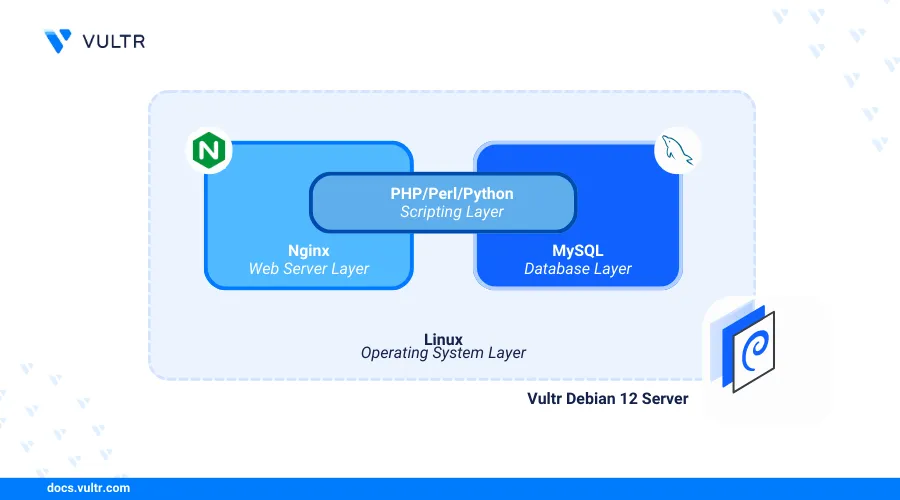
Introduction
Linux, Nginx, MySQL, and PHP (LEMP) Stack is a collection of open source applications that enable the development and deployment of web applications on a server. Linux works as the operating system, Nginx handles webserver functionalities, MySQL manages the database, and PHP processes dynamic web contents.
This article explains how to install the LEMP stack on Debian 12 to deliver dynamic web applications on the server.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- Deploy a Debian 12 instance on Vultr.
- Create a new domain A record pointing to the instance IP address.
- Access the instance using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
- Update the instance.
Install Nginx
Nginx is available in the default package repositories on Debian 12. Follow the steps below to install Nginx using the APT package manager on your server.
Install Nginx.
console$ sudo apt install nginx -y
Verify the installed Nginx version.
console$ nginx -v
Output:
nginx version: nginx/1.22.1Enable Nginx to automatically start at boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable nginx
Start the Nginx service.
console$ sudo systemctl start nginx
View the Nginx service status and verify that it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status nginx
Output:
nginx.service * A high performance webserver and a reverse proxy server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Fri 2024-08-09 06:59:07 UTC; 2min 4s ago Docs: man:nginx(8) Main PID: 1586 (nginx) Tasks: 2 (limit: 4637) Memory: 1.7M CPU: 11ms
Install MySQL
MySQL is not available in the default package repositories on Debian 12. Follow the steps below to add the MySQL repository information and install the database.
Download the latest MySQL package repository setup file.
console$ sudo wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/mysql-apt-config_0.8.32-1_all.deb
Visit the MySQL APT repository page to verify the latest Debian package file to download on your server.
Run the file to install the latest MySQL repository information on your server.
console$ sudo dpkg -i mysql-apt-config_0.8.32-1_all.deb
Select the MySQL Server & Cluster option and press Enter when prompted.
┌─────────────────────────────────┤ Configuring mysql-apt-config ├─────────────────────────────────┐ │ Which MySQL product do you wish to configure? │ │ │ │ MySQL Server & Cluster (Currently selected: mysql-8.4-lts) │ │ MySQL Connectors (Currently selected: Enabled) │ │ Ok │ │ │ │ <Ok> │ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Use Up and Down arrow keys to select your preferred MySQL server version and press Enter. For example, select
mysql-8.4-ltsversion.┌─────────────────────────────────┤ Configuring mysql-apt-config ├─────────────────────────────────┐ │ Which server version do you wish to receive? │ │ │ │ mysql-8.0 │ │ mysql-innovation │ │ mysql-8.4-lts │ │ mysql-cluster-8.0 │ │ mysql-cluster-innovation │ │ mysql-cluster-8.4-lts │ │ None │ │ │ │ <Ok> │ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Press the Down arrow key to select Ok and press Enter to save changes.
┌─────────────────────────────────┤ Configuring mysql-apt-config ├─────────────────────────────────┐ │ Which MySQL product do you wish to configure? │ │ │ │ MySQL Server & Cluster (Currently selected: mysql-8.4-lts) │ │ MySQL Connectors (Currently selected: Enabled) │ │ Ok │ │ │ │ <Ok> │ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Update the server's package index to apply the new MySQL package information.
console$ sudo apt update
Install the MySQL database server package.
console$ sudo apt install mysql-server -y
Enter a new
rootdatabase user password when prompted and press Enter.Enter root password:Enter the password again to validate it and press Enter to update the
rootdatabase user.Re-enter root password:
View the installed MySQL version on your server.
console$ mysql --version
Your output should be similar to the one below.
mysql Ver 8.4.2 for Linux on x86_64 (MySQL Community Server - GPL)Enable the MySQL service to automatically start at system boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable mysql
Start the MySQL system service.
console$ sudo systemctl start mysql
View the MySQL service status and verify that it's running on your server.
console$ sudo systemctl status mysql
Your output should be similar to the one below.
