Introduction
PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) is a popular general-purpose server-side scripting language for developing dynamic and interactive web applications. PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) enhances PHP performance to handle heavy loads through advanced process management, worker pools, and more. On Debian 12, a stable and secure Linux distribution, installing PHP and PHP-FPM ensures efficient handling of complex web applications while maximizing server performance.
This article explains how to install PHP and PHP-FPM on Debian 12, helping you create an environment for dynamic and interactive web development. If you're working on different systems, you may also explore our articles on Install PHP and PHP-FPM on Ubuntu 24.04 and Install PHP and PHP-FPM on FreeBSD 14.0.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- Deploy a Debian 12 Cloud Compute instance on Vultr.
- Access the instance using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Install PHP on Debian 12
PHP is available in the default package repositories on Debian 12, but the available version might be out-of-date. Follow the steps below to download the SURY PHP PPA repository, which includes the latest PHP package information and install PHP 8.3 on Debian 12. While this guide focuses on PHP 8.3, the repository also supports other versions like PHP 7.4, PHP 8.0, PHP 8.1, PHP 8.2, and the latest PHP 8.4 on Debian 12.
Update the server's package information index.
console$ sudo apt update -y
Upgrade all existing packages.
console$ sudo apt upgrade -y
Install the necessary dependency packages for HTTPS transport and certificate management.
console$ sudo apt -y install lsb-release apt-transport-https ca-certificates
Download the SURY GPG key.
console$ wget -O /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/php.gpg https://packages.sury.org/php/apt.gpg
Add the SURY PPA repository information to your APT sources.
console$ echo "deb https://packages.sury.org/php/ $(lsb_release -sc) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/php.list
Update the server's package information index to apply the repository changes.
console$ sudo apt update -y
View all the available PHP versions in the APT repository sources.
console$ sudo apt policy php
Output:
php: Installed: (none) Candidate: 2:8.3+94+0~20240205.51+debian12~1.gbp6faa2e Version table: 2:8.3+94+0~20240205.51+debian12~1.gbp6faa2e 500 500 https://packages.sury.org/php bookworm/main amd64 Packages 2:8.2+93 500 500 https://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm/main amd64 Packages 500 https://debian.mirror.constant.com bookworm/main amd64 PackagesFrom the above output, PHP 8.3 is the latest version you can install from the SURY PPA repository.
Install the latest PHP version.
console$ sudo apt install -y php
Verify the PHP version.
console$ php -v
Output:
PHP 8.3.9 (cli) (built: Jul 8 2024 10:27:02) (NTS)
Install PHP Extensions on Debian 12
PHP extensions add functionalities for running most dynamic web applications. Follow the steps below to install common PHP extensions.
Install PHP extensions.
console$ sudo apt install -y php-mysql php-curl php-json php-xml php-mbstring
The above command installs the following PHP extensions:
php-mysql: Connects PHP with MySQL databases.php-curl: Allows PHP to create HTTP requests.php-json: Enables PHP to handle JSON data.php-xml: Enables support for XML data.php-mbstring: Manages multi-byte strings.
View the available extensions on your server.
console$ php -m
Output:
[PHP Modules] ... curl json mbstring mysqli xml ... [Zend Modules] Zend OPcache
Install and Configure PHP-FPM on Debian 12
PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) manages the connection between PHP and other applications, such as web servers, to process dynamic content. Follow the steps below to install and configure PHP-FPM based on the PHP version on your server.
