How to Install PHP 5.6 on Ubuntu 24.04
PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is an open-source server-side scripting language widely used for web development. It enables developers to build dynamic websites, process form data, manage sessions, and integrate with databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL. PHP is highly extensible and supports multiple extensions you can use to build modern web applications.
This article explains how to install PHP 5.6 on Ubuntu 24.04. While PHP 5.6 has reached end-of-life, multiple applications still depend on it. You will install PHP 5.6 and configure PHP-FPM to integrate it with applications such as web servers.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, you need to:
- Have access to an Ubuntu 24.04 instance as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
- Create a domain A record pointing to your instance's public IP address.
Add the PHP PPA Repository
PHP 5.6 reached its end of life (EOL), and it's not available in the official Ubuntu repositories by default. However, you can still install it through the Ondřej Surý Personal Package Archive (PPA) source.
Add PHP PPA to the APT package repository sources.
console$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php
Update the APT package index.
console$ sudo apt update
Install PHP 5.6
Follow the steps below to install PHP 5.6 and all necessary dependencies.
Install PHP 5.6, along with the command-line interface (CLI) and common PHP modules.
console$ sudo apt install php5.6 php5.6-cli php5.6-common -y
Verify the installed PHP version.
console$ php -v
Your output should be similar to the one below.
PHP 5.6.40-81+ubuntu24.04.1+deb.sury.org+1 (cli) Copyright (c) 1997-2016 The PHP Group Zend Engine v2.6.0, Copyright (c) 1998-2016 Zend Technologies with Zend OPcache v7.0.6-dev, Copyright (c) 1999-2016, by Zend TechnologiesIf multiple PHP versions are installed on your workstation, useNotesudo update-alternatives --config phpto set PHP 5.6 as the default version.
Install PHP 5.6 FPM
PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) handles PHP script execution efficiently when integrating it with web servers like Apache or Nginx. PHP-FPM is a process manager that runs PHP as a separate background service, handling requests independently from the web server, resulting in improved performance. Follow the steps below to install PHP 5.6 FPM to use it with other applications like web servers.
Install PHP-FPM for PHP 5.6.
console$ sudo apt install php5.6-fpm -y
Start the PHP-FPM service.
console$ sudo systemctl start php5.6-fpm
Enable the PHP-FPM service to automatically start at boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable php5.6-fpm
View the PHP-FPM service status and verify that it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status php5.6-fpm
Your output should be similar to the one below.
● php5.6-fpm.service - The PHP 5.6 FastCGI Process Manager Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/php5.6-fpm.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Thu 2025-03-20 12:35:08 UTC; 33min ago Docs: man:php-fpm5.6(8) Main PID: 47045 (php-fpm5.6) Status: "Processes active: 0, idle: 2, Requests: 0, slow: 0, Traffic: 0req/sec" Tasks: 3 (limit: 2265) Memory: 10.2M (peak: 11.4M) CPU: 260ms CGroup: /system.slice/php5.6-fpm.service ├─47045 "php-fpm: master process (/etc/php/5.6/fpm/php-fpm.conf)" ├─47047 "php-fpm: pool www" └─47048 "php-fpm: pool www"
Test and Use PHP 5.6
You can use PHP in different environments, such as the command line, interactive shells, and web server applications. Follow the steps below to test and verify the PHP installation on your server.
Create a new
test.phpfile in your web root directory, such as/var/www/html.console$ sudo nano /var/www/html/test.php
Add the following PHP code to the file.
php<?php echo "Greetings from Vultr! \n"; ?>
Save and close the file.
Execute the PHP script.
console$ php /var/www/html/test.php
Output:
Greetings from Vultr!
Test PHP 5.6 with a Web Server
Follow the steps below to run PHP 5.6 with a web server such as Apache.
Create a new
phpinfo.phpfile in your web root directory, such as/var/www/html.console$ sudo nano /var/www/html/phpinfo.php
Add the following PHP code to the file.
php<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Save and close the file.