● mysql.service - MySQL Community Server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/mysql.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2024-08-13 20:20:56 UTC; 7min ago Docs: man:mysqld(8) http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/en/using-systemd.html Main PID: 4331 (mysqld) Status: "Server is operational" Tasks: 35 (limit: 2299) Memory: 443.5M CPU: 1.924s CGroup: /system.slice/mysql.service └─4331 /usr/sbin/mysqldRun the MySQL secure installation script to secure the database server.
console$ sudo mysql_secure_installation
Enter the
rootdatabase user password you set earlier and press Enter.Enter password for user root:Enter Y when prompted to setup the VALIDATE PASSWORD component.
Would you like to setup VALIDATE PASSWORD component? Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No: YSet the preferred password strength policy for your MySQL database server. For example, enter 2 to enable the use of strong passwords on your server.
There are three levels of password validation policy: LOW Length >= 8 MEDIUM Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, and special characters STRONG Length >= 8, numeric, mixed case, special characters and dictionary file Please enter 0 = LOW, 1 = MEDIUM and 2 = STRONG: 2Enter N when prompted to change the
rootdatabase user password, or enter Y to change the password.Change the password for root ? ((Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : NEnter Y when prompted to remove anonymous users on your MySQL database server.
Remove anonymous users? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : YEnter Y when prompted to disallow remote login for the
rootuser.Disallow root login remotely? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : YEnter Y when prompted to remove the test database from your MySQL database server.
Remove test database and access to it? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : YEnter Y to reload the MySQL privileges table and apply all configuration changes.
Reload privilege tables now? (Press y|Y for Yes, any other key for No) : YOutput:
All done!
Install PHP and PHP-FPM
PHP is available in the default package repositories on Debian 12. Follow the steps below to install PHP, PHP-FPM, and recommended web application modules on your server.
Install PHP and PHP-FPM.
console$ sudo apt install php php-fpm -y
Install PHP modules.
console$ sudo apt install php-mysql php-cli -y
The above command installs the following PHP modules:
php-mysql: Allows PHP to connect to the MySQL database server and perform SQL operations.php-cli: Enables PHP scripts to run in your terminal session.
View the installed PHP version on your server.
console$ php -v
Your output should be similar to the one below.
PHP 8.2.20 (cli) (built: Jun 17 2024 13:33:14) (NTS) Copyright (c) The PHP Group Zend Engine v4.2.20, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies with Zend OPcache v8.2.20, Copyright (c), by Zend TechnologiesStart the PHP-FPM service depending on your installed PHP version. For example, PHP
8.2.console$ sudo systemctl start php8.2-fpm
Enable PHP-FPM to start automatically at system boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable php8.2-fpm
View the PHP-FPM service status and verify that it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status php8.2-fpm
Output:
● php8.2-fpm.service - The PHP 8.2 FastCGI Process Manager Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/php8.2-fpm.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Tue 2024-08-13 20:40:54 UTC; 1min 52s ago Docs: man:php-fpm8.2(8) Main PID: 13661 (php-fpm8.2) Status: "Processes active: 0, idle: 2, Requests: 0, slow: 0, Traffic: 0.00req/sec" Tasks: 3 (limit: 2299) Memory: 9.5M CPU: 31ms CGroup: /system.slice/php8.2-fpm.service ├─13661 "php-fpm: master process (/etc/php/8.2/fpm/php-fpm.conf)" ├─13662 "php-fpm: pool www" └─13663 "php-fpm: pool www"
Configure PHP-FPM
PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) is a process manager for PHP that handles webserver requests for dynamic PHP applications. PHP-FPM offers several enhancements, including process management, server-specific configuration, and improved performance. Follow the steps below to configure PHP-FPM on your server.
Open the default PHP-FPM pool
www.confconfiguration using a text editor such asnano.console$ sudo nano /etc/php/8.2/fpm/pool.d/www.conf
View the PHP-FPM pool name and verify that it's set to
www.ini[www]Find the following directives and verify that the values are set to
www-data.iniuser = www-data group = www-data listen.owner = www-data listen.group = www-data
Find the
listendirective and verify that it is set to the PHP-FPM unix socket path/run/php/php8.2-fpm.sock.inilisten = /run/php/php8.2-fpm.sock
Find the following directives and modify the values depending on your server specifications and available resources.
pm: Specifies the process manager type. Thedynamicvalue allows PHP child processes to adjust automatically based on server needs.pm.max_children: Defines the maximum number of PHP child processes to run simultaneously.pm.start_servers: Sets the number of child processes created on startup, providing an initial pool to handle requests.pm.min_spare_servers: Sets the minimum number of idle child processes. If the number of idle processes is less than the specified value, new child processes are created.pm.max_spare_servers: Sets the maximum number of idle child processes allowed. If the number of idle child processes exceeds the specified value, the excess idle child processes are stopped.
