
PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is a widely used server-side scripting language for building dynamic web applications. PHP 5.6 is an older, end-of-life release that is still required for maintaining certain legacy applications that depend on deprecated features or extensions. It lacks the security and performance improvements of newer PHP versions but remains in use where application upgrades are not yet possible.
This article explains how to install PHP 5.6 and PHP-FPM on FreeBSD 14.0 by compiling from source, as PHP 5.6 is unavailable in the default pkg repositories. It also covers testing the setup with a basic PHP file.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, you need to:
- Have access to a FreeBSD 14.0 as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Install Required Dependencies
This section covers installing the necessary build tools and libraries for compiling PHP 5.6.
Update the package index.
console$ sudo pkg update
Install build dependencies.
console$ sudo pkg install -y gcc autoconf libxml2 curl png freetype2 gmp readline libxslt icu
Compile and Install PHP 5.6
Due to changes in system libraries, PHP 5.6 requires compatibility patches to compile on FreeBSD 14.0. This section explains how to compile PHP 5.6 from the source with the required dependencies.
Switch to the
/tmpdirectory.console$ cd /tmp
Download the PHP 5.6.40 source code, which is the final release of the 5.6 branch. You can find additional PHP 5.x versions at the PHP Museum archive.
console$ fetch https://museum.php.net/php5/php-5.6.40.tar.gz
Extract the PHP source.
console$ tar -xzf php-5.6.40.tar.gz
Enter the PHP directory.
console$ cd php-5.6.40
Apply compatibility patches for FreeBSD 14. PHP 5.6 has compatibility issues with modern
libxml2in FreeBSD 14. Apply the following fixes to resolve compilation errors.Fix
ATTRIBUTE_UNUSEDmacro compatibility. This patch removes an unnecessary macro that causes an error with modern compilers.console$ sed -i.bak 's/int compression ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)/int compression)/' ext/libxml/libxml.c
Fix
xmlStructuredErrorFunctype casting. This patch adds an explicit type cast to resolve a function pointer mismatch.console$ sed -i.bak 's/xmlSetStructuredErrorFunc(NULL, php_libxml_structured_error_handler);/xmlSetStructuredErrorFunc(NULL, (xmlStructuredErrorFunc)php_libxml_structured_error_handler);/' ext/libxml/libxml.c
Fix
xmlGetLastErrorreturn type. This patch adds an explicit type cast to the return value ofxmlGetLastErrorto match the newerlibxml2library's definition.console$ sed -i.bak 's/error = xmlGetLastError();/error = (xmlErrorPtr)xmlGetLastError();/' ext/libxml/libxml.c
Configure PHP with FPM support and disable DOM.
console$ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/php-5.6.40 --enable-mbstring --with-pdo-mysql --with-mysqli --enable-fpm --disable-dom
The --disable-dom flag avoids compilation errors due to type mismatches with modernNotelibxml2. Omit this if DOM support is required and you've resolved the dependency manually.Compile PHP.
console$ make -j$(sysctl -n hw.ncpu)
Install PHP.
console$ sudo make install
Verify PHP installation.
console$ /usr/local/php-5.6.40/bin/php -v
Quick Test with PHP Built-in Server
This section covers testing the PHP CLI using the built-in development server.
Create a new sample test file named
info.php.console$ vi /tmp/info.php
Add the following PHP code to the file.
php<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Save and exit the file.
Launch the PHP built-in server.
console$ /usr/local/php-5.6.40/bin/php -S 0.0.0.0:8080 -t /tmp
This command starts the PHP built-in web server. The
-Sflag specifies the address and port to listen on.0.0.0.0means it will listen on all available network interfaces. The-tflag sets the document root to the/tmpdirectory, where theinfo.phpfile is located.In your browser, visit
http://SERVER-IP:8080/info.php.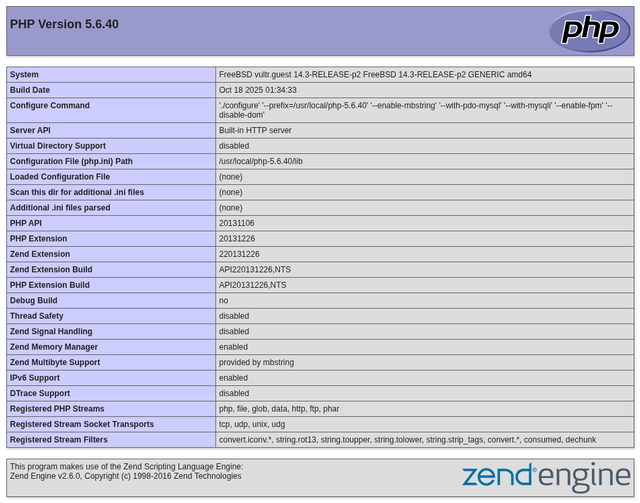
You should see the PHP configuration page. When you are done, press Ctrl + C to stop the server.
Remove the test file after verification.
console$ sudo rm /tmp/info.php
Compile and Install PHP 5.6 FPM
This section explains how to install and configure PHP-FPM.
Return to the PHP source directory.
console$ cd /tmp/php-5.6.40
The PHP source code includes two sample configuration files,
php.ini-developmentandphp.ini-production. Copy the production PHP configuration file.console$ sudo cp php.ini-production /usr/local/php-5.6.40/lib/php.ini
Create PHP-FPM configuration directory.
console$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/php-5.6.40/etc/php-fpm.d
Create the main PHP-FPM configuration file.
console$ sudo vi /usr/local/php-5.6.40/etc/php-fpm.conf
Add the following content.
ini[global] pid = /var/run/php56-fpm.pid error_log = /var/log/php56-fpm.log include=/usr/local/php-5.6.40/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf
Save and close the file.
