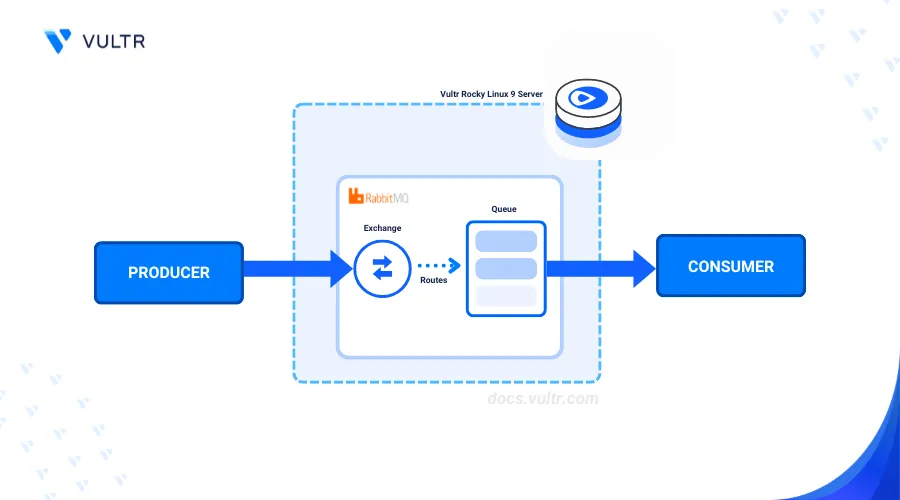
Introduction
RabbitMQ is an open-source message broker that uses the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) to exchange messages between applications. RabbitMQ works as a distributed system that handles high-throughput workloads to efficiently improve applications' performance and stability.
In this article, you'll install RabbitMQ on Rocky Linux 9 and manage message queues on the server.
Prerequisites
Before you begin:
- Deploy a Rocky Linux 9 instance on Vultr.
- Create a new domain A record pointing to the instance's public IP address. For example,
rabbitmq.example.com. - Access the instance using SSH as a non-root user with sudo privileges.
- Update the instance.
Install RabbitMQ on Rocky Linux 9
RabbitMQ is not available in the default package repositories on Rocky Linux 9. Follow the steps below to install the RabbitMQ repository information and dependency packages.
Import the RabbitMQ primary signing keys.
console$ sudo rpm --import 'https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/rabbitmq-release-signing-key.asc'
Import the Erlang signing keys.
console$ sudo rpm --import 'https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/cloudsmith.rabbitmq-erlang.E495BB49CC4BBE5B.key'
Import the RabbitMQ server signing keys.
console$ sudo rpm --import 'https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/cloudsmith.rabbitmq-server.9F4587F226208342.key'
Create a new
/etc/yum.repos.d/rabbitmq.repoRabbitMQ repository file using a text editor likenano.console$ sudo nano /etc/yum.repos.d/rabbitmq.repo
Add the following contents to the file.
ini# In /etc/yum.repos.d/rabbitmq.repo ## ## Zero dependency Erlang RPM ## [modern-erlang] name=modern-erlang-el9 # Use a set of mirrors maintained by the RabbitMQ core team. # The mirrors have significantly higher bandwidth quotas. baseurl=https://yum1.rabbitmq.com/erlang/el/9/$basearch https://yum2.rabbitmq.com/erlang/el/9/$basearch repo_gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/cloudsmith.rabbitmq-erlang.E495BB49CC4BBE5B.key gpgcheck=1 sslverify=1 sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt metadata_expire=300 pkg_gpgcheck=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md [modern-erlang-noarch] name=modern-erlang-el9-noarch # Use a set of mirrors maintained by the RabbitMQ core team. # The mirrors have significantly higher bandwidth quotas. baseurl=https://yum1.rabbitmq.com/erlang/el/9/noarch https://yum2.rabbitmq.com/erlang/el/9/noarch repo_gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/cloudsmith.rabbitmq-erlang.E495BB49CC4BBE5B.key https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/rabbitmq-release-signing-key.asc gpgcheck=1 sslverify=1 sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt metadata_expire=300 pkg_gpgcheck=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md [modern-erlang-source] name=modern-erlang-el9-source # Use a set of mirrors maintained by the RabbitMQ core team. # The mirrors have significantly higher bandwidth quotas. baseurl=https://yum1.rabbitmq.com/erlang/el/9/SRPMS https://yum2.rabbitmq.com/erlang/el/9/SRPMS repo_gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/cloudsmith.rabbitmq-erlang.E495BB49CC4BBE5B.key https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/rabbitmq-release-signing-key.asc gpgcheck=1 sslverify=1 sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt metadata_expire=300 pkg_gpgcheck=1 autorefresh=1 ## ## RabbitMQ Server ## [rabbitmq-el9] name=rabbitmq-el9 baseurl=https://yum2.rabbitmq.com/rabbitmq/el/9/$basearch https://yum1.rabbitmq.com/rabbitmq/el/9/$basearch repo_gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 # Cloudsmith's repository key and RabbitMQ package signing key gpgkey=https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/cloudsmith.rabbitmq-server.9F4587F226208342.key https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/rabbitmq-release-signing-key.asc