Enable the
proxy_fcgimodule for Apache to communicate with PHP-FPM and thesetenvifmodule to manage environment variables.console$ sudo a2enmod proxy_fcgi setenvif
Restart the Apache service to apply the module changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Open the
000-default.confApache virtual host configuration.console$ sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
Add the following configuration block within the
<VirtualHost *:80>section to enable Apache to process PHP requests using the PHP 5.6 FPM socket.apacheconf<FilesMatch \.php$> SetHandler "proxy:unix:/var/run/php/php5.6-fpm.sock|fcgi://localhost/" </FilesMatch>
Save and close the file.
Test the Apache configuration for syntax errors.
console$ sudo apache2ctl -t
Output:
... Syntax OKRestart the Apache web server to apply the changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Allow HTTP connections through the firewall.
console$ sudo ufw allow 80
Reload the firewall configuration.
console$ sudo ufw reload
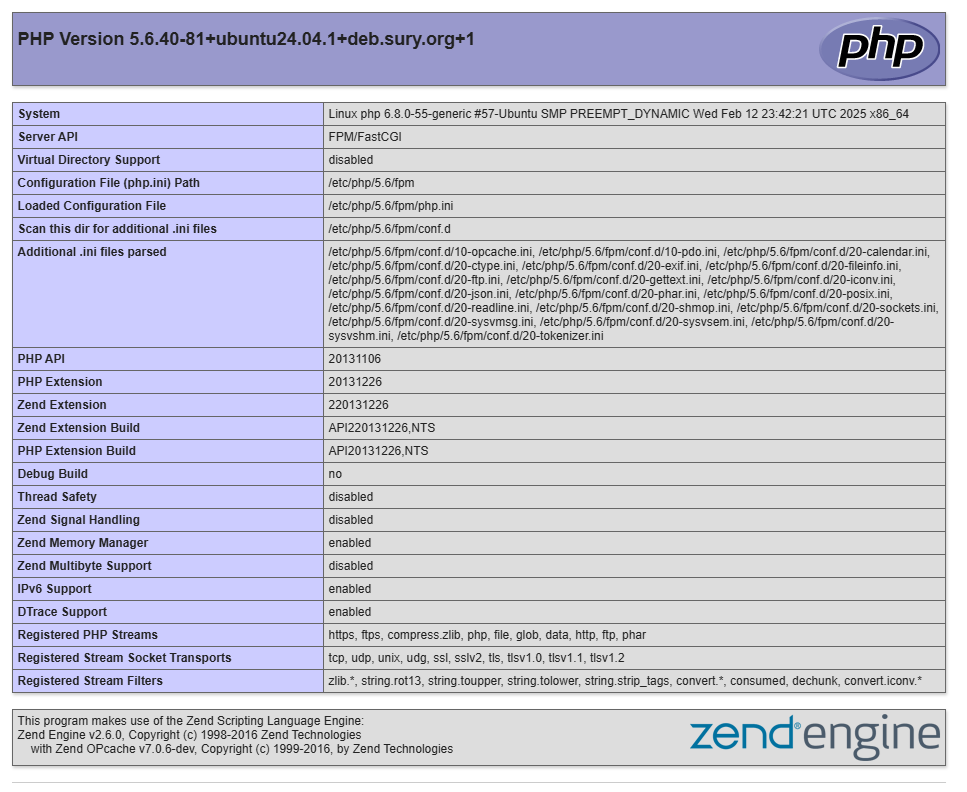
Access the
/phpinfo.phppath using your server's IP address in a web browser such as Chrome.http://app.example.com/phpinfo.phpVerify that your PHP 5.6 information displays in the web browser and all installed extensions.
Conclusion
You have installed PHP 5.6 on Ubuntu 24.04 and configured it to run with PHP-FPM. You can execute PHP scripts from the command line, the PHP shell, or serve applications on your web server using Apache or Nginx. Visit the PHP 5 Documentation for more information.