Install PHP-FPM.
console$ sudo apt install -y php-fpm
Enable PHP-FPM to automatically start at boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable php8.3-fpm
Start the PHP-FPM service.
console$ sudo systemctl start php8.3-fpm
Verify the PHP-FPM service status and verify that it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status php8.3-fpm
Output:
● php8.3-fpm.service - The PHP 8.3 FastCGI Process Manager Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/php8.3-fpm.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2024-07-29 07:16:08 UTC; 20s ago Docs: man:php-fpm8.3(8) Main PID: 28097 (php-fpm8.3) Status: "Processes active: 0, idle: 2, Requests: 0, slow: 0, Traffic: 0.00req/sec" Tasks: 3 (limit: 9468) Memory: 13.5M CPU: 64ms CGroup: /system.slice/php8.3-fpm.service ├─28097 "php-fpm: master process (/etc/php/8.3/fpm/php-fpm.conf)" ├─28098 "php-fpm: pool www" └─28099 "php-fpm: pool www"
Test PHP and PHP-FPM
Follow the steps below to create a sample application to display the available PHP version information.
Install Apache web server package.
console$ sudo apt install -y apache2
Start the Apache web server.
console$ sudo systemctl start apache2
Create a new
info.phpPHP application file in the default/var/www/htmlweb root directory.console$ sudo nano /var/www/html/info.php
Add the following contents to the file.
php<?php echo "<br><h1 align='center'> Greetings from Vultr </h1>"; ?>
Save and close the file.
Enable the PHP-FPM configuration for Apache.
console$ sudo a2enconf php8.3-fpm
Output:
Enabling conf php8.3-fpm. To activate the new configuration, you need to run: systemctl reload apache2Allow network connections to the Apache HTTP port
80through the firewall.console$ sudo ufw allow 80/tcp
Reload UFW to apply the new changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
Open a web browser such as Chrome and access your server's public IP address. Then, load the
/info.phpfile to access the PHP application.http://SERVER-IP/info.php
Install Multiple PHP Versions
Multiple web development projects may require specific PHP versions to run on your server. Follow the steps below to install multiple PHP versions and use separate PHP-FPM pools to manage each PHP version.
Install PHP 8.0 and common extensions.
console$ sudo apt install -y php8.0 php8.0-fpm php8.0-mysql php8.0-curl php8.0-xml php8.0-mbstring
Enable PHP-FPM for PHP 8.0 to automatically start at boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable php8.0-fpm
Start the PHP-FPM service for PHP 8.0.
console$ sudo systemctl start php8.0-fpm
Install PHP 7.4 and common extensions.
console$ sudo apt install -y php7.4 php7.4-fpm php7.4-mysql php7.4-curl php7.4-json php7.4-xml php7.4-mbstring
Enable PHP-FPM for PHP 7.4 to start at boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable php7.4-fpm
Start the PHP-FPM service for PHP 7.4.
console$ sudo systemctl start php7.4-fpm
Enable the PHP 8.0 FPM configuration for Apache.
console$ sudo a2enconf php8.0-fpm
Enable the PHP 7.4 FPM configuration.
console$ sudo a2enconf php7.4-fpm
Restart Apache to apply the configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart apache2
Create a new Apache virtual host configuration file.
console$ sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/php-multi.conf
Add the following configurations to the file.
apache<VirtualHost *:80> DocumentRoot /var/www/html <Directory /var/www/html> Options Indexes FollowSymLinks AllowOverride None Require all granted </Directory> <Location /php83> ProxyPass "unix:/run/php/php8.3-fpm.sock|fcgi://localhost/var/www/html/php83" </Location> <Location /php80> ProxyPass "unix:/run/php/php8.0-fpm.sock|fcgi://localhost/var/www/html/php80" </Location> <Location /php74> ProxyPass "unix:/run/php/php7.4-fpm.sock|fcgi://localhost/var/www/html/php74" </Location> </VirtualHost>
Save and close the file.
The above Apache virtual host configuration listens for connection requests on all server interfaces and forwards specific requests to the appropriate PHP-FPM version for processing.
