Introduction
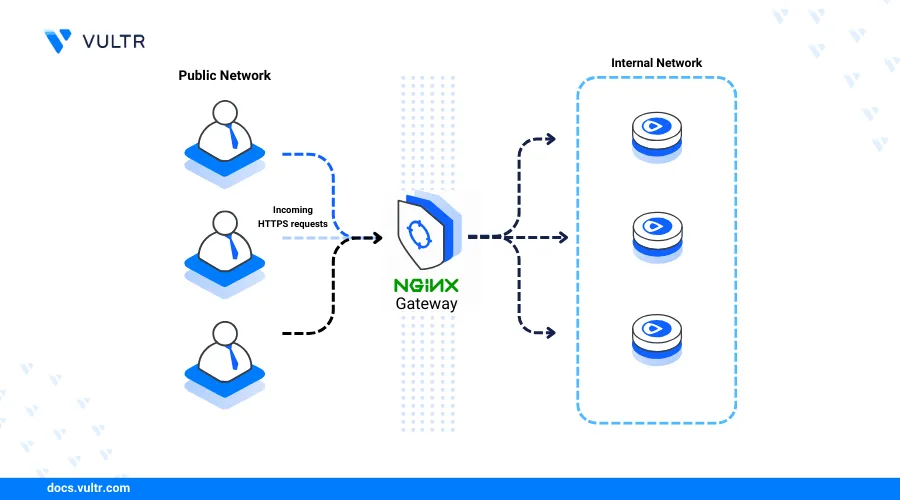
Nginx is an open-source, high-performance web server application widely used for hosting websites, reverse proxying, and load balancing to efficiently manage high traffic. It supports modern protocols like HTTP/2 and HTTPS, enabling the secure serving of static and dynamic web content, caching, and traffic encryption with SSL/TLS. To leverage its flexibility, scalability, and reliability, you can easily install Nginx webserver on Rocky Linux 9, making it a preferred choice for a wide range of web applications, from small websites to large-scale enterprise solutions.
This article explains how to install the Nginx webserver on Rocky Linux 9 and set up virtual hosts to run web applications on the server.
Install Nginx on Rocky Linux 9
Nginx is available in the default package repositories on Rocky Linux 9. Follow the steps below to update the server's package index and install Nginx using the dnf package manager.
Update the server's package information index.
console$ sudo dnf update
Install Nginx.
console$ sudo dnf install nginx -y
View the installed Nginx version.
console$ sudo nginx -version
Output:
nginx version: nginx/1.20.1Allow network connections to the HTTP port
80through the default firewall.console$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
Reload
firewall-cmdto apply the firewall changes.console$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Manage the Nginx System Service
The nginx systemd service profile controls the webserver's runtime and processes on a server. Follow the steps below to enable the Nginx system service to start at boot and manage it on your server.
Enable the Nginx service to automatically start at boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable nginx
Output:
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.Start the Nginx service.
console$ sudo systemctl start nginx
View the Nginx service status and verify that it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status nginx
Output:
● nginx.service - A high performance webserver and a reverse proxy server Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Sat 2024-08-24 07:00:58 UTC; 1min 35s ago Docs: man:nginx(8) Process: 2560 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t -q -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 2561 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on; (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 2584 (nginx) Tasks: 2 (limit: 1091) Memory: 1.7M CPU: 12ms CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service ├─2584 "nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_process on;" └─2585 "nginx: worker process"The Nginx service is active and running based on the above
Active: active (running)output.Stop the Nginx service.
console$ sudo systemctl stop nginx
Restart the Nginx service.
console$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Access your server's IP using a web browser such as Chrome to verify that the default Nginx page displays.
http://SERVER-IP
Create a New Nginx Virtual Host Configuration
Nginx virtual host configurations enable the webserver to map web application directories to specific network addresses or domains on a server. A virtual host configuration consists of multiple directives that include the server name, webroot directory, log paths, and index pages used to serve web applications. Follow the steps below to create a new Nginx virtual host to serve a basic HTML web application using the app.example.com domain.
Create a new virtual host webroot directory such as
app.example.com.console$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/app.example.com
Create a new
index.htmlweb application file in the directory.console$ sudo nano /var/www/html/app.example.com/index.html
Add the following HTML application contents to the file.
html<html> <head></head> <body> <h1>Greetings from Vultr</h1> </body> </html>
Save and close the file.
The above HTML web application displays a "Greetings from Vultr" message when accessed using the
app.example.comvirtual host domain.Grant the
nginxwebserver user and group ownership privileges to the webroot directory.console$ sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www/html/app.example.com
Create a new
app.example.com.confNginx virtual host configuration in the/etc/nginx/conf.ddirectory.console$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/app.example.com.conf
Add the following configurations to the file. Replace
app.example.comwith your actual domain.nginxserver { listen 80; listen [::]:80; server_name app.example.com; root /var/www/html/app.example.com; index index.html; location / { try_files $uri $uri/ =404; } }
Save and close the file.