gpgcheck=1 sslverify=1 sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt metadata_expire=300 pkg_gpgcheck=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md [rabbitmq-el9-noarch] name=rabbitmq-el9-noarch baseurl=https://yum2.rabbitmq.com/rabbitmq/el/9/noarch https://yum1.rabbitmq.com/rabbitmq/el/9/noarch repo_gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 # Cloudsmith's repository key and RabbitMQ package signing key gpgkey=https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/cloudsmith.rabbitmq-server.9F4587F226208342.key https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/rabbitmq-release-signing-key.asc gpgcheck=1 sslverify=1 sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt metadata_expire=300 pkg_gpgcheck=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md [rabbitmq-el9-source] name=rabbitmq-el9-source baseurl=https://yum2.rabbitmq.com/rabbitmq/el/9/SRPMS https://yum1.rabbitmq.com/rabbitmq/el/9/SRPMS repo_gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://github.com/rabbitmq/signing-keys/releases/download/3.0/cloudsmith.rabbitmq-server.9F4587F226208342.key gpgcheck=0 sslverify=1 sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt metadata_expire=300 pkg_gpgcheck=1 autorefresh=1 type=rpm-md
Save and close the file.
The above configuration enables access to the RabbitMQ and Erlang repositories for Rocky Linux 9.
Update the server's package information index to apply the new repository.
console$ sudo dnf update -y
Install the
socatandlogrotateRabbitMQ dependency packages.console$ sudo dnf install -y socat logrotate
Install RabbitMQ and Erlang.
console$ sudo dnf install -y erlang rabbitmq-server
Enable the RabbitMQ service to automatically start at boot.
console$ sudo systemctl enable rabbitmq-server
Start the RabbitMQ service.
console$ sudo systemctl start rabbitmq-server
View the RabbitMQ service status and verify it's running.
console$ sudo systemctl status rabbitmq-server
Output:
● rabbitmq-server.service - RabbitMQ broker Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/rabbitmq-server.service; enabled; preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Wed 2024-08-14 17:57:40 IST; 1 day 20h ago Main PID: 995 (beam.smp) Tasks: 32 (limit: 48585) Memory: 178.0M CPU: 37.462s CGroup: /system.slice/rabbitmq-server.service ├─ 995 /usr/lib64/erlang/erts-14.2.5/bin/beam.smp -W w -MBas ageffcbf -MHas ageffcbf -MBlmbcs 512 -MHlmbcs 512 -MMmcs 30> ├─1048 erl_child_setup 32768 ├─1366 sh -s disksup ├─1368 /usr/lib64/erlang/lib/os_mon-2.9.1/priv/bin/memsup ├─1369 /usr/lib64/erlang/lib/os_mon-2.9.1/priv/bin/cpu_sup ├─1669 /usr/lib64/erlang/erts-14.2.5/bin/inet_gethost 4 ├─1671 /usr/lib64/erlang/erts-14.2.5/bin/inet_gethost 4 ├─1687 /usr/lib64/erlang/erts-14.2.5/bin/epmd -daemon └─2043 /bin/sh -s rabbit_disk_monitorThe RabbitMQ service is active and running on your server based on the
active (running)message in the above output.
Configure RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ uses a web console to manage application processes on the server. Follow the steps below to create a new RabbitMQ user, install rabbitmqadmin, and run the web console on the default port 15672.
Get the latest RabbitMQ server version and assign the value to a new
LATEST_VERSIONvariable.console$ LATEST_VERSION=$(curl -s https://api.github.com/repos/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/releases/latest | grep -Po '"tag_name": "\K.*?(?=")')
Download the latest
rabbitmqadminversion from the RabbitMQ GitHub repository.console$ curl -O https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/${LATEST_VERSION}/deps/rabbitmq_management/bin/rabbitmqadmin
Set the execute permissions on the
rabbitmqadminbinary.console$ chmod +x rabbitmqadmin
Move the
rabbitmqadminbinary to the/usr/local/bindirectory to enable system-wide access to the tool.console$ sudo mv rabbitmqadmin /usr/local/bin/
Enable the RabbitMQ management plugin.
