How to Install RabbitMQ on FreeBSD 13.0
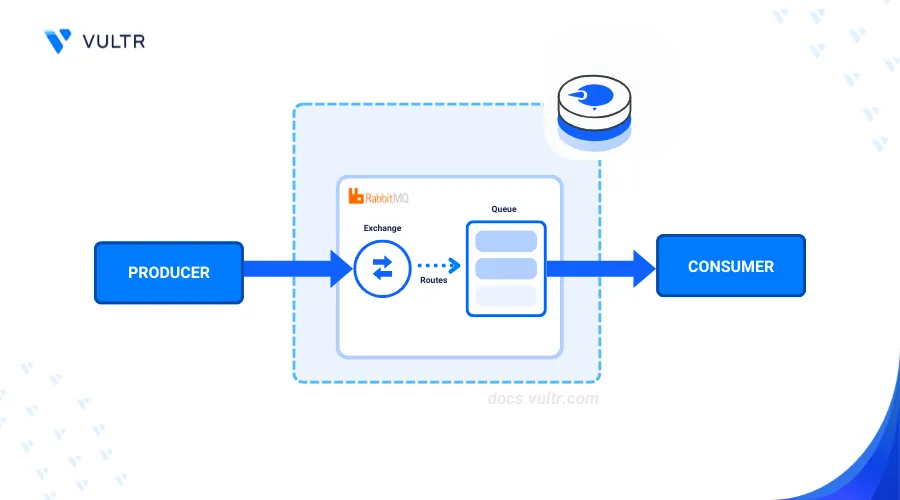
Introduction
RabbitMQ is a robust, open-source message broker that allows efficient communication between distributed applications. RabbitMQ acts as an intermediary application between message producers and consumers. This message queuing architecture uses the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol, making it ideal for handling messaging in large-scale distributed systems. To get started, you can Install RabbitMQ on FreeBSD 13 for managing message queues effectively in your environment.
This article explains how to install RabbitMQ on FreeBSD 13.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- Deploy a FreeBSD 13.0 instance on Vultr.
- Set Up a domain A record pointing to the instance's public IP address. For example,
rabbitmq.example.com. - Access the instance using SSH.
- Create a non-root user with sudo privileges and switch to the user.
Install RabbitMQ on FreeBSD 13
RabbitMQ is available in the default package repositories on FreeBSD. The RabbitMQ package includes all dependencies, such as Erlang. Follow the steps below to install RabbitMQ using the default pkg package manager.
Update the server's package information index.
console$ sudo pkg update
Install RabbitMQ.
console$ sudo pkg install -y rabbitmq
Enable RabbitMQ to automatically start at boot.
console$ sudo sysrc rabbitmq_enable=yes
Output:
rabbitmq_enable: -> yesStart the RabbitMQ service.
console$ sudo service rabbitmq start
View the RabbitMQ service status and verify it's running.
console$ sudo service rabbitmq status
Output:
Status of node rabbit@test-freebsd-server-3 ... Runtime OS PID: 1353 OS: FreeBSD Uptime (seconds): 47 Is under maintenance?: false RabbitMQ version: 3.13.7 RabbitMQ release series support status: see https://www.rabbitmq.com/release-information
Configure RabbitMQ on FreeBSD 13
RabbitMQ uses the rabbitmq_management and rabbitmqadmin plugins to enable CLI access and a web administration dashboard on the default TCP port 15672. Follow the steps below to enable the RabbitMQ management plugins, create an administrative user account, and grant the user full permissions to the application processes.
Enable the RabbitMQ management plugin.
console$ sudo rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
Copy the
/var/db/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookiefile to/root/.erlang.cookie.console$ sudo cp /var/db/rabbitmq/.erlang.cookie /root/.erlang.cookie
Enable the
400permissions mode to grant the owner read privileges on the file.console$ sudo chmod 400 /root/.erlang.cookie
Restart the RabbitMQ service.
console$ sudo service rabbitmq restart
Create a new RabbitMQ user and set a strong user password. Replace
example_userwith your desired username andexample_passwordwith a strong password:console$ sudo rabbitmqctl add_user example_user example_password
Assign the user a specific role such as
administrator.console$ sudo rabbitmqctl set_user_tags example_user administrator
Grant the user full privileges to the RabbitMQ processes.
console$ sudo rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / example_user ".*" ".*" ".*"
In the above command:
.*: Grants the user configuration privileges..*: Grants the user write privileges to any resource..*: Grants the user read privileges to any resource.