The above Nginx configuration creates a new virtual host that listens for incoming connections using the
app.example.comdomain and delivers web application files from the/var/www/html/app.example.comwebroot directory.Test the Nginx configuration for errors.
console$ sudo nginx -t
Output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successfulReload the Nginx service to apply the configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl reload nginx
View the SELinux status on your server and verify that it's set to
Enforcing.console$ getenforceOutput:
EnforcingSet the
httpd_sys_content_tcontext on the webroot directory to allow Nginx to read the directory files.console$ sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t "/var/www/html/app.example.com(/.*)?"
Apply the SELinux context.
console$ sudo restorecon -R /var/www/html/app.example.com
Access your domain in a new web browser window and verify that the HTML web application displays.
http://app.example.com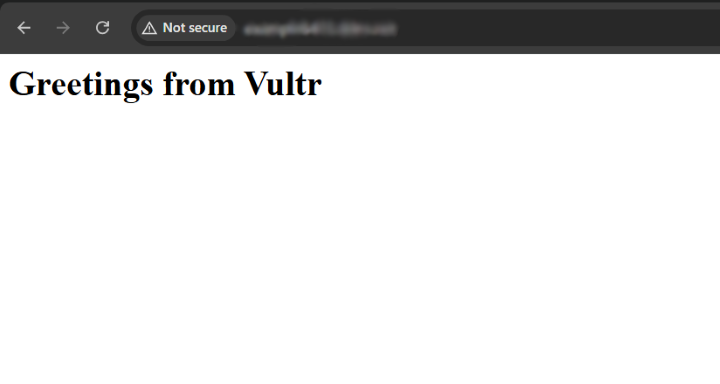
Set Up Firewall Rules
Firewalld is available and active on Vultr Rocky Linux instances by default. Follow the steps below to configure the firewall to allow incoming HTTP and HTTPS network connections to the server.
Allow HTTP service through the firewall.
console$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
Allow HTTPS service through the firewall.
console$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=https
Reload the firewall to apply the changes.
console$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
List all active firewall rules and verify that HTTP and HTTPS connections are allowed.
console$ sudo firewall-cmd --list-all
Output:
public (active) target: default icmp-block-inversion: no interfaces: enp1s0 sources: services: cockpit dhcpv6-client http https ssh ports: protocols: forward: yes masquerade: no forward-ports: source-ports: icmp-blocks: rich rules:
Secure the Nginx Web Server
SSL certificates encrypt network connections between a user's web browser and the Nginx web server using HTTPS. Nginx listens for incoming connections using HTTP which is insecure by default. To secure network connections to the server using HTTPS, generate SSL certificates using a trusted certificate authority such as Let's Encrypt. Follow the steps to install the Certbot Let's Encrypt client and generate trusted SSL certificates to secure the Nginx web server.
Install the Certbot Let's Encrypt client tool and the Nginx plugin.
console$ sudo dnf install certbot python3-certbot-nginx -y
Generate new SSL certificates using the Nginx plugin. Replace
app.example.comwith your actual domain andhello@example.comwith your active email address.console$ sudo certbot --nginx -d app.example.com -m hello@example.com --agree-tos
Verify that Certbot autorenews the SSL certificate before expiry.
console$ sudo certbot renew --dry-run
Restart Nginx to apply the configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Access your
app.example.comvirtual host domain using HTTPS and verify that your web application loads correctly.https://app.example.com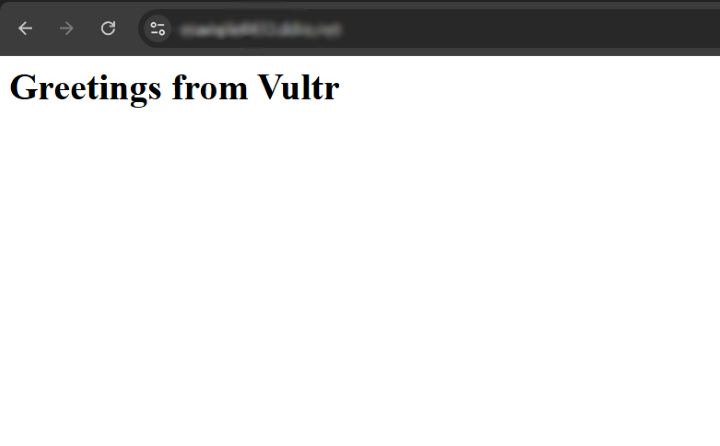
Conclusion
You have installed the Nginx web server on Rocky Linux 9 and created virtual host configurations to deliver web applications on the server. You can integrate Nginx with other application frameworks such as PHP to deliver dynamic web applications. In addition, you can use Nginx as a webserver, load balancer, or reverse proxy to securely serve backend applications. For more information and configuration options, visit the Nginx documentation.