console$ sudo rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
Create a new RabbitMQ user and set a strong password for the user. Replace
exampleuserandstrong_passwordwith your desired user details.console$ sudo rabbitmqctl add_user exampleuser strong_password
Grant the user access privileges to the RabbitMQ console.
console$ sudo rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / exampleuser ".*" ".*" ".*"
Assign the user to a specific role, such as
administrator.console$ sudo rabbitmqctl set_user_tags exampleuser administrator
Secure RabbitMQ
By default, RabbitMQ creates a guest user with full administrative privileges. Disable the user and enable secure access to the RabbitMQ console using valid SSL certificates to enable encrypted HTTPS connections. Follow the steps below to configure Nginx as a reverse proxy for RabbitMQ, disable the default guest user, and generate trusted Let's Encrypt SSL certificates to secure the RabbitMQ console.
Disable the RabbitMQ
guestuser.console$ sudo rabbitmqctl delete_user guest
Start the default
firewalldutility.console$ sudo systemctl start firewalld
Allow network connections to the HTTP port
80through the firewall to enable Let's Encrypt validations.console$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=80/tcp
Allow network connections to the HTTPS port
443through the firewall.console$ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --permanent --add-port=443/tcp
Reload
firewalldto apply the configuration changes.console$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Install Nginx.
console$ sudo dnf install nginx -y
Create a new virtual host for RabbitMQ. For example,
rabbitmq.conf.console$ sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/rabbitmq.conf
Add the following contents to the file. Replace
rabbitmq.example.comwith your domain name.nginxserver { listen 80; listen [::]:80; server_name rabbitmq.example.com; location / { proxy_pass http://localhost:15672; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; } location /mqtt { proxy_pass http://localhost:15675; proxy_http_version 1.1; proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade; proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade"; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; } }
Save and close the file.
The above Nginx configuration creates a new reverse proxy connection to the RabbitMQ port
15672and serves the web console using therabbitmq.example.comdomain on the HTTP port80.Test the Nginx configuration for errors.
console$ sudo nginx -t
Enable Nginx to connect to localhost ports through the default SELinux configuration.
console$ sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect 1
Restart Nginx to apply the new changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart nginx
Install the Certbot Let's Encrypt client tool and plugin for Nginx.
console$ sudo dnf install -y certbot python3-certbot-nginx -y
Generate a new SSL certificate for your virtual host domain. Replace
rabbitmq.example.comwith your domain andhello@example.comwith your active email address.console$ sudo certbot --nginx -d rabbitmq.example.com -m hello@example.com --agree-tos
Test the Certbot automatic SSL certificate renewal process.
console$ sudo certbot renew --dry-run
Restart RabbitMQ to apply the new changes.
console$ sudo systemctl restart rabbitmq-server
Access RabbitMQ
Follow the steps below to test access to the RabbitMQ CLI and web console on your server.
Create a new queue in RabbitMQ to store and manage messages.
console$ rabbitmqadmin -u exampleuser -p strong_password declare queue name=testqueue durable=true
Publish a new message to the queue.
console$ rabbitmqadmin -u exampleuser -p strong_password publish routing_key=testqueue payload="Greetings from Vultr"
Retrieve and view a message from the queue.
console$ rabbitmqadmin -u exampleuser -p strong_password get queue=testqueue
Output:
+-------------+----------+---------------+----------------+---------------+------------------+------------+-------------+ | routing_key | exchange | message_count | payload | payload_bytes | payload_encoding | properties | redelivered | +-------------+----------+---------------+----------------+---------------+------------------+------------+-------------+ | testqueue | | 0 | Greetings from Vultr | 14 | string | | False | +-------------+----------+---------------+----------------+---------------+------------------+------------+-------------+Access your domain using a web browser such as Chrome to manage queues using the RabbitMQ web console.
https://app.example.comEnter the administrative user's details you created earlier and click Login to acccess the web console.