Create the PHP-FPM pool configuration file.
console$ sudo vi /usr/local/php-5.6.40/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
Add the following content.
ini[www] user = www group = www listen = 127.0.0.1:9000 listen.owner = www listen.group = www listen.mode = 0660 pm = dynamic pm.max_children = 5 pm.start_servers = 2 pm.min_spare_servers = 1 pm.max_spare_servers = 3
Save and close the file.
Add PHP to PATH.
console$ echo 'PATH="/usr/local/php-5.6.40/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.shrc
Reload the shell configuration.
console$ . ~/.shrc
Create a PHP-FPM user.
console$ sudo pw user show www || sudo pw user add -n www -s /sbin/nologin -c "PHP-FPM User"
Create the
rc.ddirectory if it doesn't exist.console$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/etc/rc.d
Create a service script for PHP-FPM.
console$ sudo vi /usr/local/etc/rc.d/php56_fpm
Add the following service script.
ini#!/bin/sh # # PROVIDE: php56_fpm # REQUIRE: LOGIN # KEYWORD: shutdown . /etc/rc.subr name="php56_fpm" rcvar="php56_fpm_enable" start_cmd="php56_fpm_start" stop_cmd="php56_fpm_stop" status_cmd="php56_fpm_status" php56_fpm_start() { if [ -x "/usr/local/php-5.6.40/sbin/php-fpm" ]; then echo "Starting php56-fpm." /usr/local/php-5.6.40/sbin/php-fpm \ -c /usr/local/php-5.6.40/lib/php.ini \ --fpm-config /usr/local/php-5.6.40/etc/php-fpm.conf sleep 1 else echo "Error: /usr/local/php-5.6.40/sbin/php-fpm not found or not executable." exit 1 fi } php56_fpm_stop() { if [ -f "/var/run/php56-fpm.pid" ]; then echo "Stopping php56-fpm." kill -TERM "$(cat /var/run/php56-fpm.pid)" else echo "php56-fpm is not running (PID file not found)." fi } php56_fpm_status() { if [ -f "/var/run/php56-fpm.pid" ]; then _pid="$(cat /var/run/php56-fpm.pid)" if ps -p "$_pid" > /dev/null; then echo "php56_fpm is running as pid $_pid." else echo "php56_fpm is not running (PID file exists but process is gone)." fi else echo "php56_fpm is not running." fi } load_rc_config $name run_rc_command "$@"
Save and close the file.
Set permissions for the service script.
console$ sudo chmod +x /usr/local/etc/rc.d/php56_fpm
Enable PHP-FPM.
console$ sudo sysrc php56_fpm_enable="YES"
Start PHP-FPM.
console$ sudo service php56_fpm start
Verify PHP-FPM status.
console$ sudo service php56_fpm status
Test and Use PHP 5.6
This section covers testing PHP 5.6 by creating a sample file and accessing it via Nginx.
Install Nginx.
console$ sudo pkg install -y nginx
Create the web root directory.
console$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/www/php56
Configure Nginx to process PHP files.
console$ sudo vi /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Find the default
serverblock inside thehttp {}block. Make the following changes:Set the
server_nameto your server's IP address or domain name.Change the
rootdirective to/usr/local/www/php56, which is the directory you created earlier.Add
index.phpto theindexdirective.Add the following
locationblock to handle PHP files:inilocation ~ \.php$ { fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; }
Save and close the file.
Test Nginx configuration.
console$ sudo nginx -t
Enable Nginx.
console$ sudo sysrc nginx_enable="YES"
Start Nginx.
console$ sudo service nginx start
Create a test PHP file.
console$ sudo vi /usr/local/www/php56/index.php
Add the following PHP code to the file.
php<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Save and close the file.
Visit
http://SERVER-IP/in your browser to view PHP information.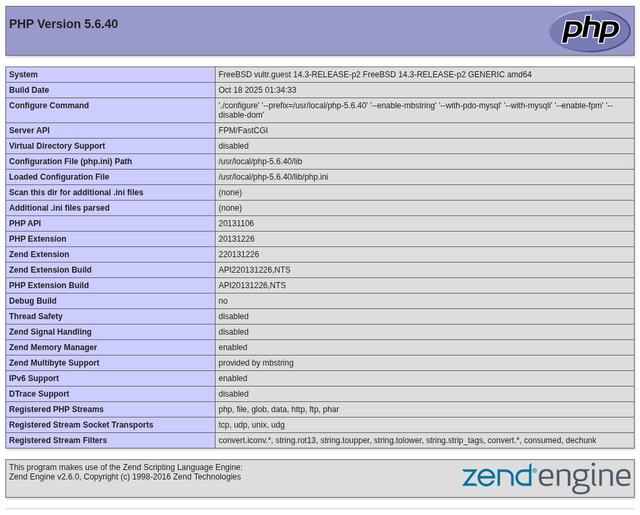
You should see the PHP information page displaying PHP 5.6.40 with details about the installation, loaded extensions, and configuration.
Conclusion
This article explained how to install PHP 5.6 and PHP-FPM on FreeBSD 14.0 by compiling from the source and applying necessary compatibility patches. You configured Nginx to process PHP files and verified the setup with a test page. To extend this setup, consider adding more PHP extensions or integrating it with a database like MySQL. For more details, check the PHP documentation.