Disable the default Apache virtual host.
console$ sudo a2dissite 000-default.conf
Enable the new virtual host.
console$ sudo a2ensite php-multi.conf
Enable the necessary Apache proxying and rewrite modules.
console$ sudo a2enmod proxy proxy_fcgi rewrite
Create new directories to store PHP 8.3, PHP 8.0, and PHP 7.4 files.
console$ sudo mkdir -p /var/www/html/php83 /var/www/html/php80 /var/www/html/php74
Create a sample
info.phpfile under the/var/www/html/php83directory.console$ sudo nano /var/www/html/php83/info.php
Add the following contents to the file.
php<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Save and close the file.
Repeat the above steps and create additional
info.phpfiles in the/var/www/html/php80and/var/www/html/php74directories.Open a web browser and access the following paths. Each web page should display the respective PHP version.
PHP Version 8.3:
http://SERVER-IP/php83/info.php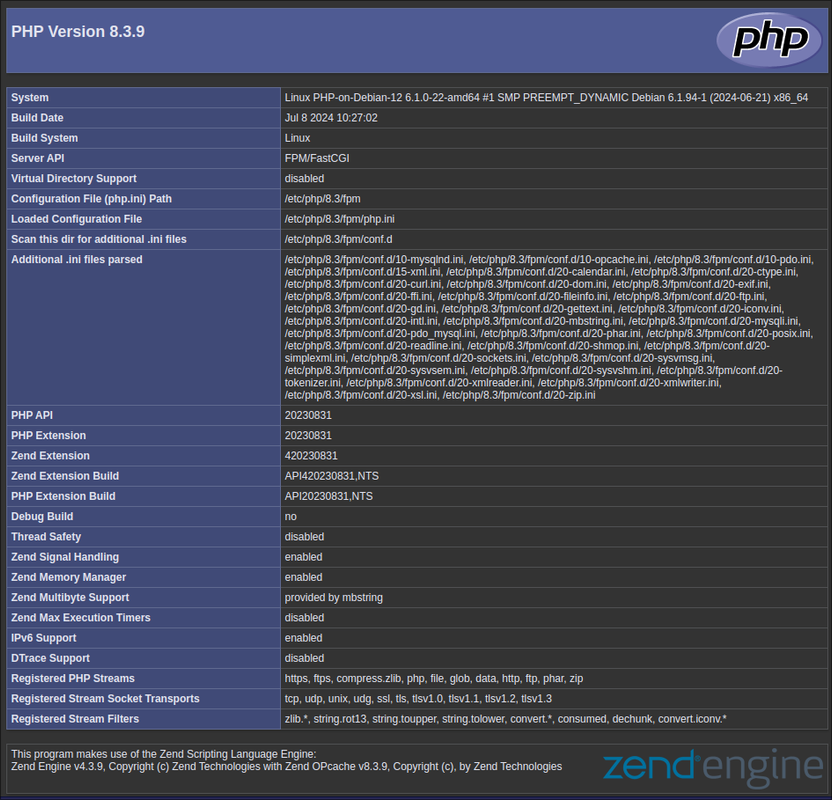
PHP Version 8.0:
http://SERVER-IP/php80/info.php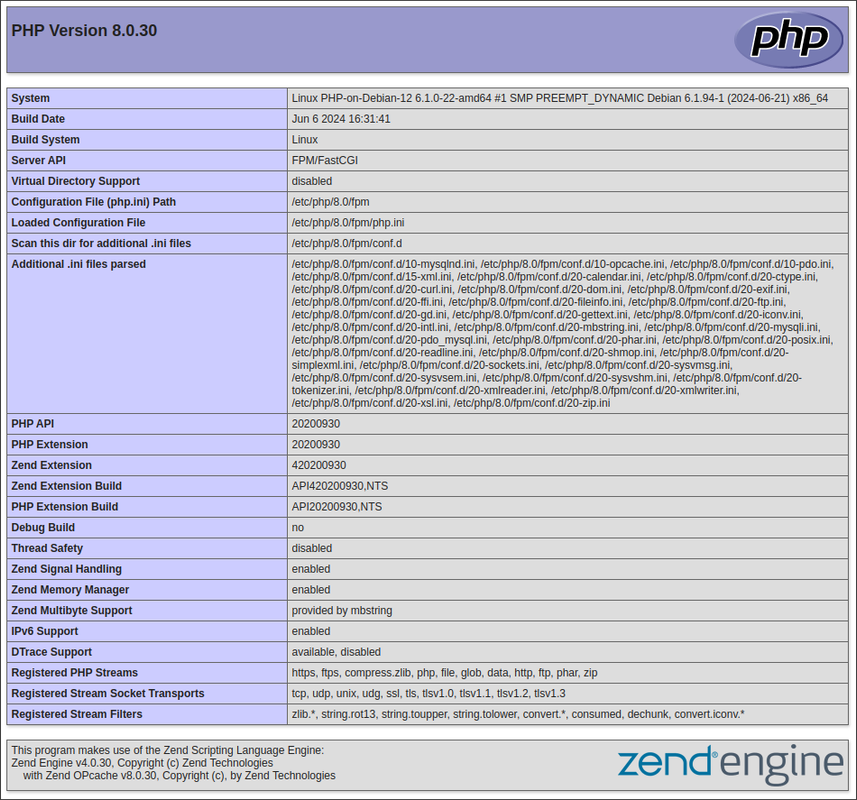
PHP Version 7.4:
http://SERVER-IP/php74/info.php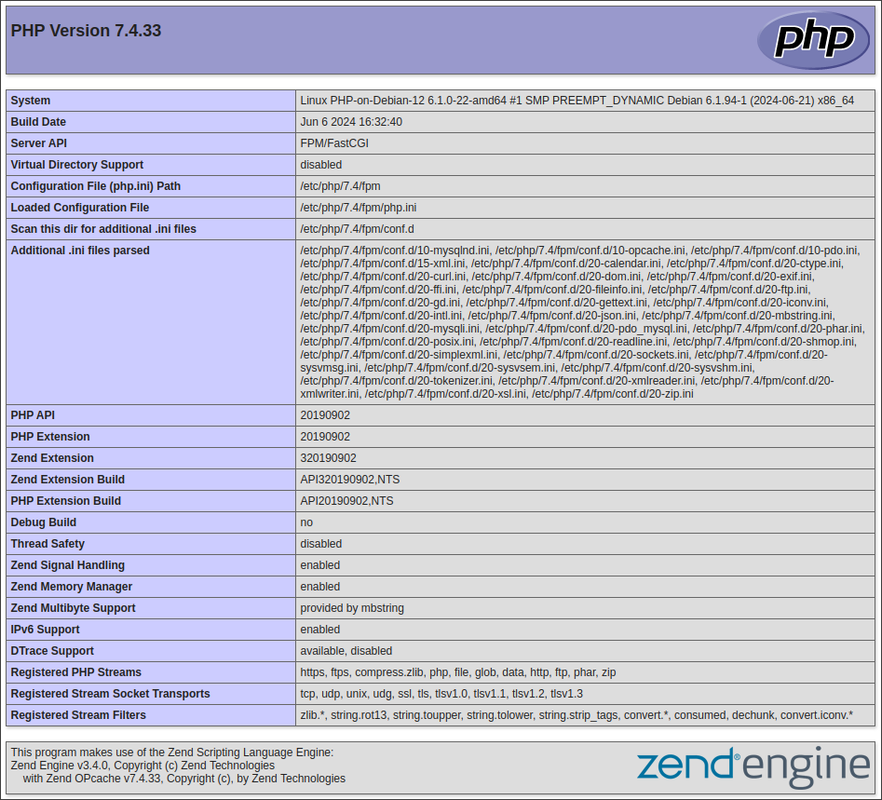
Conclusion
You have installed PHP and PHP-FPM on Debian 12. You can integrate PHP with multiple applications to deliver and process dynamic web applications using PHP-FPM pools. For more information, visit the PHP documentation.