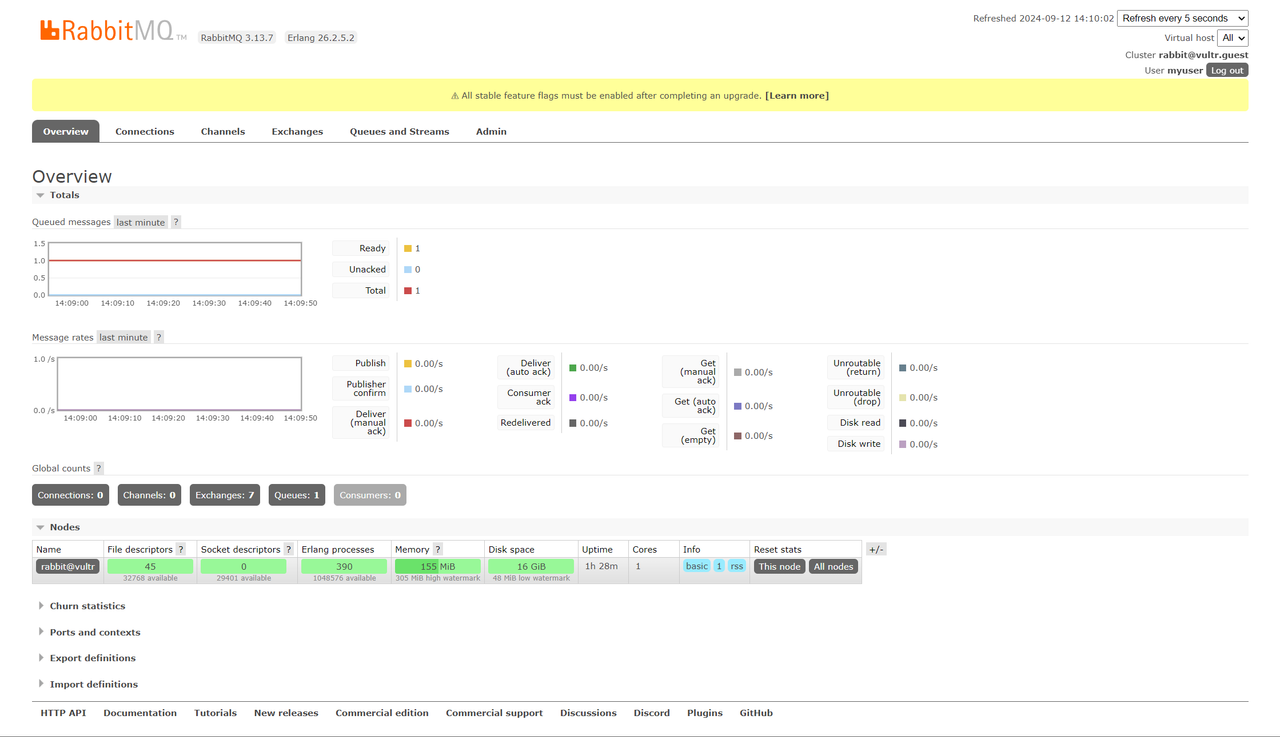
Expand the Nodes group to view your RabbitMQ node information.
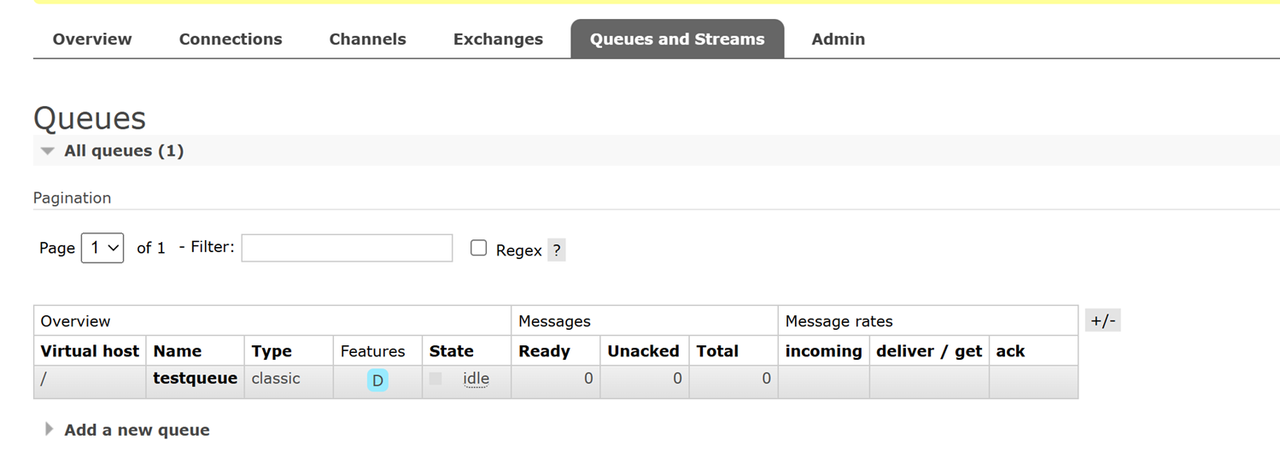
Navigate to the Queues and Streams tab to manage RabbitMQ queues.
Conclusion
You have installed RabbitMQ on a Rocky Linux 9 and enabled access to the web console. RabbitMQ securely handles message exchanges between microservices. For more information and advanced configuration options, visit the RabbitMQ Documentation.