Save and close the file.
Restart the PHP-FPM service to apply your configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart php8.2-fpm
Configure Nginx With PHP-FPM
Follow the steps below to configure Nginx to process PHP scripts by creating a new virtual host configuration that connects to the PHP-FPM service to process dynamic application requests.
Create a new virtual host configuration file in the
/etc/nginx/sites-available/directory.console$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/app.example.com
Add the following contents to the file. Replace
app.example.comwith your actual domain.nginxserver { listen 80; server_name app.example.com; root /var/www/app.example.com; index index.php index.html index.htm; location / { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } location ~ \.php$ { include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf; fastcgi_pass unix:/var/run/php/php-fpm.sock; } location ~ /\.ht { deny all; } }
Save and close the file.
The above Nginx configuration creates a new virtual host that listens for connections using the
app.example.comdomain and delivers web application files from the/var/www/app.example.comdirectory. All PHP file requests are forwarded to the/var/run/php/php-fpm.sockPHP-FPM Unix socket for processing.Create a new symbolic link to the
/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/directory to activate the virtual host configuration.console$ sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/app.example.com /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
Test the Nginx configuration for errors.
console$ sudo nginx -t
Output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successfulReload Nginx to apply the configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl reload nginx
Create a new web root directory to store your web application files.
console$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/app.example.com
Create a new
phpinfo.phpweb application file in the directory.console$ sudo nano /var/www/app.example.com/phpinfo.php
Add the following contents to the file.
php<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Save and close the file.
The above application displays the PHP information on your server when accessed using your virtual host's domain.
Allow HTTP connections through the firewall.
console$ sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
Reload UFW to apply changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
Access the
/phpinfodomain path using a web browser such as Chrome.http://app.example.com/phpinfo.php
Set Up Firewall Rules
Uncomplicated Firewall (UFW) is active and available on Vultr Debian servers by default. Follow the steps below to allow connections to the HTTP and HTTPS ports to enable Nginx deliver web application on the server.
View the UFW status and verify that it's active.
console$ sudo ufw status
Output:
Status: activeAllow HTTP and HTTPS connections on the server using the
Nginx Fullservice profile.console$ sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'
View the UFW status and verify that the new rules are available.
console$ sudo ufw status
Output:
Status: active To Action From -* -----* ---- Nginx Full ALLOW Anywhere Nginx Full (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Test the LEMP Stack Installation
Nginx processes HTTP requests and forwards them to PHP-FPM for handling. The php-mysql extension connects PHP to the MySQL database, enabling data retrieval and storage. Follow these steps to create a PHP application that displays a 'Greetings from Vultr' message retrieved from your MySQL database.
Log in to the MySQL database server as the
rootdatabase user.console$ mysql -u root -p
Create a new
test_dbdatabase.sqlmysql> CREATE DATABASE test_db;
Switch to the
test_dbdatabase.sqlmysql> USE test_db;
Create a new sample database user
test_userwith a strong password. ReplaceStrong)P@ssword123with your desired password.sqlmysql> CREATE USER 'test_user'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Strong)P@ssword123';
Grant the user full privileges to the
test_dbdatabase.sqlmysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON test_db.* TO 'test_user'@'localhost';
Reload the MySQL privileges table to apply changes.
sqlmysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Create a new
greetingstable with two columns:id(for numeric data) andmessage(for text):sqlmysql> CREATE TABLE greetings (id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY, message VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL);
Insert a
Greetings from Vultrrecord into thegreetingstable.sqlmysql> INSERT INTO greetings (message) VALUES ('Greetings from Vultr');
Query the
greetingstable to verify that the records are available.sqlmysql> SELECT * FROM greetings;
Output:
+----+----------------------+ | id | message | +----+----------------------+ | 1 | Greetings from Vultr | +----+----------------------+Exit the MySQL console.
sqlEXIT;
Create a new PHP application file
greetings.phpin your/var/www/app.example.com/web root directory.console$ sudo nano /var/www/app.example.com/greetings.php
Add the following contents to the file.
php<?php $servername = "localhost"; $username = "test_user"; $password = "Strong)P@ssword123"; $dbname = "test_db"; // Create database connection $conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password, $dbname); // Check database connection if ($conn->connect_error) { die("Database Connection Failed: " . $conn->connect_error); } // Retrieve the record from greetings Table $sql = "SELECT message FROM greetings"; $result = $conn->query($sql); if ($result->num_rows > 0) { $row = $result->fetch_assoc(); echo "<h1 align='center'>" . $row["message"]. "</h1>"; } else { echo "<h1 align='center'>No message found.</h1>"; } $conn->close(); ?>
Save and close the file.
The above application code displays a
Greetings from Vultrmessage from the MySQL database when accessed using your virtual host's domain.Access the
/greetings.phpdomain path to test access to the PHP application.http://app.example.com/greetings.php
Conclusion
You have installed the LEMP stack on your Debian 12 server. You set up Nginx as the webserver, MySQL as the database backend, and PHP with PHP-FPM to process dynamic web application contents. For more information and configuration options for each application within the stack, visit the following resources.