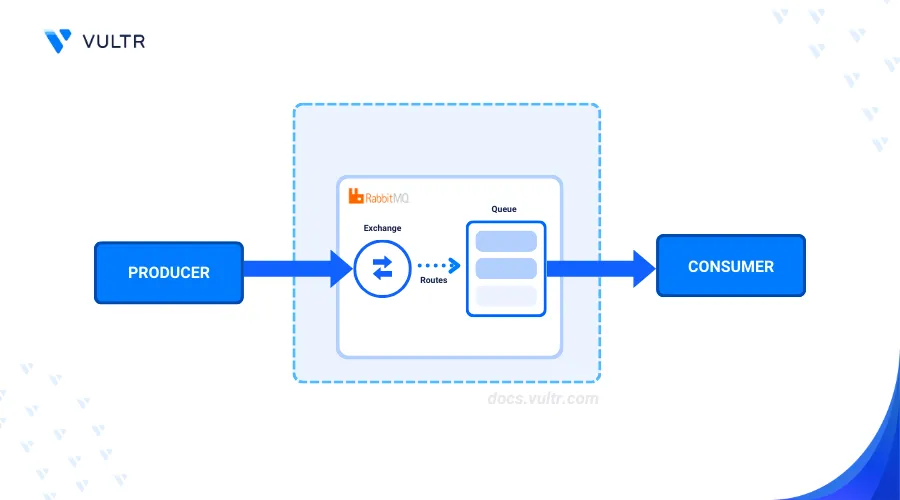
RabbitMQ is an open-source message broker that enables reliable communication between distributed systems. It supports various messaging protocols and is highly extensible through plugins, making it a useful tool for integrating different applications and ensuring efficient message handling.
This article explains the steps to install and secure RabbitMQ on Ubuntu 22.04.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
Have an Ubuntu 22.04 server.
Create a domain name A record pointing to the server IP address.
Access the server using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
Install RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is available in the default repositories on Ubuntu 22.04. Follow the steps below to install the Erlang dependency package and RabbitMQ on your server.
Update the server package index.
console$ sudo apt update
View the available RabbitMQ APT repository information.
console$ sudo apt-cache policy rabbitmq-server
Output:
rabbitmq-server: Installed: (none) Candidate: 3.9.27-0ubuntu0.2 Version table: 3.9.27-0ubuntu0.2 500 500 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-updates/main amd64 Packages 500 http://ubuntu.mirror.constant.com jammy-updates/main amd64 Packages 500 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy-security/main amd64 Packages 500 http://ubuntu.mirror.constant.com jammy-security/main amd64 Packages 3.9.13-1 500 500 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu jammy/main amd64 Packages 500 http://ubuntu.mirror.constant.com jammy/main amd64 PackagesInstall the
erlangandgnupgdependency packages.console$ sudo apt install gnupg erlang -y
Install RabbitMQ.
console$ sudo apt install rabbitmq-server -y
Manage the RabbitMQ System Service
RabbitMQ runs as the rabbitmq-server service on Ubuntu 22.04. Follow the steps below to control the service and ensure the RabbitMQ server is active on your system.
Enable the RabbitMQ service to start at boot time.
console$ sudo systemctl enable rabbitmq-server
Start the RabbitMQ service.
console$ sudo systemctl start rabbitmq-server
View the RabbitMQ service status and verify that it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status rabbitmq-server
Output:
● rabbitmq-server.service - RabbitMQ Messaging Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/rabbitmq-server.service; enabled; preset: enabled) Active: active (running) since Fri 2024-07-05 15:42:24 UTC; 26s ago Main PID: 4122 (beam.smp) Tasks: 24 (limit: 9438) Memory: 98.8M (peak: 106.2M) CPU: 4.186s
Configure RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ includes a management plugin that provides a web-based interface for monitoring and configuring the server. Follow the steps below to activate the plugin, create an admin user, and assign full access permissions.
Enable the RabbitMQ management plugin.
console$ sudo rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
Create a new administrative user account with a strong password. Replace
adminwith your actual user andStrongPasswordwith your desired user password.console$ sudo rabbitmqctl add_user admin StrongPassword
Grant the user administrative privileges.
console$ sudo rabbitmqctl set_user_tags admin administrator
Grant the user full permissions to all RabbitMQ resources on the server.
console$ sudo rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / admin ".*" ".*" ".*"
Within the above command:
.*: Grants configuration privileges to the user..*: Grants write privileges to the user on any resource..*: Grants read privileges to the user read.
Secure RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ listens for incoming connections on TCP port 15672. To improve security, you can configure a reverse proxy like Nginx to route traffic through a standard port, such as HTTP port 80. Additionally, you can secure connections with SSL certificates to enable HTTPS access, as outlined in the following sections.
Set Up Nginx as a Reverse Proxy to Expose RabbitMQ
Install Nginx.
console$ sudo apt install nginx -y
Enable Nginx to start at boot time.
console$ sudo systemctl enable nginx
Start the Nginx service.
console$ sudo systemctl start nginx
Disable the default Nginx configuration file.
console$ sudo rm /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/default
Create a new Nginx virtual host configuration such as
rabbitmq.confusing a text editor such asnano.console$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/rabbitmq.conf
Add the following contents to the file. Replace
rabbitmq.example.comwith your actual domain.iniserver { listen 80; server_name rabbitmq.example.com; location / { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:15672; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; proxy_redirect off; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_max_temp_file_size 0; proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade; } }
Save and close the file.
The Nginx configuration sets up a virtual host that listens on HTTP port
80for your domainrabbitmq.example.comand forwards all requests to RabbitMQ onlocalhost:15672.Enable the virtual host configuration.
console$ sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/rabbitmq.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/
Test the Nginx configuration for errors.
console$ sudo nginx -t
Restart the Nginx service to apply the configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Allow incoming connections to the HTTP port
80through the default UFW firewall configuration.console$ sudo ufw allow 80
Reload UFW to apply your configuration changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
Secure the RabbitMQ Console with Trusted SSL Certificates
Install the Certbot Let's Encrypt Client tool.
console$ sudo snap install certbot --classic
Generate a new SSL certificate using your domain available in the Nginx virtual host configuration. Replace
rabbitmq.example.comandadmin@example.comwith your actual details.console$ sudo certbot --nginx -d rabbitmq.example.com -m admin@example.com --agree-tos
Restart the Nginx service to apply your SSL configuration changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Allow incoming connections to the HTTPS port
443through the default UFW firewall configuration.console$ sudo ufw allow 443
Reload UFW to apply your configuration changes.
console$ sudo ufw reload
Restart the RabbitMQ service.
console$ sudo systemctl restart rabbitmq-server
Access the RabbitMQ Console
Access your domain using a web browser such as Chrome to access the RabbitMQ web administration console.
https://rabbitmq.example.comLog in to the RabbitMQ Console using the admin user credentials you created earlier when prompted.
Click Nodes within the RabbitMQ console to view your active node statistics.
Conclusion
In this article, you installed RabbitMQ on an Ubuntu 22.04 server and secured it to enable reliable message streaming between applications.