Download the
rabbitmqadminplugin binary to enable CLI access to the RabbitMQ.console$ wget http://localhost:15672/cli/rabbitmqadmin
Enable execute permissions on the file.
console$ chmod +x rabbitmqadmin
Move the
rabbitmqadminfile to/usr/local/bin/.console$ sudo mv rabbitmqadmin /usr/local/bin/
Verify the installed
rabbitmqadminplugin version.console$ rabbitmqadmin --version
Output:
rabbitmqadmin 3.13.7If you're looking for a different setup, you can also check out how to install RabbitMQ in Ubuntu to enhance your application’s message handling capabilities.
Secure RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ creates a guest user with full administrative privileges by default. Disable the guest user and enable secure access to the RabbitMQ console with valid SSL certificates to enable encrypted HTTPS connections on the server. Follow the steps below to disable the default guest user, set up Nginx as a reverse proxy, and generate trusted Let's Encrypt SSL certificates.
Disable the RabbitMQ guest user.
console$ sudo rabbitmqctl delete_user guest
Install Nginx.
console$ sudo pkg install -y nginx
Create a new
/usr/local/etc/nginx/conf.d/virtual host configuration directory.console$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/etc/nginx/conf.d/
Create a new RabbitMQ virtual host configuration using a text editor such as
vim.console$ sudo vim /usr/local/etc/nginx/conf.d/rabbitmq.conf
Add the following contents to the file. Replace
rabbitmq.example.comwith your actual domain.nginxserver { listen 80; server_name rabbitmq.example.com; location / { proxy_pass http://localhost:15672; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; } location /mqtt { proxy_pass http://localhost:15675; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; } }
Save and close the file.
The above Nginx configuration creates a new reverse proxy connection to the RabbitMQ port
15672and serves the web console using therabbitmq.example.comdomain on the HTTP port80.Open the main
nginx.confconfiguration file.console$ sudo vim /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Add the following directive within the
httpblock at the end of the file before the closing}mark.nginxinclude /usr/local/etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
Save and close the file.
The above configuration enables Nginx to read virtual configuration files in the
/usr/local/etc/nginx/conf.d/directory.Test Nginx for configuration errors.
console$ sudo nginx -t
Output:
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successfulEnable Nginx to automatically start at boot.
console$ sudo sysrc nginx_enable=yes
Start the Nginx service.
console$ sudo service nginx start
Output:
Performing sanity check on nginx configuration: nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful Starting nginx.Search the default package repositories to view the available Certbot package version.
console$ pkg search certbot
Output:
py311-certbot-2.11.0,1 Let's Encrypt client py311-certbot-apache-2.11.0 Apache plugin for Certbot py311-certbot-nginx-2.11.0 NGINX plugin for CertbotInstall the Certbort Let's Encrypt client tool and plugin for Nginx.
console$ sudo pkg install -y py311-certbot py311-certbot-nginx
Generate a new SSL certificate for your RabbitMQ virtual host domain. Replace
rabbitmq.example.comwith your domain andhello@example.comwith your active email address.console$ sudo certbot --nginx -d rabbitmq.example.com -m hello@example.com --agree-tos
Output:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log Requesting a certificate for rabbitmq.example.com Successfully received certificate. Certificate is saved at: /usr/local/etc/letsencrypt/live/rabbitmq.example.com/fullchain.pem Key is saved at: /usr/local/etc/letsencrypt/live/rabbitmq.example.com/privkey.pem This certificate expires on 2025-01-07. These files will be updated when the certificate renews. Deploying certificate Successfully deployed certificate for rabbitmq.example.com to /usr/local/etc/nginx/conf.d/rabbitmq.conf Congratulations! You have successfully enabled HTTPS on rabbitmq.example.comVerify that Certbot autorenews the SSL certificate upon expiry.
console$ sudo certbot renew --dry-run
Output:
Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Processing /usr/local/etc/letsencrypt/renewal/rabbitmq.example.com.conf - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Account registered. Simulating renewal of an existing certificate for rabbitmq.example.com - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Congratulations, all simulated renewals succeeded: /usr/local/etc/letsencrypt/live/rabbitmq.example.com/fullchain.pem (success) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -Restart Nginx to apply the changes.
console$ sudo service nginx restart
Access the RabbitMQ Console
Follow the steps below to access RabbitMQ, create a new queue, publish and retrieve messages.
Create a new RabbitMQ queue, such as
testqueueusing your administrative user. Replaceexample_userandexample_passwordwith the actual user and password you set earlier.console$ rabbitmqadmin -u example_user -p example_password declare queue name=testqueue durable=true
Output:
queue declaredPublish a new message to the queue. For example,
Greetings from Vultr.console$ rabbitmqadmin -u example_user -p example_password publish routing_key=testqueue payload="Greetings from Vultr"
Retrieve all messages in the queue.
console$ rabbitmqadmin -u example_user -p example_password get queue=testqueue
Output:
+-------------+----------+---------------+-----------------------------+---------------+------------------+------------+-------------+ | routing_key | exchange | message_count | payload | payload_bytes | payload_encoding | properties | redelivered | +-------------+----------+---------------+-----------------------------+---------------+------------------+------------+-------------+ | testqueue | | 0 | Greetings from Vultr Server | 27 | string | | False | +-------------+----------+---------------+-----------------------------+---------------+------------------+------------+-------------+Access your RabbitMQ domain using a web browser like Chrome to log in to the web administration console.
https://rabbitmq.example.comLog in using your RabbitMQ username and password to access the web console.
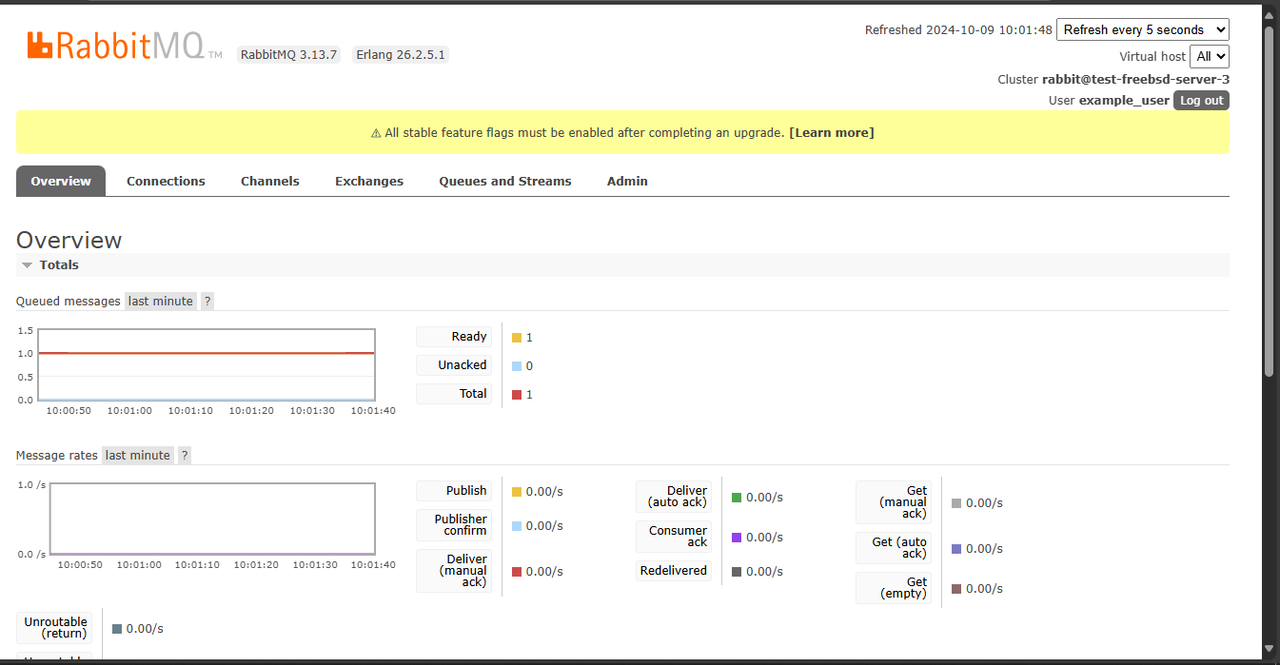
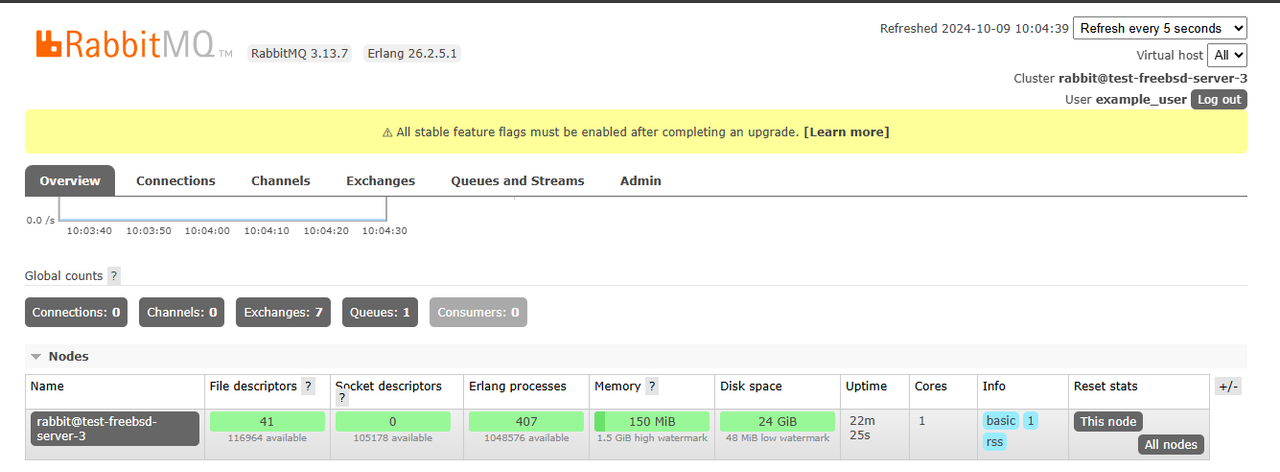
Find and expand the Nodes group to view your RabbitMQ node information.
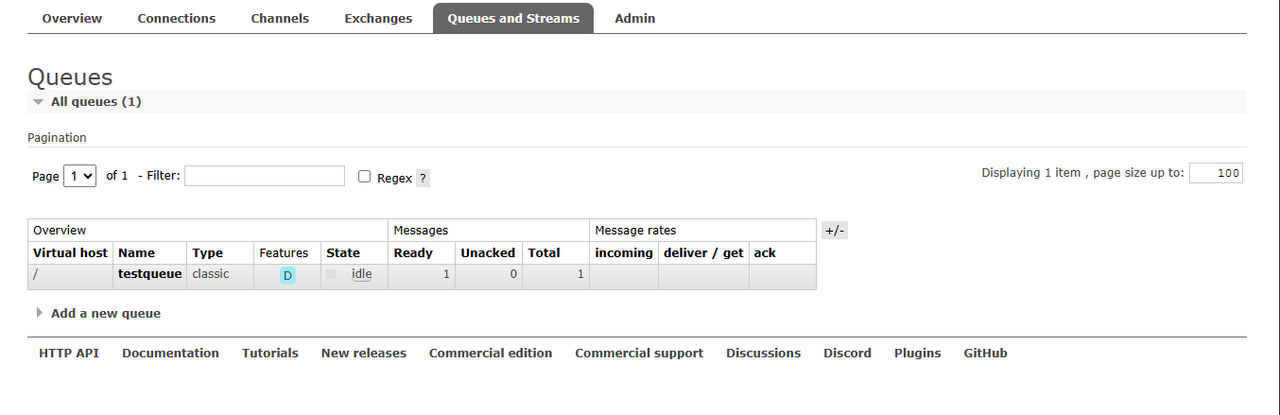
Navigate to the Queues and Streams tab to manage the RabbitMQ queues on your server.
Conclusion
You have installed RabbitMQ on your FreeBSD 13 server, created a new administrative user, and enabled access to the web administration console. After you Install RabbitMQ on FreeBSD 13, RabbitMQ securely handles message exchanges between microservices and applications on your server. For more information and advanced configuration options, visit the RabbitMQ Documentation.